Rigidity-reinforced type bridge head structure for operating highway and governing bump at bridge head and construction method
A bridge head jumping and construction method technology, which is applied to roads, bridges, roads, etc., can solve the problems of high maintenance cost, low maintenance cost, poor reliability, etc., and achieve the effect of easy operation, preventing rainwater seepage, and eliminating looseness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
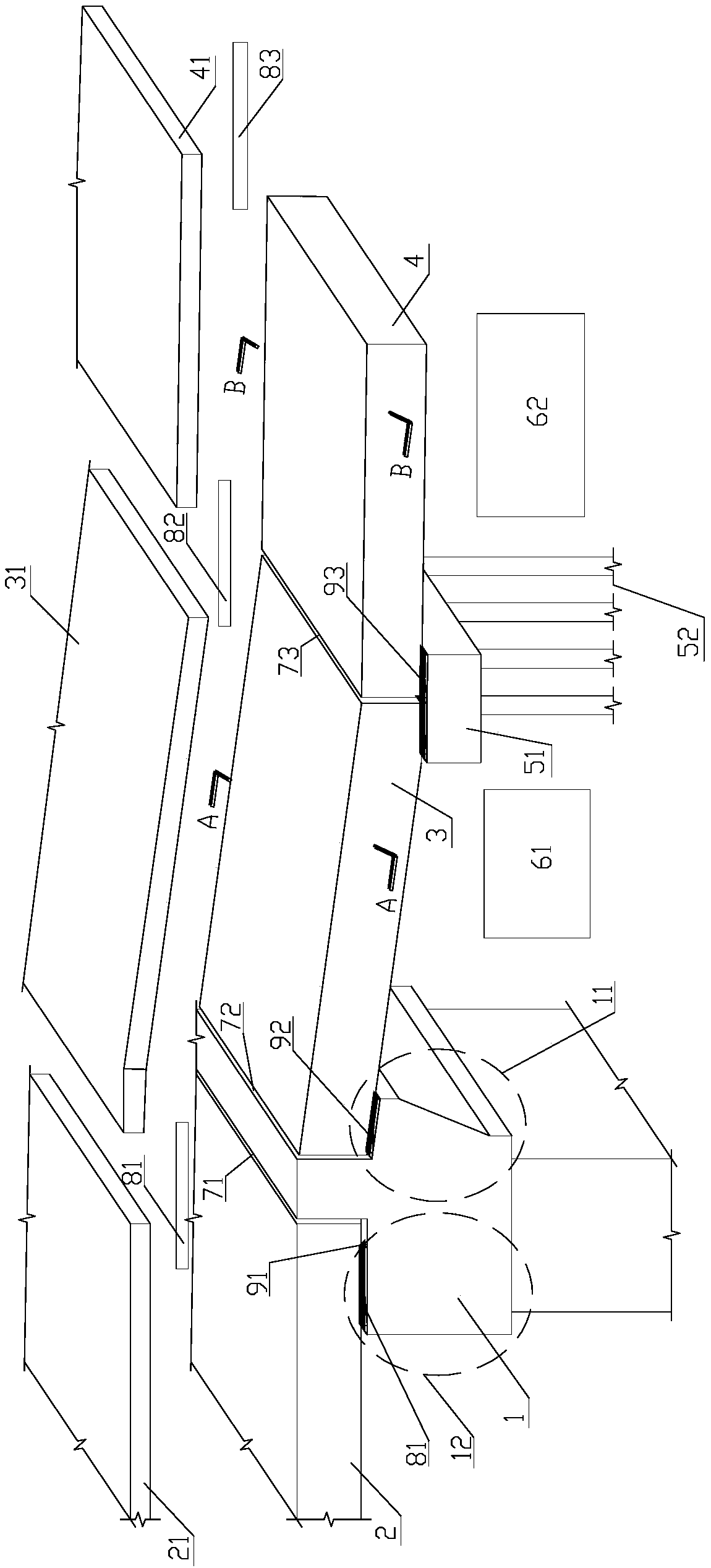
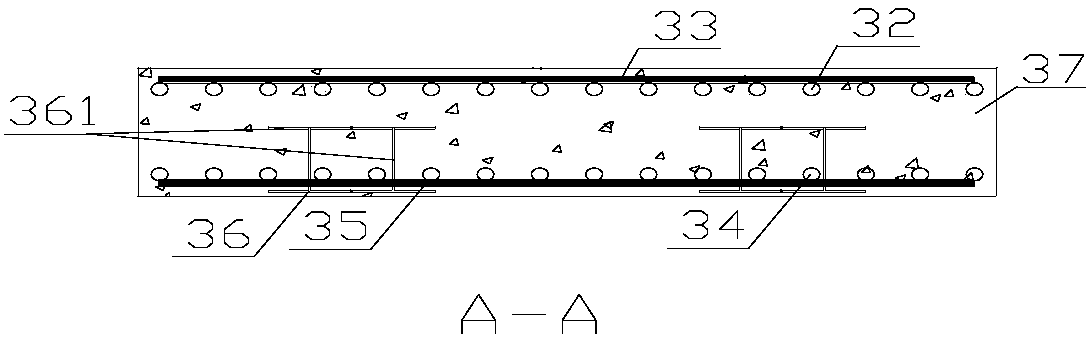
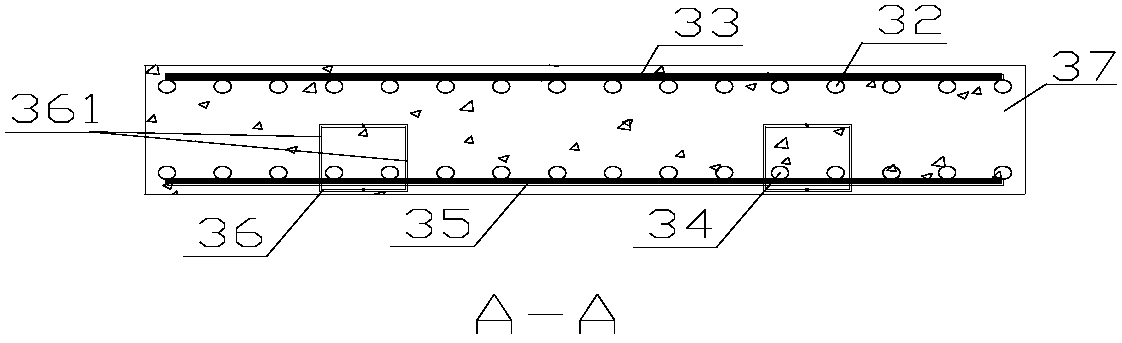
[0051] Refer to as Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 , Figure 8 ~ Figure 11 as well as Figure 13 , a rigidity-reinforced bridge head structure used to control bridge head jumping in operation roads, including abutment 1, abutment corbel 11, abutment support 12; bridge side span slab 2, bridge deck pavement 21; Slab 3, first-order pavement layer 31, upper longitudinal reinforcement 32, upper transverse reinforcement 33, lower longitudinal reinforcement 34, lower transverse reinforcement 35, concealed beam 36, concealed beam member 361, concrete 37 (or concealed beam upper reinforcement 381, concealed Beam upper reinforcement 382, concealed beam stirrup 383 and concrete 37); second-order slab 4, second-order pavement layer 41, upper longitudinal reinforcement 2 42, upper transverse reinforcement 2 43, lower longitudinal reinforcement 2 43, lower transverse reinforcement 2 44 ; supporting platform 51, foundation 52; roadbed one 61, roadbed two 62; first expansion joint 71, second expans...
Embodiment 2
[0063] refer to Figure 5 to Figure 12 and Figure 14 As shown, the bridge is two-way six-lane, with a total width of 22.5m. It is a rigidity-reinforced bridge head structure used for operating roads to control bridge head jumping, including abutment 1, abutment corbel 11, and abutment support 12; Bridge side span slab 2, bridge deck pavement 21; first-order slab 3, first-order pavement layer 31, upper longitudinal reinforcement 32, upper transverse reinforcement 33, lower longitudinal reinforcement 34, lower transverse reinforcement 35, concealed beam 36, concealed Beam member 361, concrete 37 (or concealed beam upper reinforcement 381, concealed beam upper reinforcement 382, concealed beam stirrup 383 and concrete 37); second-order slab 4, second-order pavement layer 41, upper longitudinal reinforcement 2 42, upper transverse Reinforcement 2 43, lower longitudinal reinforcement 2 43, lower transverse reinforcement 2 44; supporting platform 51, foundation 52; subgrade 1 61...
Embodiment 3
[0075] A construction method for a rigidity-reinforced bridge head structure used for bridge head jumping in operation of road management, comprising the following steps:
[0076] (1) Carry out ground treatment to the soft soil foundation, fill the roadbed and carry out surcharge preloading on the soft soil foundation;
[0077] (2) After the preload period expires, excavate the subgrade, construct the piles, abutments, beam slabs and expansion joints of the bridge; pre-embed dowel bars on the side of the abutment back;
[0078] (3) Backfill with graded crushed stone, and carry out layered rolling, and the compaction degree reaches the design standard;
[0079] (4) Set up the foundation of the supporting platform at the abutment end of the abutment in the range where the settlement increases near the abutment along the vehicle driving direction, and then carry out the cast-in-place and maintenance work of the supporting platform;
[0080] (5) Simultaneously with (4), and then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com