Maritime search and rescue wireless sensing network synergic positioning method
A wireless sensor network and co-location technology, applied in wireless communication, wireless communication services, machine-to-machine/machine-type communication services, etc., can solve the problem of complex dynamic space relative position estimation and analysis, and the accuracy of node signal index measurement. lowering etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
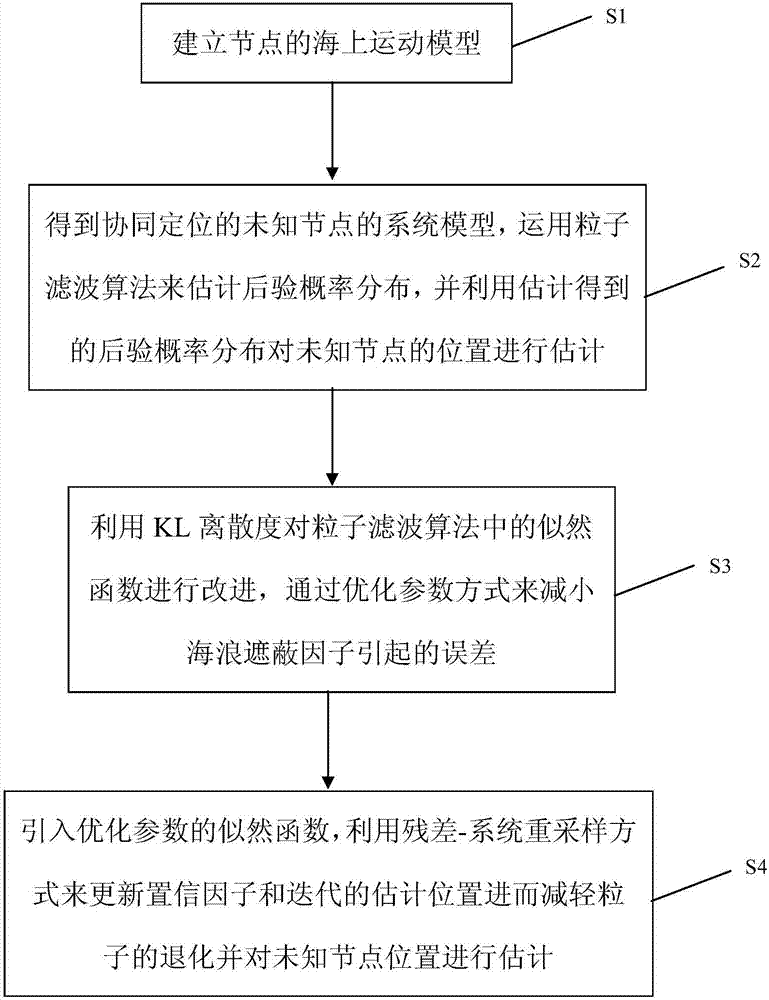
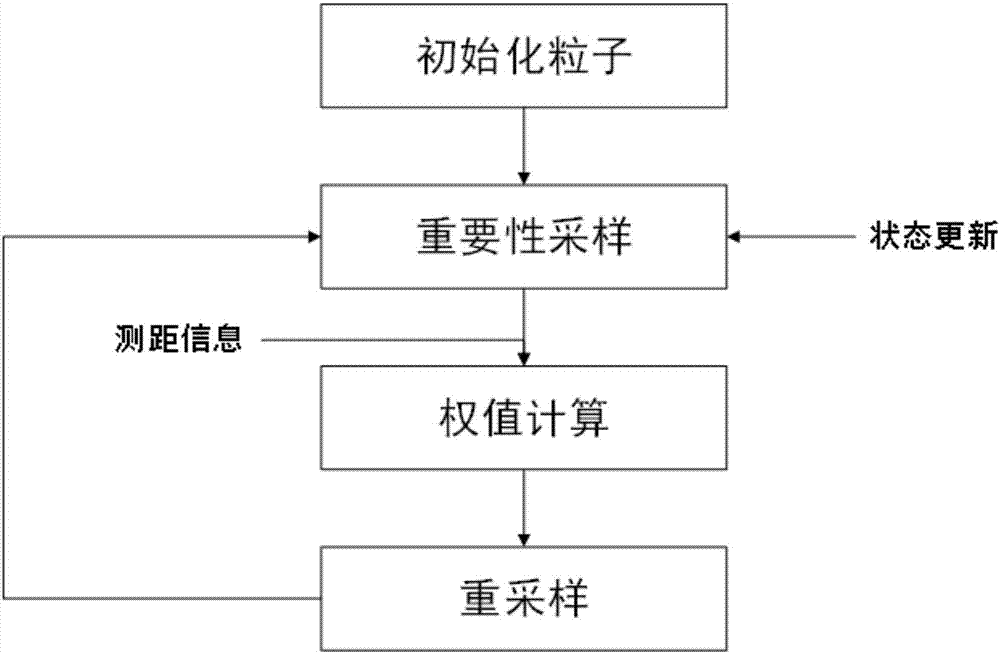
[0087] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, by describing a preferred specific embodiment in detail, the present invention is further elaborated.
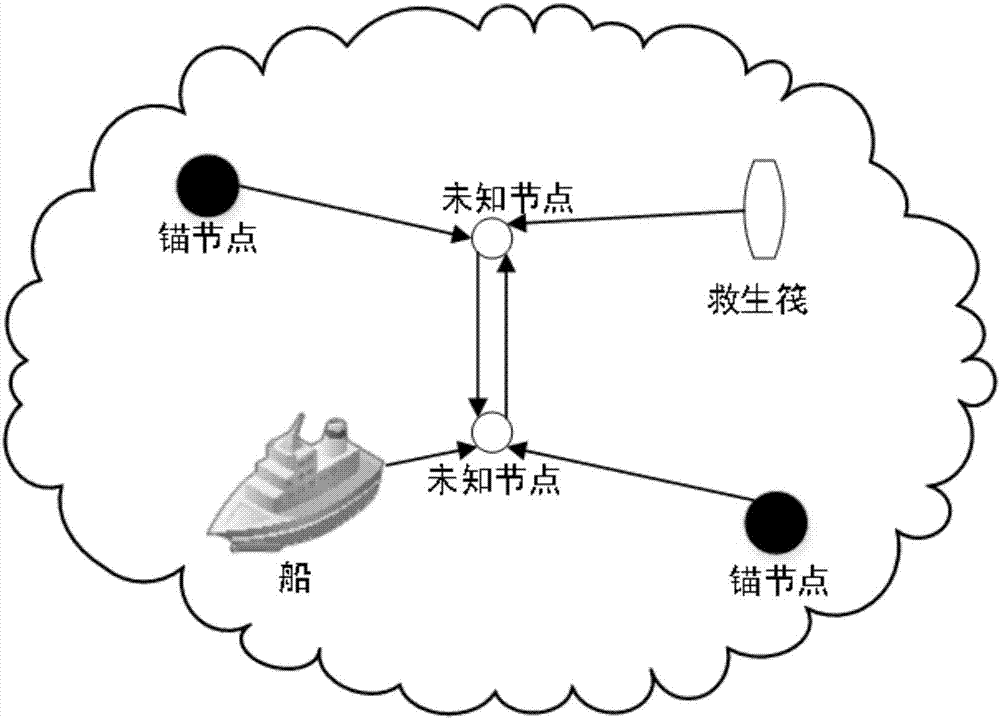
[0088] figure 2 Denotes a schematic diagram of maritime co-location in wireless sensor networks. People carrying unknown node lifejackets can interact with ships or lifeboats with GPS information, and they can communicate with anchor nodes or other unknown nodes deployed at sea without fixed positions. The distribution nodes (that is, all nodes, including unknown nodes and anchor nodes) are in the search and rescue sea area, and the nodes establish their wireless sensor network through the Zigbee protocol. Suppose there are s anchor nodes and n unknown nodes in the network. S and N represent the set of anchor nodes and the set of unknown nodes respectively, that is, n∈N, s∈S. The location set of the anchor node at time t can be expressed as a vector T stands for transpose. The location set of the same unknown node...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com