Method for weaving 2.5D angle-interlock preformed part with section gradually decreasing
A prefabricated, corner interlocking technology, used in textiles, papermaking, fabrics, textiles, etc., can solve the problems of increased processes, inability to complete, and reduced performance of parts, to improve quality and performance, reduce fiber damage, and reduce processing. The effect of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
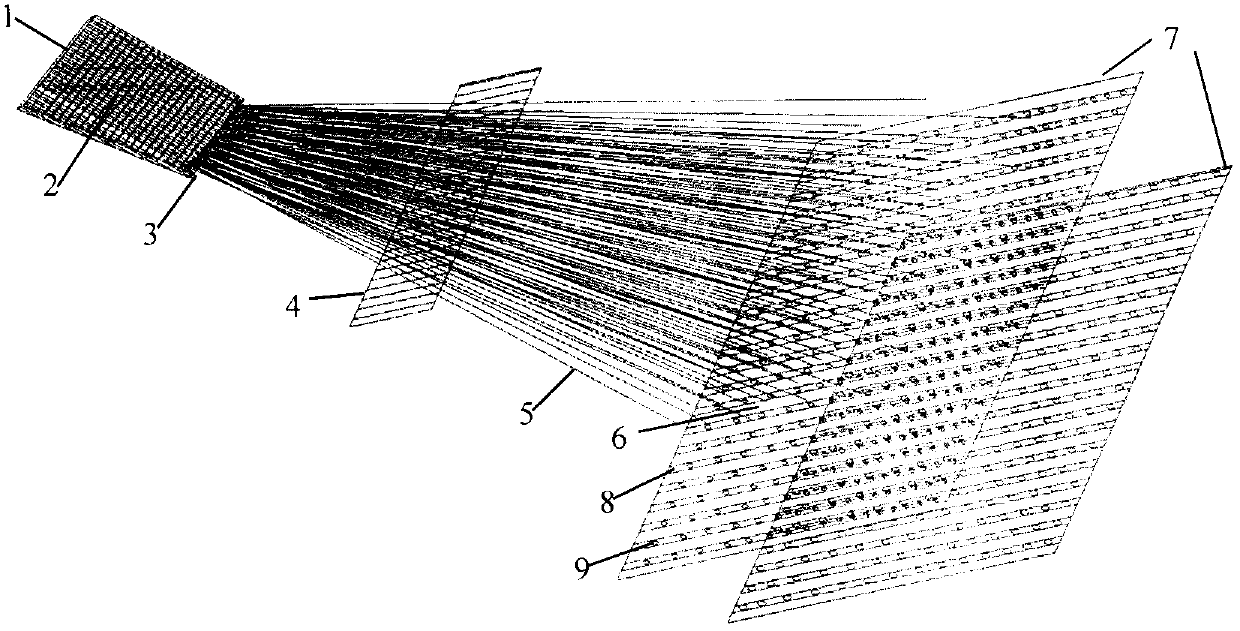
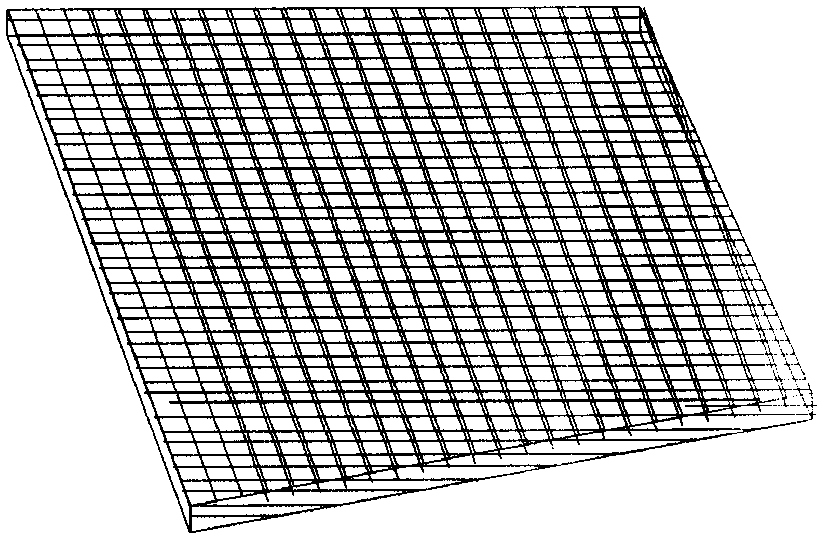
[0029] Adopt the trapezoidal body component (referring to of the inventive method weaving) Image 6 ). The cross-sectional size of its large end is 100mm×1.5mm (width×thickness), the trapezoid height is 100mm, the warp yarn density is 10 yarns / cm, the weft yarn density is 8 yarns / cm, the warp and weft yarns are carbon fiber T300-3K, and the reed used is 10 teeth / cm. According to the size requirements and density of the workpiece, the number of warp yarns required is 500, and the length of the warp yarns must be at least greater than 100mm.
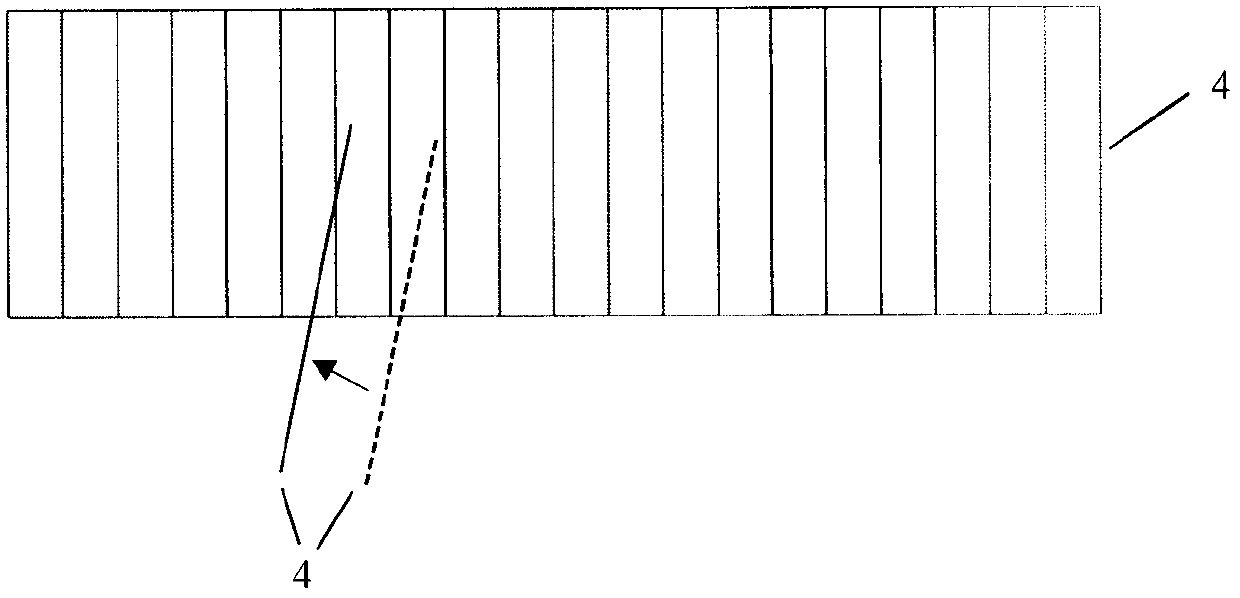
[0030] Warp yarn 5 is passed through reed 4 according to the requirement of warp density, and is suspended on the yarn hanging point 9 on the machine chassis 7 . The up and down reciprocating motion of the machine chassis 7 drives the warp yarn 5 to reciprocate up and down, and 6 or 4 channels are formed between the warp yarns 5 during the up and down reciprocating process. At this time, the weft yarn 3 is passed through the channels in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com