Constant tool face angle drilling trace control method
A tool face angle and trajectory control technology, which is applied to the automatic control system of drilling, drilling equipment, earthwork drilling and production, etc., can solve the problems of imperfection, single parameter solution method, and lack of universal applicability, so as to facilitate on-site construction, Improved work efficiency, easy matching effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0034] 1. Design model of track with constant tool face angle
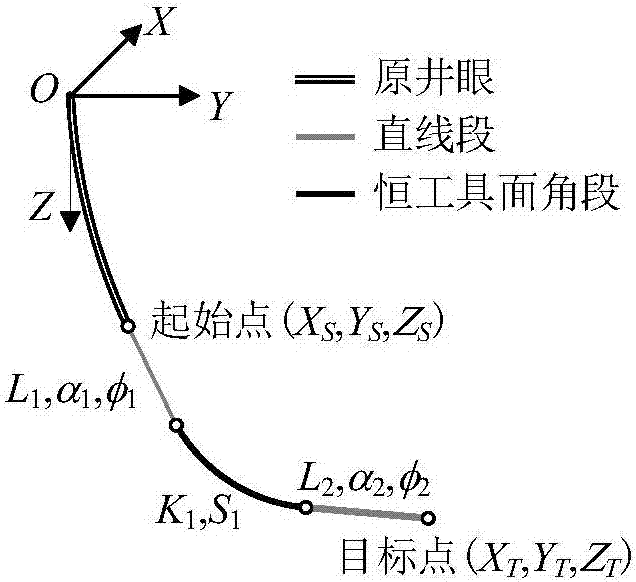
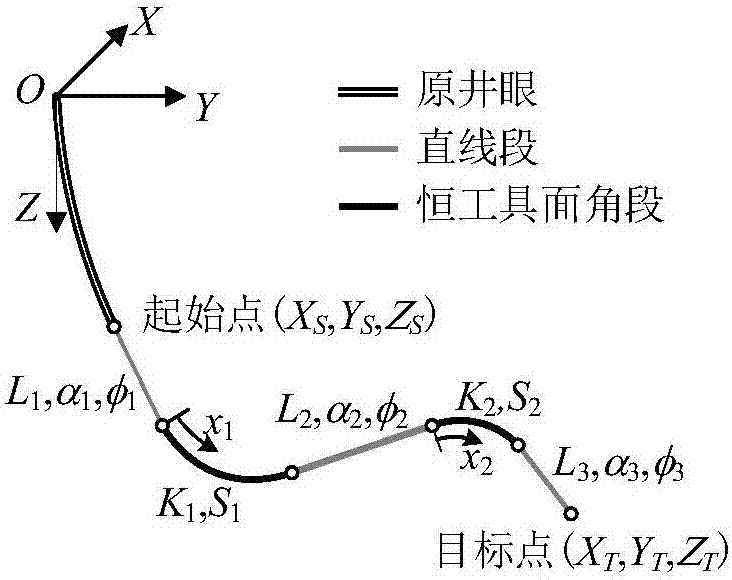
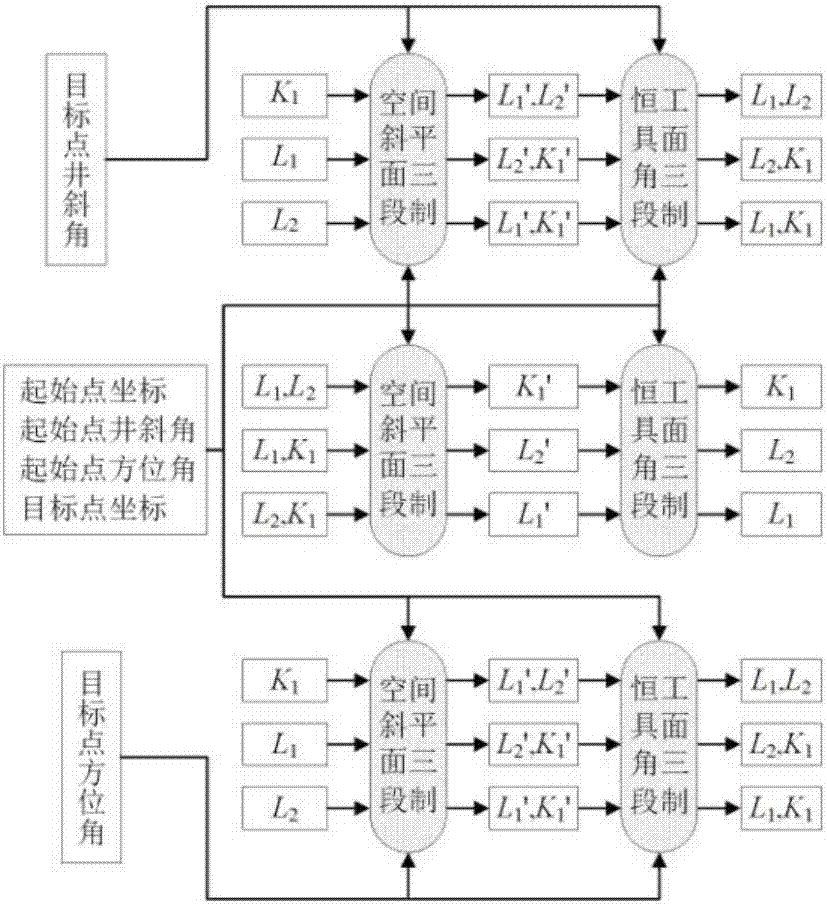
[0035] The wellbore track design adopts the North East coordinate system OXYZ, O is the wellhead, the X axis points to the true north, the Y axis points to the true east, and the Z axis points to the vertical direction. In order to meet the needs of trajectory design for directional wells and horizontal wells, two types of "straight line segment-constant tool face angle segment-straight segment" and "straight line segment-constant tool face angle segment-straight segment-constant tool face angle segment-straight segment" are established. The design model, in which the length of the straight line segment can be zero, can satisfy two typical orbital design requirements of defining the target position and simultaneously defining the target position and direction.
[0036] Two constant tool face angle track design models such as figure 1 with 2 As shown, its constraint equation is:
[0037]
[0038] Among them, ...
example 1
[0125] Example 1: The coordinates of the current point of a directional well are: X S = 100m, Y S =-100m, Z S =2000m; well inclination angle and azimuth angle are α 1 = 10°, φ 1 = 315°. The coordinates of the target point are: X T =200m, Y T =-1100m, Z T = 4000m. If you continue to drill into L in the current direction 1 =200m, and then the ramping capacity is K 1 =3° / 30m tool to adjust the wellbore trajectory. The design result is to drill S with a constant tool face angle ω=-33.28° 1 =235.54m and then use the stabilized drilling tool to drill L 2 =1821.75m can accurately reach the design target point. The wellbore trajectory data are shown in Table 1.
[0126] Table 1 Design data of directional well track (three-section track)
[0127]
example 2
[0128] Example 2: Coordinate X of the end point of a 3D horizontal well T =31.70m, Y T =-1288.80m, Z T =869.42m, horizontal section inclination angle α 3 =90.36°, azimuth φ 3 =270°, segment length L 3 =941.72m. Build-up from the vertical well section, the build-up point is deep L 1 =532m, curvature K 1 =K 2 = 6° / 30m, using the constant tool face angle method to design the wellbore trajectory.
[0129] Using the dual-constant tool-face angle orbit design model, the length, inclination angle, and azimuth angle of the corresponding circular arc orbit stable section are obtained, which are used as the initial value of the quasi-Newton method to solve the constant tool-face angle orbit constraint equation, and are calculated after 2 numerical iterations , and the result is L 2 =80.706m, α 2 =46.164°, φ 2 =277.686°, see Table 2 for borehole trajectory data.
[0130] Table 2 Horizontal well track design data (five-segment track)
[0131]
[0132] It can be seen from T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com