Multivariate big data fusion method and system based on BLOB (Binary Large OBject)
A fusion method and big data technology, applied in the fields of database, semantic web and big data, can solve the problem of lack of binary large objects, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing coupling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
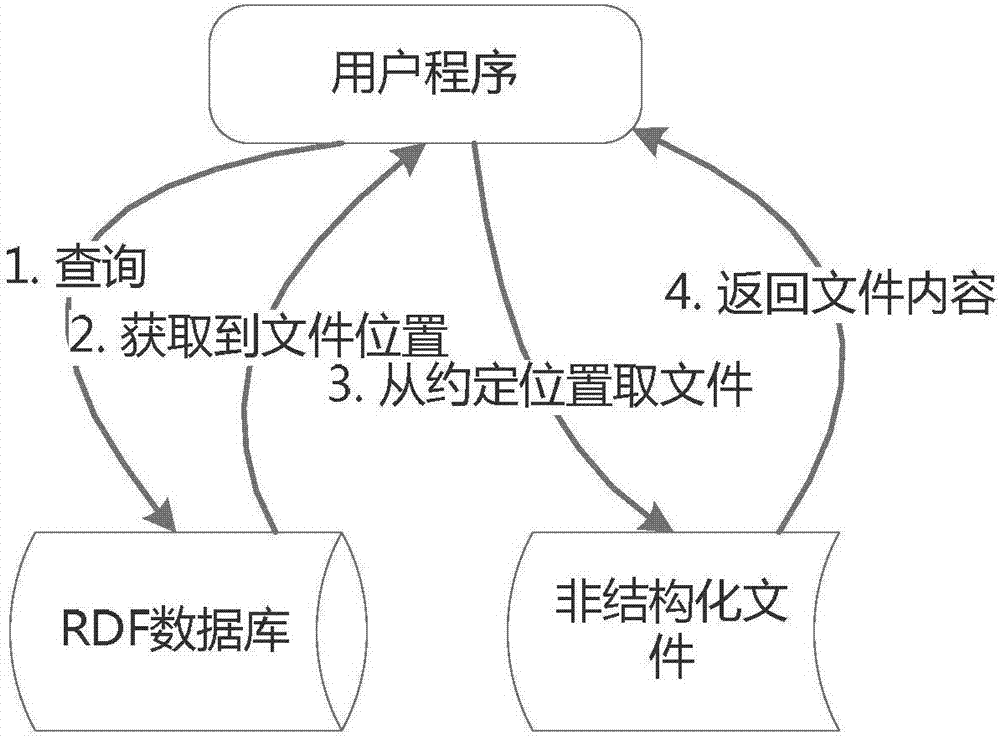
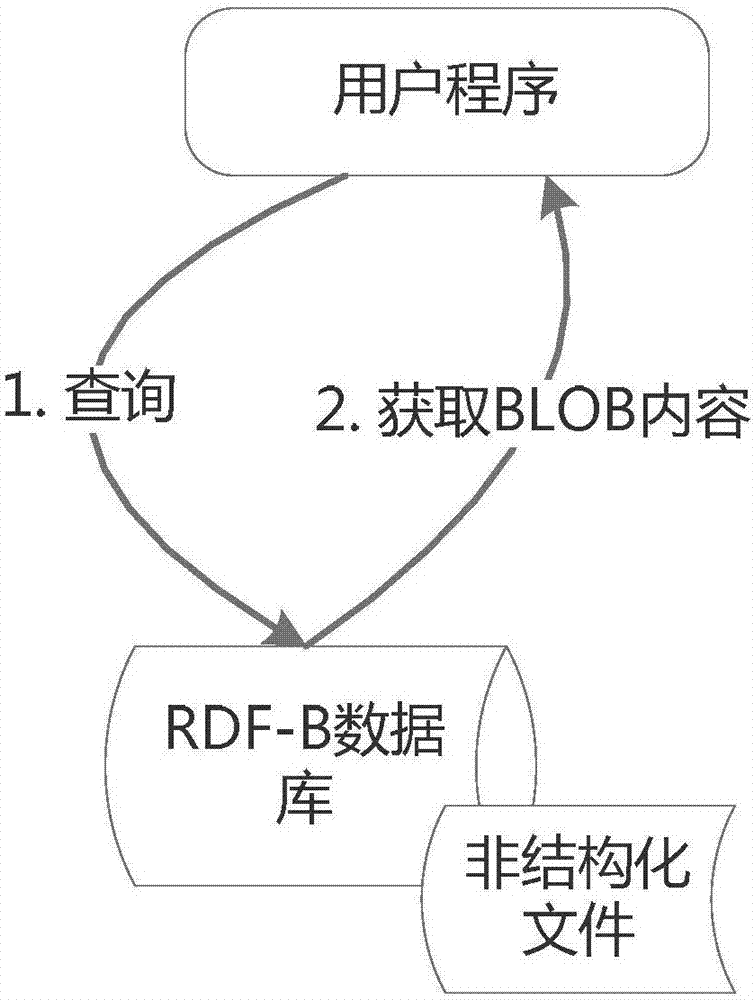
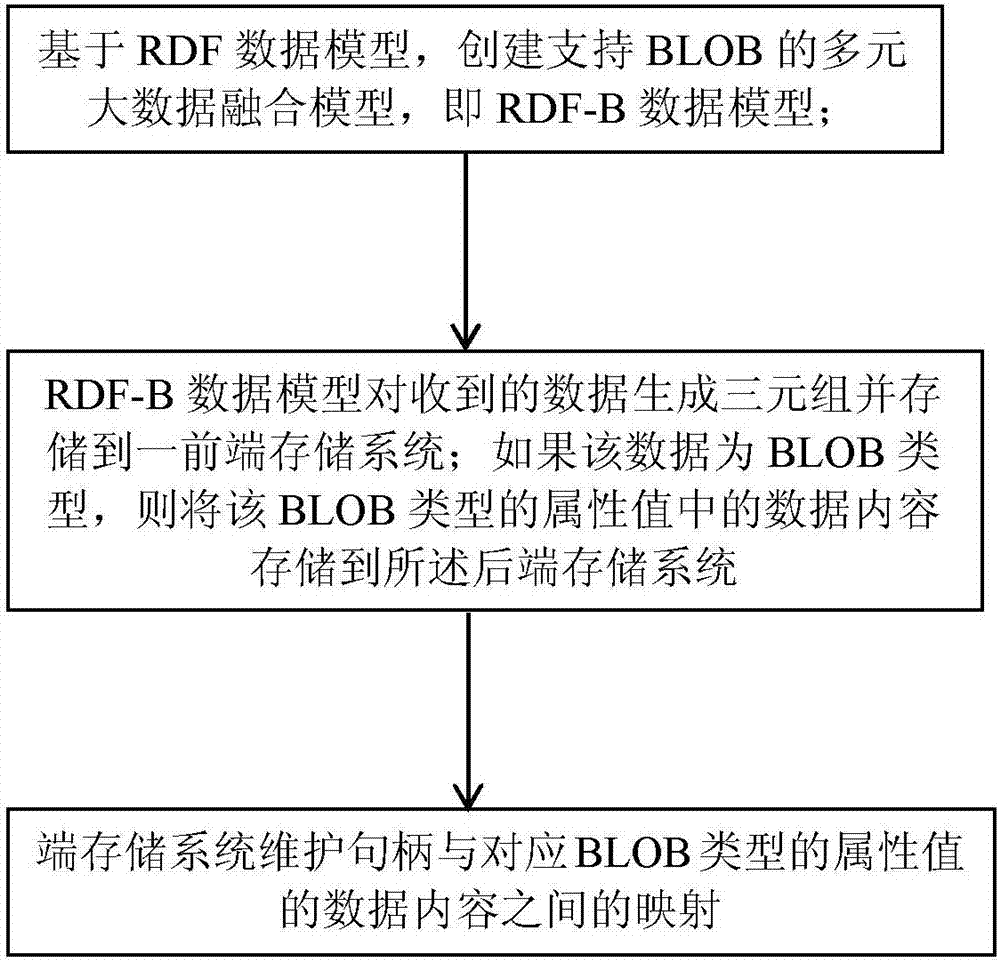
[0041] Embodiment 1, multivariate big data fusion management model RDF-B
[0042] RDF-B is mainly extended based on the RDF model (https: / / www.w3.org / TR / 2014 / REC-rdf11-concepts-20140225 / ), so it has all the features of the RDF model such as triples and directed graphs. The definition of the model consists of 3 parts:
[0043] (1) RDF-B model: Same as the public RDF model, the RDF-B model uses the triple form of to express the attributes (predicates) and Its attribute value (object), the attribute value can be a text type, Boolean type, numeric type, time type, or even another resource. The difference is that the attribute value of RDF-B can be of BLOB type;
[0044] (2) Attribute definition of BLOB attribute value: The attribute value of BLOB type has its own attributes, including content (content), length (length), digest (digest), and a 32-bit mark (mark). As shown in Table 1.
[0045] Table 1 is the attribute table of the BLOB attribute value
[0046] ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2, the text expression method of RDF-B attribute value
[0052] The non-BLOB attribute value in the RDF-B model adopts the standard RDF text expression method, that is, XML literal is used to express the attribute value, which usually includes two parts: vocabulary and IRI of the data type. The former represents the text of the attribute value, and the latter To represent the type of value, such as: "hello"^^xsd:string, "1"^^xsd:integer.
[0053] For BLOB attribute values, RDF-B uses the following expressions:
[0054] ::=" "^^
[0055] ::=content: ,length: ,digest: , mark:
[0056] Among them: content-value, length-value, digest-value, and mark-value respectively correspond to the content (content), length (length), digest (digest) of the BLOB attribute value, and a 32-bit mark (mark).
[0057] The following code shows two RDF-B triples. The first line is a standard RDF triple, and the second line contains a BLOB attribute value.
...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3, the creation method of BLOB attribute value
[0064] This invention provides methods for creating BLOB attribute values from different data sources:
[0065] Literal create(byte[]bytes): Generate BLOB attribute values based on byte arrays
[0066] Literal create(File file): Generate BLOB attribute values based on files
[0067] Literal create(InputStreamSource source): Generate BLOB attribute value according to input stream data source;
[0068] Literal create(String text): Generate BLOB attribute values based on text strings
[0069] Take create(File file) as an example, the pseudocode is as follows:
[0070] val bl = new BlobLiteral {
[0071] val mark32=IOUtils.readBytes(openStream(),32); / / Read the first 32-bit flag
[0072] def openStream()=new FileInputStream(fileName); / / open file input stream
[0073] def getLength()=file.length(); / / Get the length of the file
[0074] def getDigest() = DigestUtils.md5Hex(op...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com