PMSM rotor position detection device and method based on improved sliding-mode observer
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor position detection technology, which is applied in motor control, electronic commutation motor control, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as phase lag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
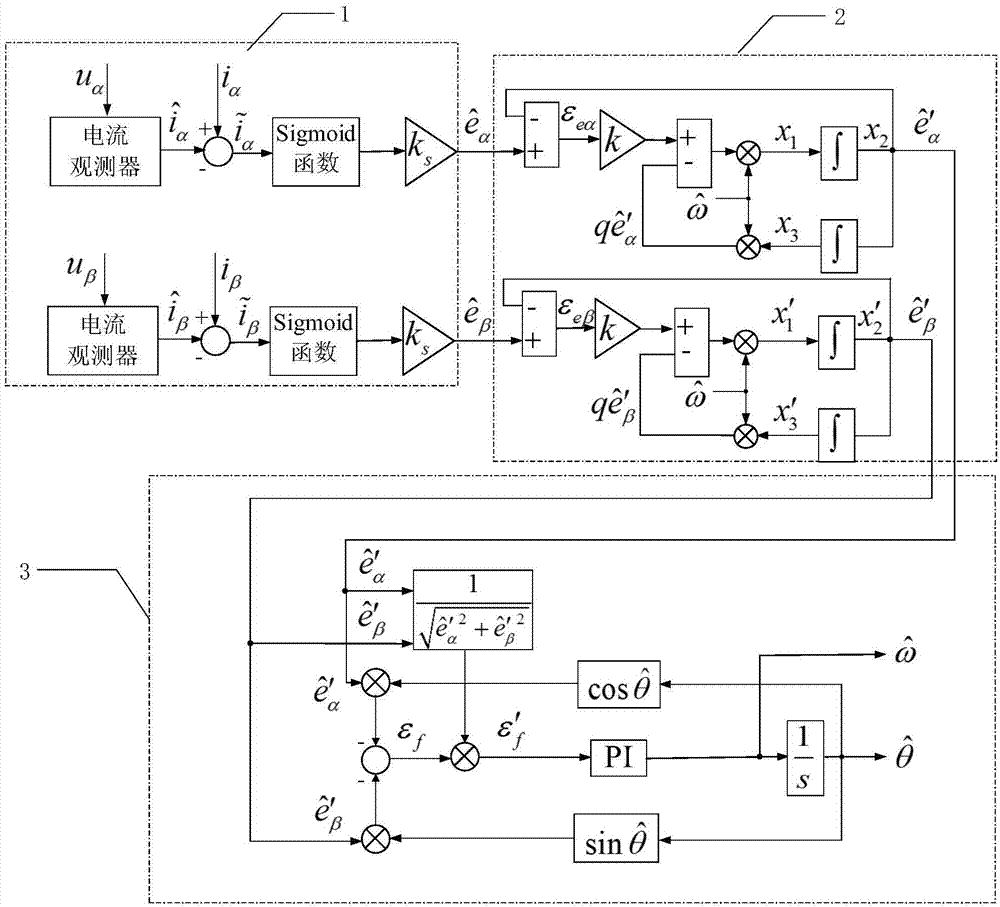
[0027] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position detection device based on the improved sliding mode observer described in this method includes a back EMF estimation part 1, a second-order generalized integral filter part 2 and a normalized quadrature phase-locked loop 3 .
[0028] The back EMF estimation part 1 is provided with four input terminals, which are respectively the α-axis voltage u in the two-phase stationary coordinate system α , β-axis voltage u β , α-axis current i α and β-axis current i β , set the two output terminals as the equivalent value of the back EMF of the α axis and the equivalent value of the back EMF of the β axis The second-order generalized integral filter part 2 sets the two input terminals as the equivalent value of the back EMF of the α axis and the equivalent value of the back EMF of the β axis Respectively with the back EMF equivalent value of the ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further limitation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position detection device based on the improved sliding mode observer described in specific embodiment 1. The back EMF estimation part 1 includes a current observer part, a sigmoid Function Section, Gain Section and Subtractor Section.
[0030] The setting of the back EMF estimation part 1 The four inputs are respectively the α-axis voltage u α Input and β-axis voltage u β Input, α-axis current i α and β-axis current i β . Among them, the current observer part sets the α-axis voltage u in the two-phase stationary coordinate system α Input and β-axis voltage u β input, sets the alpha axis to estimate the current output and beta-axis estimated current output. The output of the current detection part is used as the input of two subtractors, and the input of the subtractor also includes the α-axis current i α and β-axis current i β . α-axis current i ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0031] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is a further limitation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position detection device based on the improved sliding mode observer described in specific embodiment one, and the second-order generalized integral filter part 2 includes four subtractors , two gain links, four multipliers and four integrators.
[0032] The input of the second-order generalized integral filter part 2 is connected with the output of the back EMF estimation part 1, that is, the input of the second-order generalized integral filter part 2 is the back EMF equivalent value of the α axis and the equivalent value of the back EMF of the β axis The equivalent value of the back EMF of the α axis As the input of the first subtractor of the alpha phase, and the other input of the first subtractor is the estimated value of the back EMF of the alpha axis Subtract, get α-axis back EMF error ε eα ;Equivalent value of the back EMF of the β axis A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com