Brewing technology for cooked rice wine
A technology of glutinous rice wine and craftsmanship, applied in the field of brewing technology, can solve the problems of impossible to achieve uniform quality standards, not to mention typical styles, not able to taste liquor, etc., to achieve good brewing effect, avoid flavor loss, and small differences Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
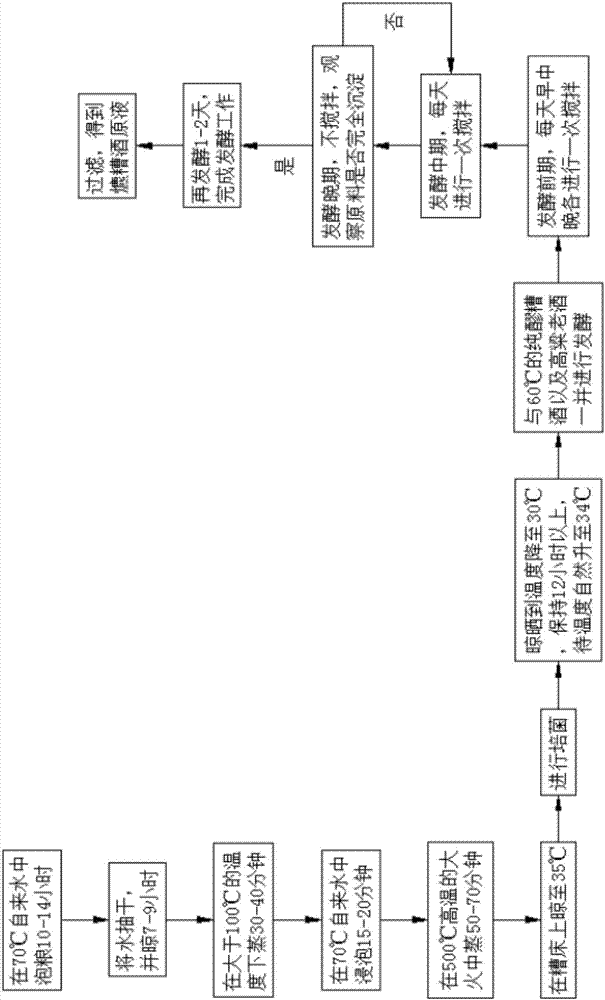
[0036] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of brewing process of distilled spirits comprises the following steps:
[0037] a. Soak grain in tap water at 70°C for 10 hours;
[0038] b. After soaking, drain the water and let it dry for 7 hours;
[0039] c. After drying, steam for 30 minutes at a temperature greater than 100°C;
[0040] d. Steam on high heat for 50 minutes;
[0041] e. Dry the steamed grain on the bad bed to 35°C, and carry out the operation of cultivating bacteria;
[0042] f. After the cultivation is completed, continue to dry, lower the temperature to 30°C, and keep it for more than 12 hours, until the temperature naturally rises to 34°C;
[0043] g. Put the grain with the temperature up to 34°C together with the pure fermented glutinous rice wine and sorghum old wine at 60°C into the fermentation tank for 6 days of fermentation.
[0044] In one of the embodiments, a brewing process of distilled spirits comprises the following steps:
[0045] a. Soak grain in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com