Termitornyces albuminosus and termite symbiotic cultivation method
A cultivation method and a technology for the fungus of Galliconia, applied in the directions of cultivation, plant cultivation, mushroom cultivation, etc., can solve the problems of quality gap of the mushroom, extremely high environmental requirements, difficult characteristic requirements, etc., so as to improve the fruiting rate and quality, Avoid excessive range of activities and improve the quality of the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
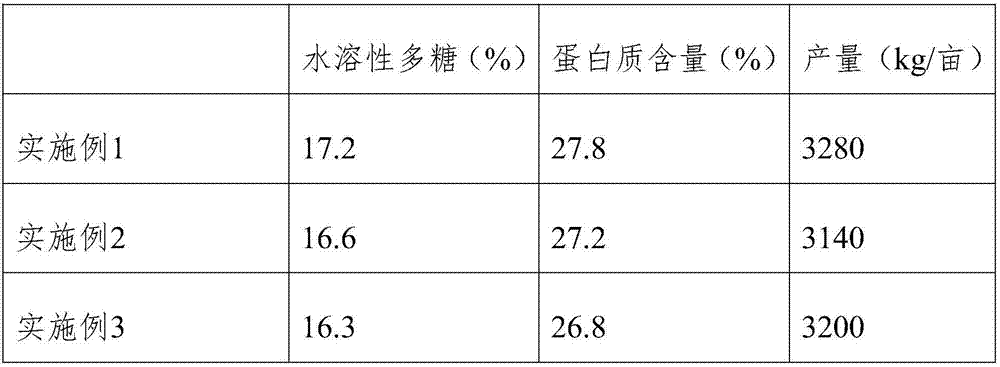
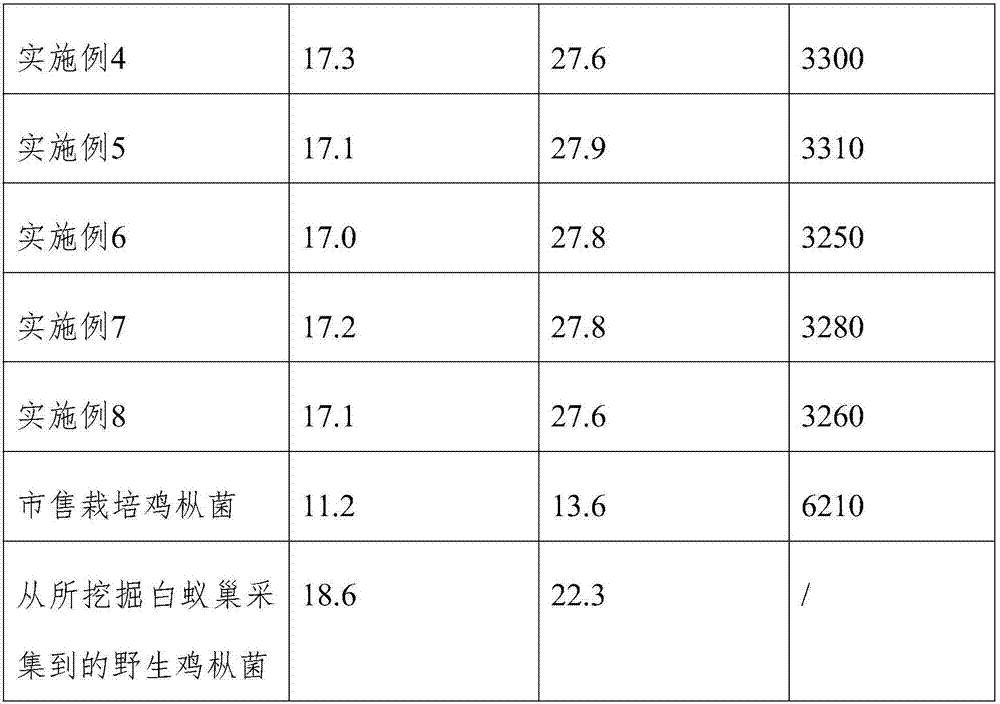
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Breeding termites:
[0034] a. Select land suitable for the growth of termites as a breeding garden, digging an area of 1.85m 2 , The deep pit with a depth of 2m is used as an ant nest, and the distance between the deep pits is 1.75m. Dig a canal around the ant nest, and the canal surrounds the ant nest to provide water for the ant colony. In the outermost circle of the breeding garden, open a ditch with a depth of 1.75m , with a width of 40cm, keep the water flow in it, and plant Asarum and Litsea Cubeba in a ratio of 1:1 on the edge of the ditch to prevent termites from approaching the edge of the breeding garden;
[0035] b. Lay boards, branches, and fresh leaves loosely on the bottom of the ant nest, and prepare food for the ant colony to be moved in;
[0036] c. From the place where ant nests are built in the wild, dig out the main nest and fungus garden with ant kings and queens and move them into the ant nests;
[0037] d. Use loose soil to cover the ant ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) Breeding termites:
[0047] a. Select land suitable for termite growth as a breeding garden, digging an area of 1.5m 2 , The deep pit with a depth of 1.8m is used as an ant nest, and the distance between the deep pits is 1.5m. Dig a canal around the ant nest, and the canal surrounds the ant nest to provide water for the ant colony. In the outermost circle of the breeding garden, open a ditch with a depth of 1.5 m, width 30cm, keep the flow of water in it, and plant Asarum and Litsea Cubeba in a ratio of 1:1 on the edge of the ditch to prevent termites from approaching the edge of the breeding garden;
[0048] b. Lay boards, branches, and fresh leaves loosely on the bottom of the ant nest, and prepare food for the ant colony to be moved in;
[0049] c. From the place where ant nests are built in the wild, dig out the main nest and fungus garden with ant kings and queens and move them into the ant nests;
[0050] d. Use loose soil to cover the ant nest slightly, spr...
Embodiment 3
[0059] (1) Breeding termites:
[0060] a. Select land suitable for the growth of termites as a breeding garden, digging an area of 2.2m 2 , The deep pit with a depth of 2.2m is used as an ant nest. The distance between the deep pits is 2m. Ditches are dug around the ant nests. The width is 50cm, keep the water flowing in it, and plant asarum and litsea cubeba in a ratio of 1:1 on the edge of the ditch to prevent termites from approaching the edge of the breeding garden;
[0061] b. Lay boards, branches, and fresh leaves loosely on the bottom of the ant nest, and prepare food for the ant colony to be moved in;
[0062] c. From the place where ant nests are built in the wild, dig out the main nest and fungus garden with ant kings and queens and move them into the ant nests;
[0063] d. Use loose soil to cover the ant nest slightly, sprinkle a layer of sawdust, wheat bran, and fresh tree leaves, and perform shading treatment on the ant nest, so that the environment around the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com