Pedestrian re-identification method based on kernelization features and random subspace integration
A technology of random subspace and identification method, which is applied in the field of pedestrian re-identification based on the integration of kernelized features and random subspaces, can solve the problems of difficult Mahalanobis distance calculation, performance degradation, insolvability, etc., and achieves accurate distance calculation and algorithm. Performance improvement, the effect of optimizing the process of sample distance calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
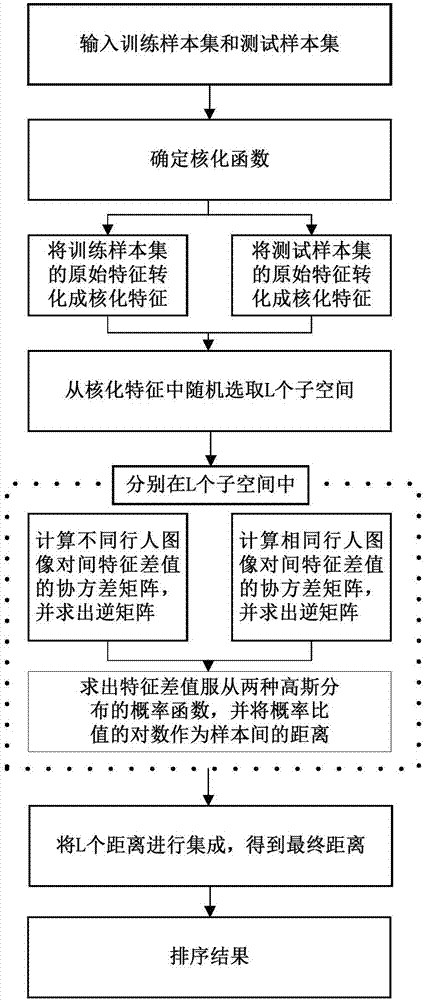
[0042] A pedestrian re-identification method based on kernelized features and random subspace integration, comprising the following steps:
[0043] Step 1: Transform the original feature into a kernelized feature representation, as described below:
[0044] Obtain a training set X∈R of pedestrian images d×m and the test set Z ∈ R d×n , where the sample feature dimension is d, the number of samples in the training set is m, the number of samples in the test set is n, and x i Indicates the i-th training sample, with z i Denotes the i-th test sample. use the kernel function Convert the training set X to kernelized features Convert the test set Z to kernelized features where σ=1. The specific conversion process can be expressed as
[0045]
[0046]Step 2: In the kernelized feature space, randomly select L different subspaces. The specific description is as follows: After step 1 is completed, the dimension of the kernelized feature space is the same as the number of ...
Embodiment approach
[0064] Such as figure 1 Shown is the flowchart of the present embodiment, and the specific implementation is as follows:
[0065] 1) Determine the kernel function;
[0066] 2) Convert the original features of the training samples into kernelized features;
[0067] 3) Convert the original features of the test samples into kernelized features;
[0068] 4) In order to judge z i and z j Whether belong to the same pedestrian, use H 0 Indicates that they are not similar, that is, they do not belong to the same pedestrian, use H 1 Indicates that they are similar, that is, belong to the same pedestrian;
[0069] 5) Randomly select L subspaces D in the kernelized feature space k (k=1,2,...,L);
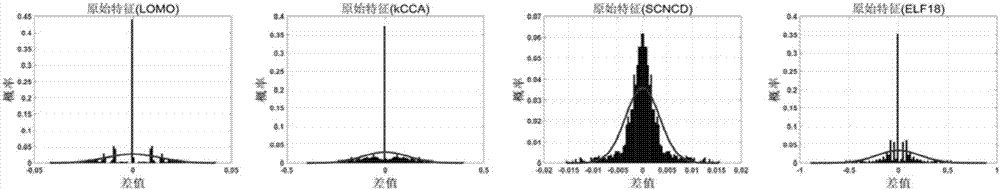
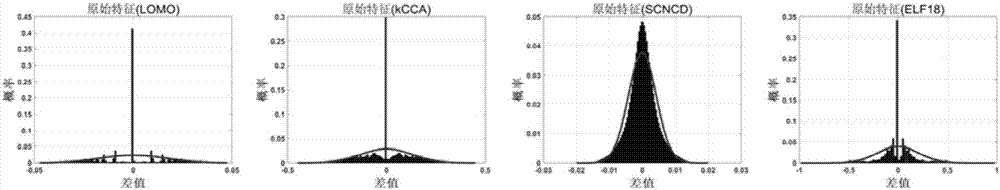
[0070] 6) In different subspaces, calculate the covariance matrix Σ of the feature difference between different pedestrian image pairs 0 , and find the inverse matrix
[0071] 7) In different subspaces, calculate the covariance matrix Σ of the feature difference between the same ped...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com