Method of consuming wind power blade waste in heat-engine plant
A wind power blade and waste technology, applied in the field of wind power blade waste disposal, can solve the problems of fuel and raw materials, and the difficulty of disposal of wind power blade waste, so as to reduce machine wear and tear, reduce initial investment and follow-up maintenance costs, and reduce toxic gases. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
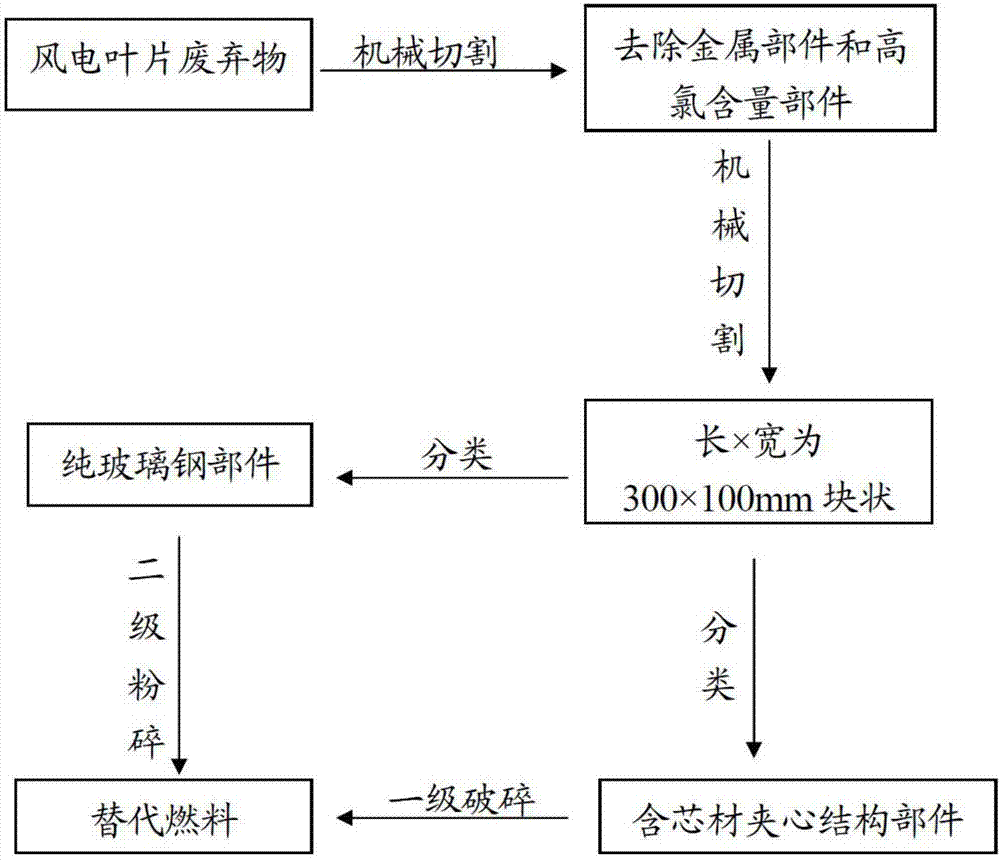
[0053] To transfer the scrapped wind power blades to the designated location, first use mechanical cutting to separate the metal parts and parts with high chlorine content from the main body of the blade. The metal parts are collected and sold in a centralized manner, and the parts with high chlorine content are temporarily stored. After the alternative fuel is blended, it enters the thermal power plant under the premise that the chlorine content of the alternative fuel is less than 0.025%.
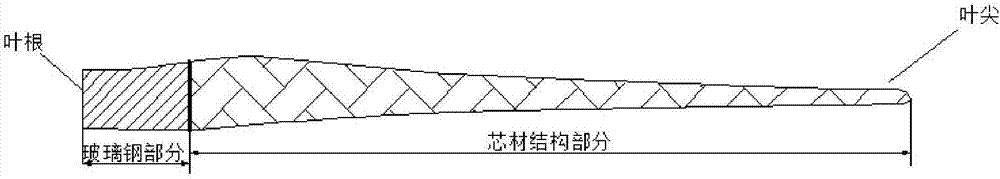
[0054] After removing the metal parts and parts with high chlorine content, cut the wind power blades into blocks with a length×width of 300×100mm, store the pure glass fiber reinforced plastic parts and the sandwich structural parts with core material, and put the glass fiber reinforced plastic parts and core materials to be pulverized The sandwich structure part is transported to the pulverizer device manually or by conveyor belt, and the pure FRP parts are pulverized by the pulverizer f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com