A Hovercraft Path Tracking Control Method Based on Second-Order Sliding Mode Control
A second-order sliding mode, control method technology, applied in adaptive control, general control system, control/regulation system, etc., can solve the problems of high robustness, no hovercraft, etc., to reduce the degree of jitter and robustness The effect of improving the robustness of the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
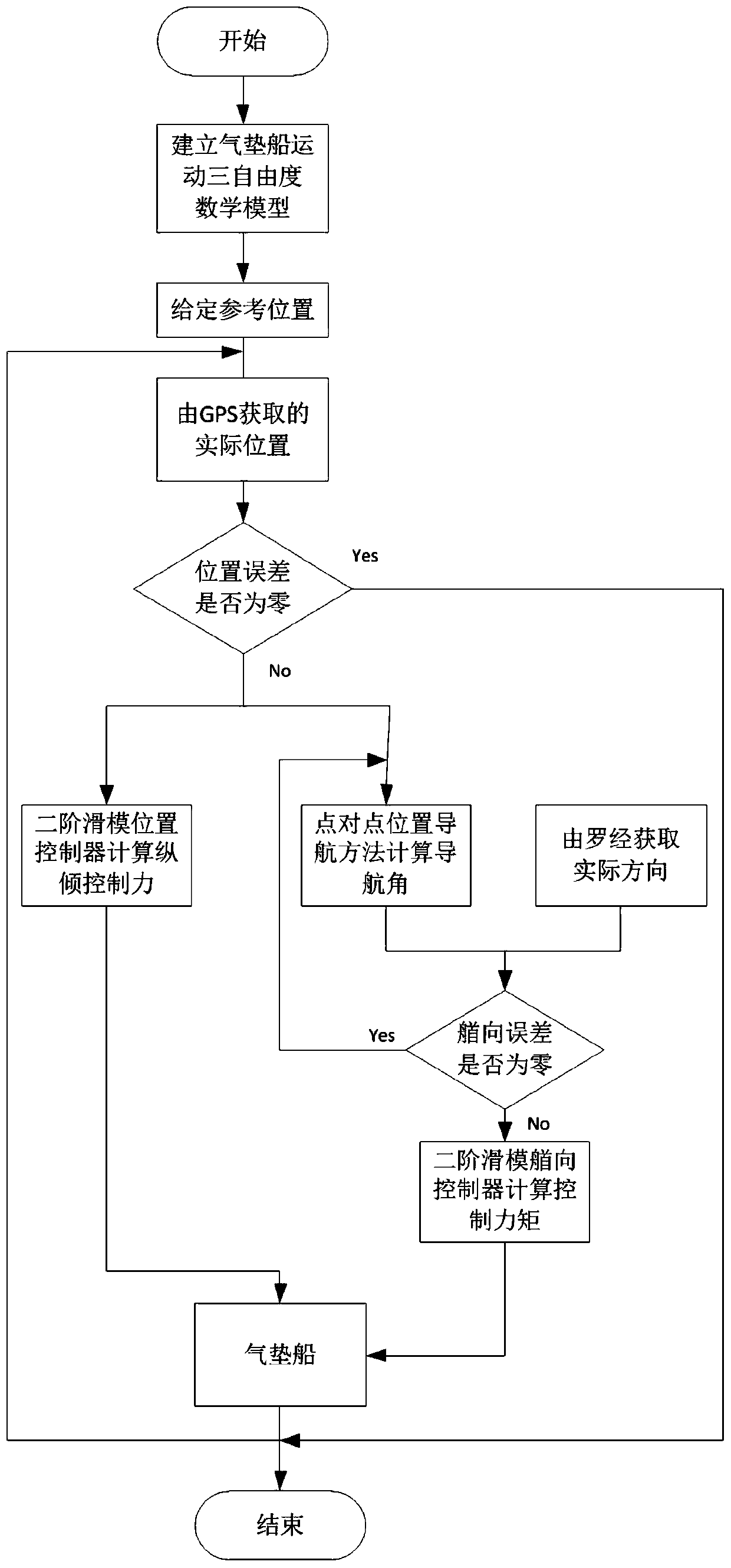
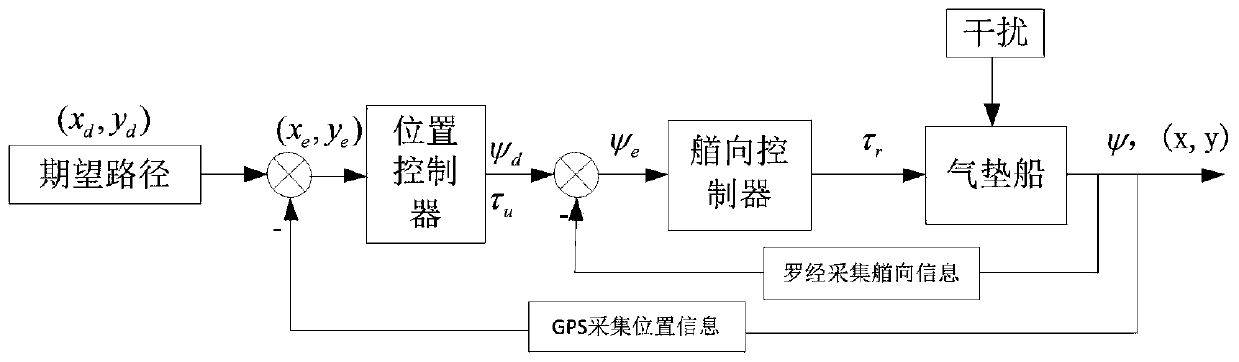
[0069] Specific embodiment one: a kind of hovercraft path tracking control method based on the second-order sliding mode control described in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0070] 1. Establish the three-degree-of-freedom mathematical model of the hovercraft motion:
[0071] Study space moving bodies, establish a fixed coordinate system and a hull motion coordinate system, and establish a three-degree-of-freedom motion mathematical model for the three degrees of freedom of the hovercraft, sway, surge, and yaw;
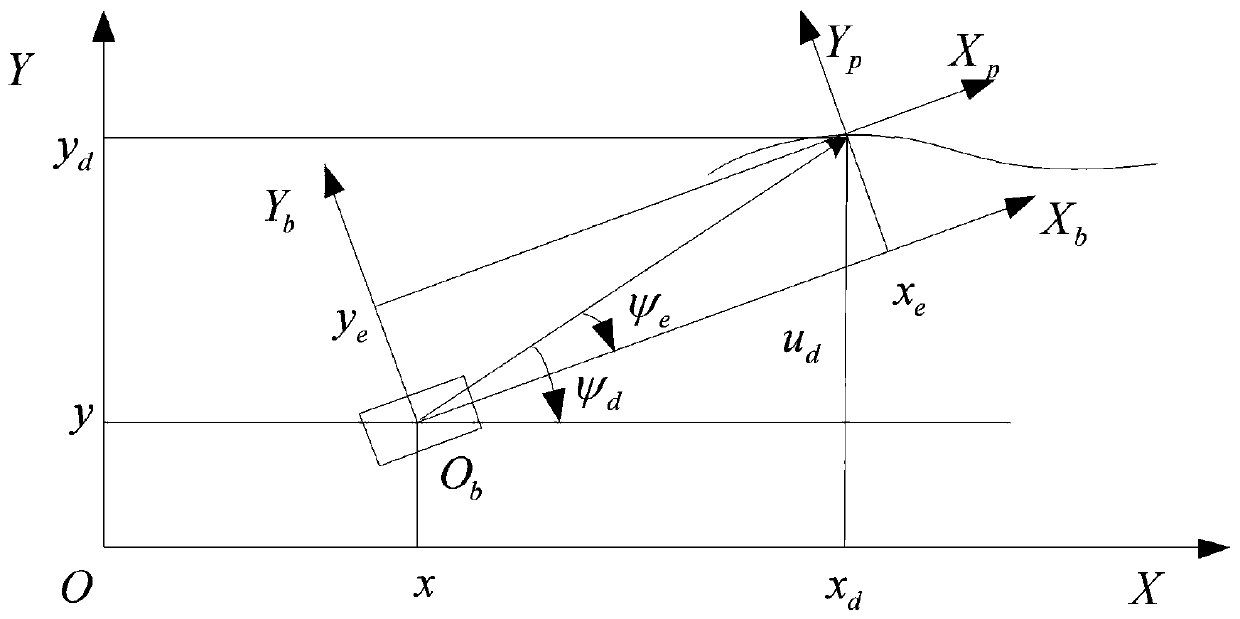
[0072] 2. Get the position error:
[0073] Obtain the actual position of the hovercraft through the global positioning system GPS, and compare it with a given reference path to obtain the actual error;
[0074] 3. Design a second-order sliding mode point-to-point position controller:
[0075] Based on the mathematical model of hovercraft motion established in step 1 and the position error in step 2, a second-order sliding mode point...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0082] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of the hovercraft path tracking control method based on second-order sliding mode control described in Embodiment 1. The specific process of establishing the three-degree-of-freedom mathematical model of the hovercraft motion in step 1 is as follows:
[0083] Establish a mathematical model for the three-degree-of-freedom water surface movement of the hovercraft:
[0084]
[0085] Where: η=[x,y,ψ] T Indicates the position and heading angle of the hovercraft; υ=[u,v,r] T Indicates the velocity and angular velocity of the hovercraft; M=diag{m,m,I z} represents the mass and moment of inertia of the hovercraft; τ=[τ u ,0,τ r ] T Indicates control force and control torque; d=[d u d v d r ] T Indicates external interference; k mi (i=1~7) represents the damping coefficient; the additional mass matrix C(υ) and the rotation matrix R(ψ) are as follows:
[0086]
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0087] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further description of the hovercraft path tracking control method based on second-order sliding mode control described in Embodiment 1. The specific process of designing the second-order sliding mode heading controller in step 6 is as follows:
[0088] Based on the three-degree-of-freedom mathematical model of the air-cushion motion established in step 1, the nonlinear second-order model of the heading subsystem of the hovercraft motion is obtained as follows:
[0089]
[0090] Aiming at the above second-order nonlinear model, the traditional sliding mode surface s is designed 1 and the nonsingular terminal sliding surface σ 1 :
[0091]
[0092] where: x 1 =ψ,x 2 = r, e 1 =x 1 -ψ d , lambda 1 >0,β 1 >0,p 1 ,q 1 It is a positive odd number, satisfying: 11 / q 1 d To refer to the heading angle, it is designed in step 3.
[0093] The design heading control torque is:
[0094]
[0095] Among them: K 1 >0 is the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com