Laser scanning and heating fusion splicing mechanism of optical fiber fusion splicer
An optical fiber fusion splicer and laser scanning technology, applied in the field of optical fiber fusion, can solve the problems of tediousness, poor fusion effect, and low success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0010] Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
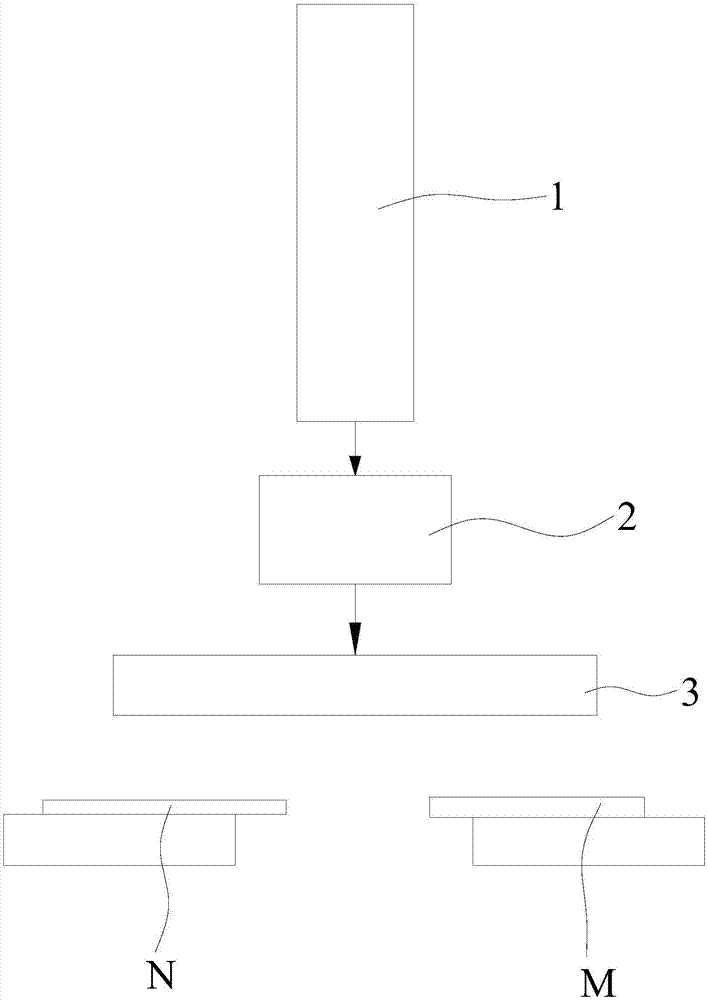
[0011] Optical fiber fusion machine laser scanning heating fusion mechanism, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a carbon dioxide laser 1, the laser output port of the carbon dioxide laser 1 is equipped with a vibrating mirror 2, and the front end of the vibrating mirror 2 is installed with a field mirror 3, and the laser beam emitted by the carbon dioxide laser 1 is scanned by the vibrating mirror 2 and focused by the field mirror 3 to form Laser spot output.
[0012] The carbon dioxide laser 1 of the present invention is installed on the optical fiber fusion splicer to replace the heat source (arc) of the existing optical fiber fusion splicer, and the vibrating mirror 2 and the field mirror 3 are installed at the laser output port of the carbon dioxide laser 1 . The fiber fusion splicing process is as follows: first, clamp the two sections of optical...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com