Microelectrolysis filler and process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater
A printing and dyeing wastewater, micro-electrolysis technology, applied in water/sewage treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. The effect of avoiding interference and simplifying the process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A micro-electrolytic filler for treating printing and dyeing wastewater. The micro-electrolytic filler is a ternary filler based on Fe, C, and Al. The composition of the ternary micro-electrolytic filler is:
[0045] Iron 20%
[0046] Activated carbon 30%
[0047] Aluminum 25%
[0048] Clay 20%
[0049] Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose 5%
[0050] After the filler granulation is completed, it is fired at 800°C for 2 hours.
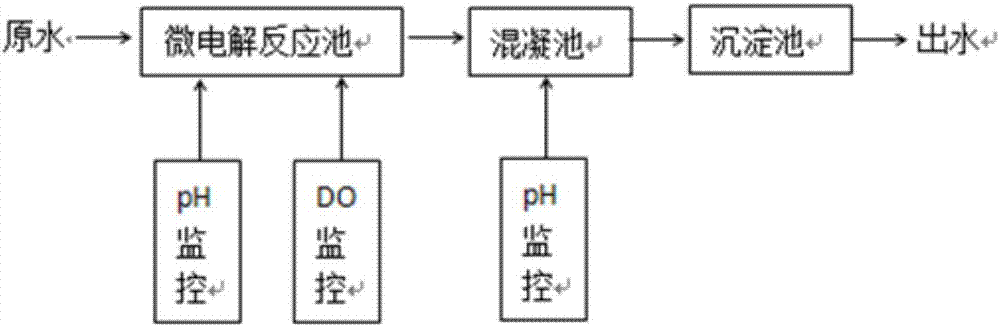
[0051] A micro-electrolysis process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater, using the above-mentioned micro-electrolysis filler, the printing and dyeing wastewater uses anthraquinone dyes as the main pollutant, comprising the following steps:
[0052] A. Introduce printing and dyeing wastewater into the micro-electrolysis reaction pool;
[0053] B, monitor the pH of the waste water to be about 8, and add sodium hydroxide reagent to adjust the pH of the printing and dyeing waste water in the micro-electrolysis reaction pool, so that the pH is...
Embodiment 2
[0059] A micro-electrolytic filler for treating printing and dyeing wastewater. The micro-electrolytic filler is a ternary filler based on Fe, C, and Al. The composition of the ternary micro-electrolytic filler is:
[0060] Iron 15%
[0061] Activated carbon 30%
[0062] Aluminum 15%
[0063] Clay 30%
[0064] Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose 10%
[0065] After the filler granulation is completed, bake at 1000°C for 2 hours
[0066] A micro-electrolysis process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater, using the above-mentioned micro-electrolysis filler, comprising the steps of:
[0067] A. Introduce printing and dyeing wastewater into the micro-electrolysis reaction pool;
[0068] B, monitor the pH of the waste water to be about 10, and add sodium hydroxide reagent to adjust the pH of the printing and dyeing waste water in the micro-electrolysis reaction pool, so that the pH is 11-12;
[0069] C. Monitor and turn on the aeration device to adjust the DO of the printing ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] A micro-electrolytic filler for treating printing and dyeing wastewater. The micro-electrolytic filler is a ternary filler based on Fe, C, and Al. The composition of the ternary micro-electrolytic filler is:
[0075] Iron 20%
[0076] Activated carbon 30%
[0077] Aluminum 20%
[0078] Clay 25%
[0079] Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose 5%
[0080] After the filler granulation is completed, bake at 900°C for 2 hours
[0081] A micro-electrolysis process for treating printing and dyeing wastewater, using the above-mentioned micro-electrolysis filler, the printing and dyeing wastewater is comprehensive wastewater from multiple printing and dyeing factories, including the following steps:
[0082] A. Introduce printing and dyeing wastewater into the micro-electrolysis reaction pool;
[0083] B, monitor the pH of this waste water to be about 11.8;
[0084] C. Monitor and turn on the aeration device to adjust the DO in the printing and dyeing wastewater in the micro-elect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com