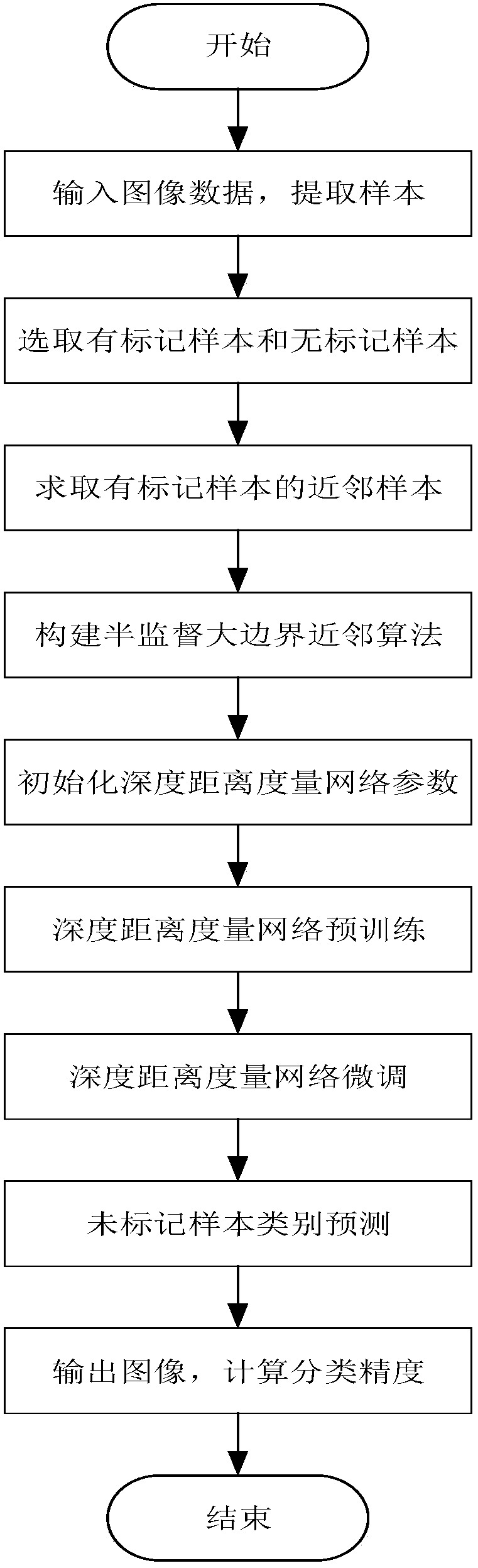
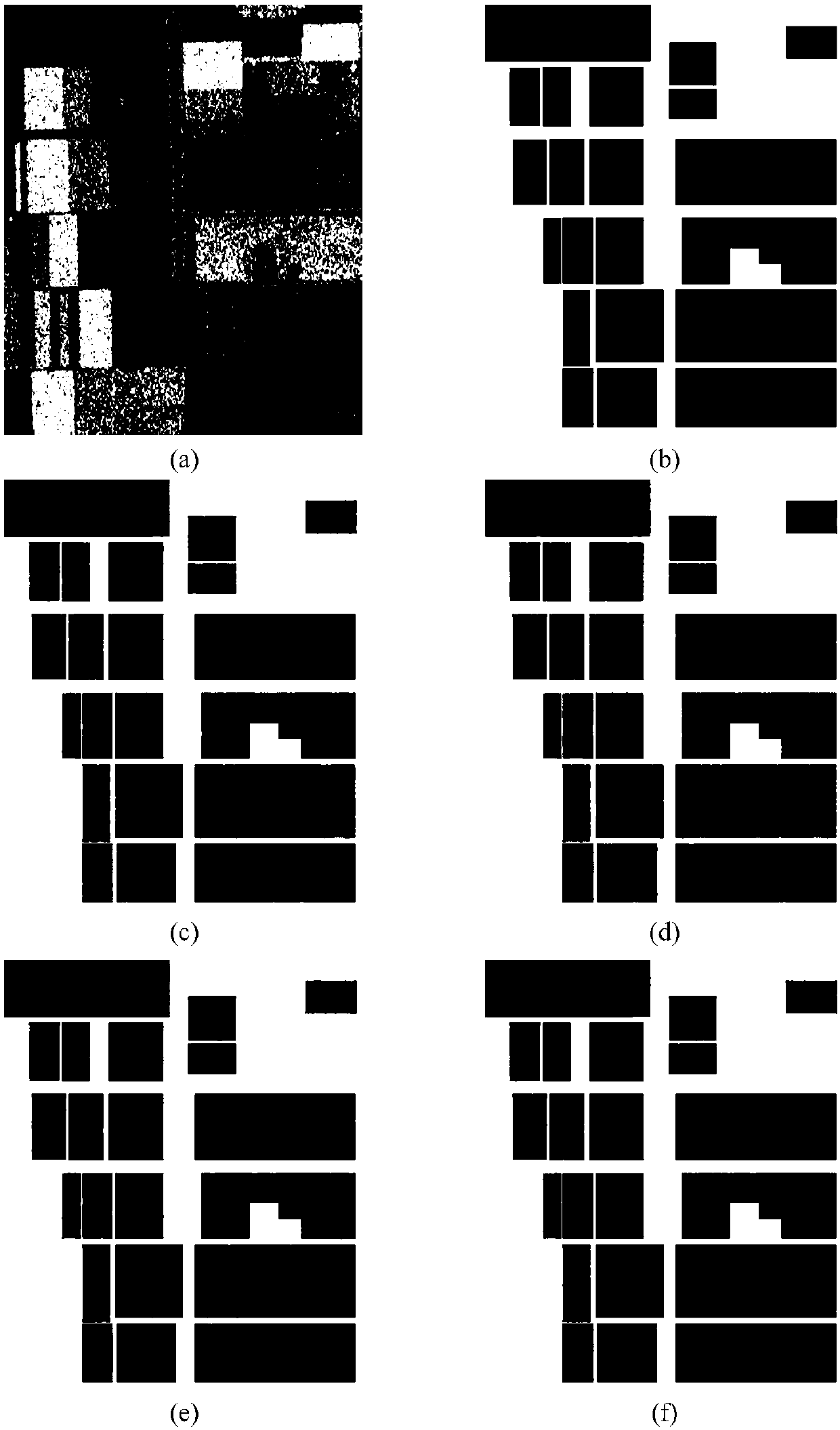
Polarized SAR image classification method based on semi-supervised depth distance metric network
A technology of depth distance and classification method, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems that the network performance cannot be guaranteed, the shallow features cannot fully reflect the intrinsic properties of the data, and the pre-training effect is not ideal, so as to improve the classification accuracy and improve The effect of lower classification accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Due to the development of remote sensing technology, it has been widely used in environmental monitoring, earth resource surveying, military systems and other fields, and the demand for polarimetric SAR image processing is also increasing. Deep learning has obvious advantages in machine learning methods. However, traditional deep learning networks are mostly unsupervised or supervised learning methods. When there are few labeled samples, unsupervised deep learning methods may underfit if they only rely on unsupervised pre-training, and a small number of labeled samples Fine-tuning cannot effectively improve network performance; for supervised deep learning methods, network training is insufficient and network performance is poor. Traditional deep learning methods do not take into account both the linear and nonlinear characteristics of samples, and the learned features cannot fully reflect the intrinsic properties of samples. In response to these current situations, the...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The polarized SAR image classification method based on the semi-supervised depth distance measurement network is the same as embodiment 1, and the Wishart nearest neighbor sample for each marked sample in step (3) includes the following steps:
[0040] 3a. The labeled sample matrix is Indicates the number of marked samples, and use the following formula to find the Wishart distance between each marked sample and the rest of the samples:
[0041] d(x i ,x j )=ln((x i ) -1 x j )+Tr((x j ) -1 x i )-q,
[0042] Among them, Tr () represents the trace of the matrix, for the radar whose transmission and reception are integrated, due to reciprocity, the constant q=3; for the radar whose transmission and reception are not integrated, the constant q=4;
[0043] 3b. Use the sort function in MATLAB to calculate the Wishart distance d(x i ,x j ) in ascending order of absolute value, taking the top K 1 labeled similar neighbor samples x j (j=1,2,...,K 1 ), K 2 unlab...
Embodiment 3
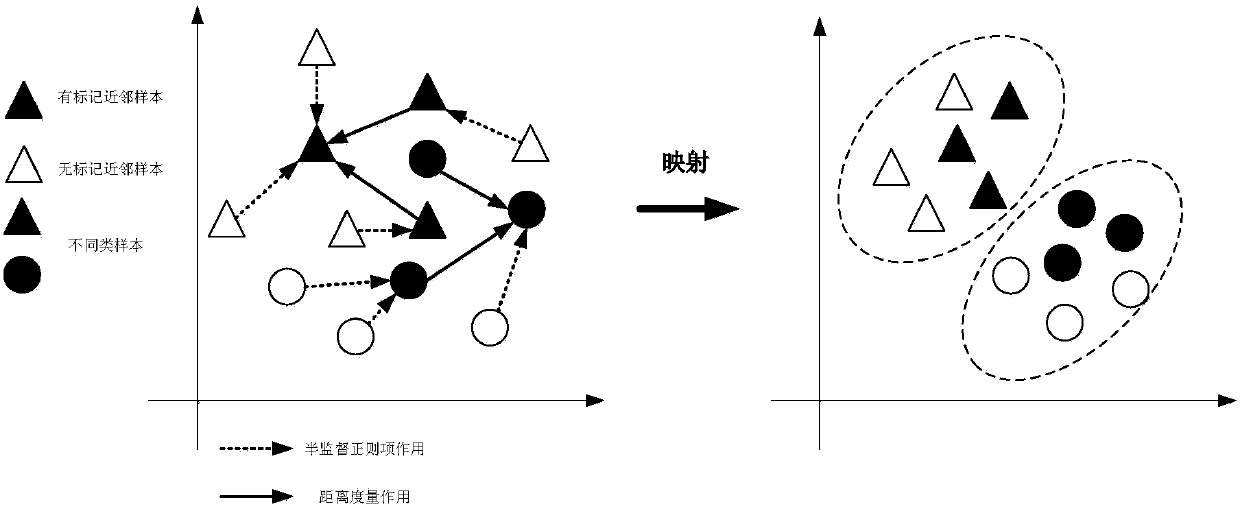
[0045] The polarized SAR image classification method based on the semi-supervised depth distance measurement network is the same as embodiment 1-2, and the process of constructing the loss function of the semi-supervised large boundary neighbor algorithm described in step (4) includes:
[0046] 4a. Find the loss function of the large boundary neighbor algorithm:
[0047] The distance square formula of the large boundary nearest neighbor algorithm is:
[0048]
[0049] Among them, L is a linear change matrix, x j is x i Similar labeled samples of . If there is a labeled sample x i x of non-homogeneous samples of l , satisfying the following formula:
[0050] ||L(x i -x l )|| 2 ≤||L(x i -x j )|| 2 +1,
[0051] Then, x l Known as an "imposter".
[0052] The large-boundary nearest neighbor algorithm can be expressed as two parts: the loss function ε between similar samples pull (L) and the loss function ε between non-similar samples push (L), ε pull (L) is used...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com