Nonwoven fabric and production method for same
A technology of non-woven fabric and thickness direction, which is applied in the field of non-woven fabric and its manufacturing, and can solve the problems of air permeability influence and high density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
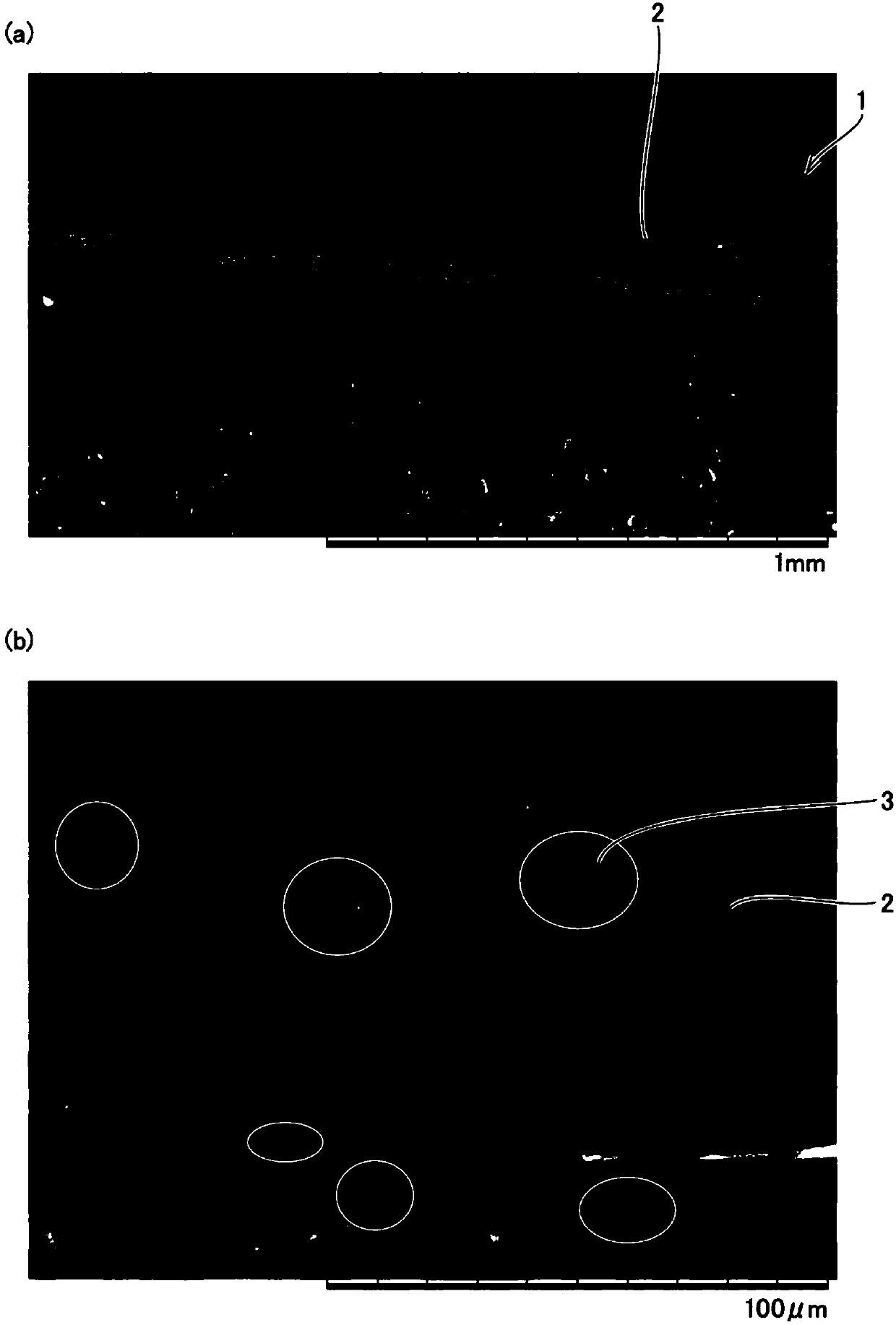
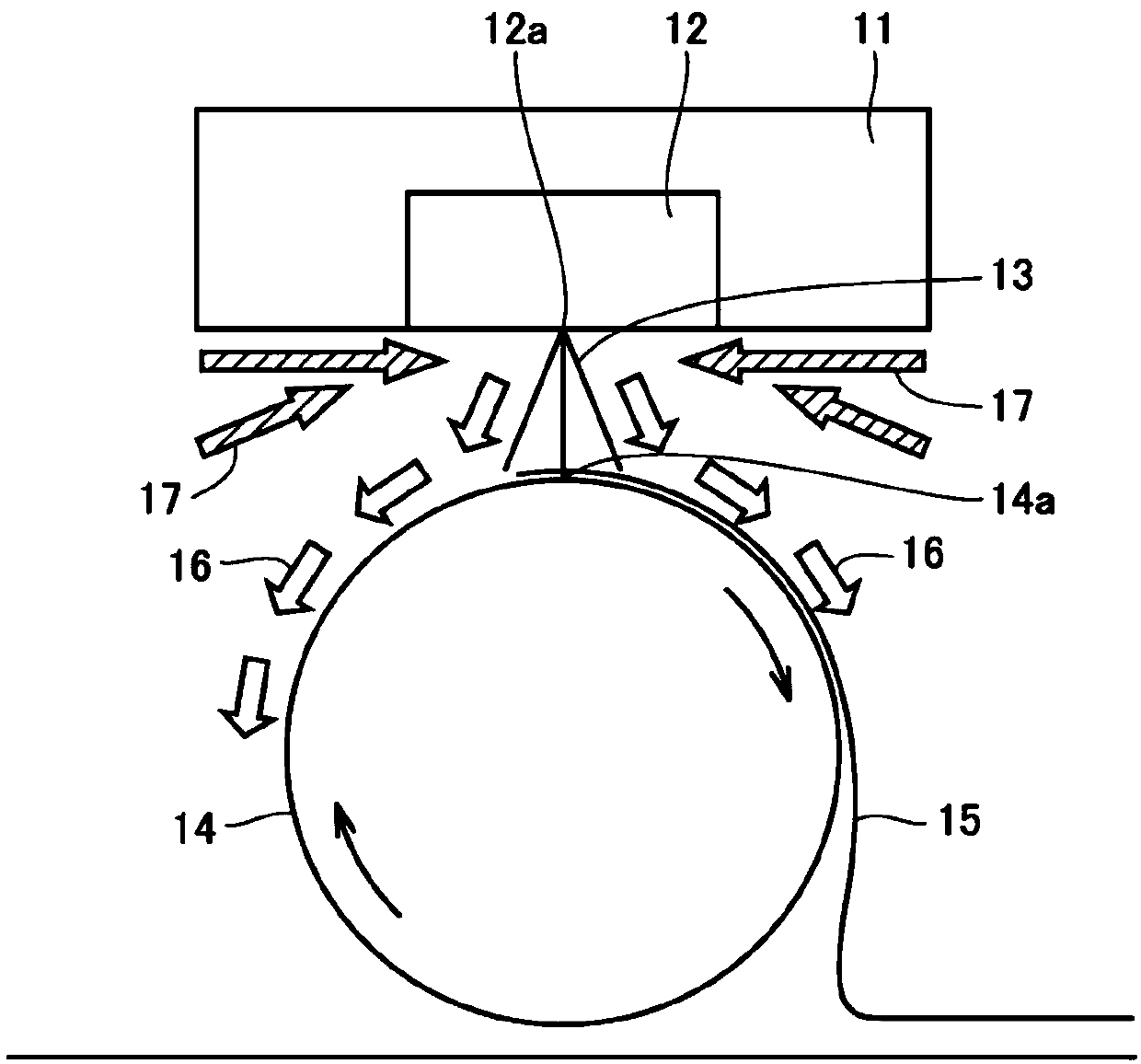
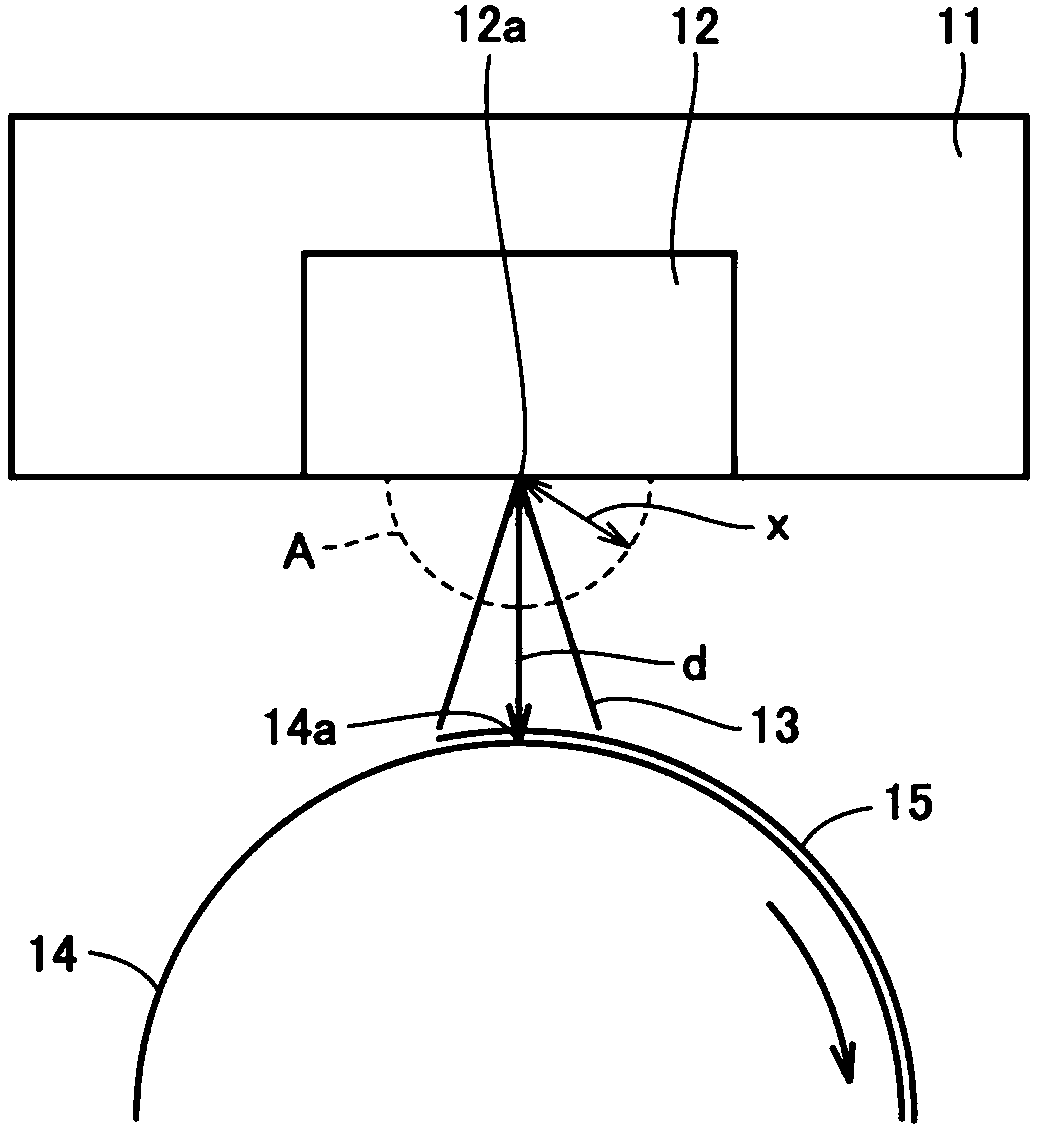
[0123] Using an amorphous polyetherimide whose melt viscosity at 330° C. is 500 Pa·S, extruded through an extruder, and supplied to a nozzle hole diameter D (diameter) of 0.3 mm, L (nozzle length) / D = 10, Meltblown device with a nozzle hole spacing of 0.75mm, a single hole discharge rate of 0.09g / min, a spinning temperature of 390°C, a hot air (primary air) temperature of 420°C, and a nozzle width of 10Nm per 1m 3 Injection is carried out under the condition of / min, and the weight per unit area is 25g / m 2 of non-woven fabrics. At this point, set as Figure 4 A hot air ejection device such as the example shown, so that hot air (secondary air) is blown into the front end of the spinning nozzle of the melt blown device, and the temperature is 2Nm 3 Hot air (secondary air) at a temperature of 260° C. was blown to the front end of the spinning nozzle at a flow rate of 100 ℃. The linear distance d between the front end of the spinning nozzle and the receiving surface of the ro...
Embodiment 2
[0125] Using amorphous polyetherimide with a melt viscosity of 900 Pa·S at 330°C, the spinning temperature is 420°C, the average fiber diameter is 3.7 μm, and the fiber is positioned at the tip of the spinning nozzle with a radius of x The temperature measured by the thermometer on the outer periphery of the hemispheric shape of = 5 cm was 253° C. (that is, the space A was maintained at 38° C. higher than the glass transition temperature of amorphous PEI of 215° C.). The linear distance d between the collection surfaces of the spun fibers, measured by a thermometer placed 1 cm from the collection surface on the straight line, was 261 °C (i.e., keeping point B at a temperature higher than that of the amorphous PEI glass The nonwoven fabric was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the transition temperature was 46°C higher than 215°C.
Embodiment 3
[0127] Set the weight per unit area to 10g / m 2 , except that, it carried out similarly to Example 2, and obtained the nonwoven fabric.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com