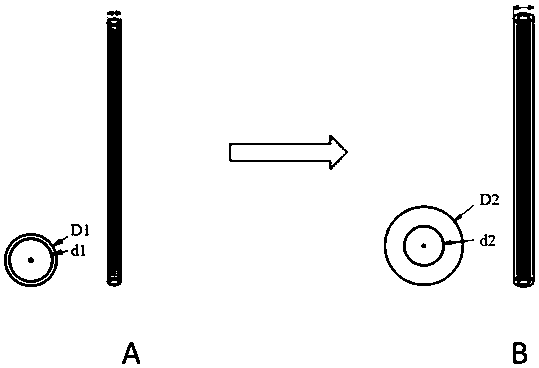
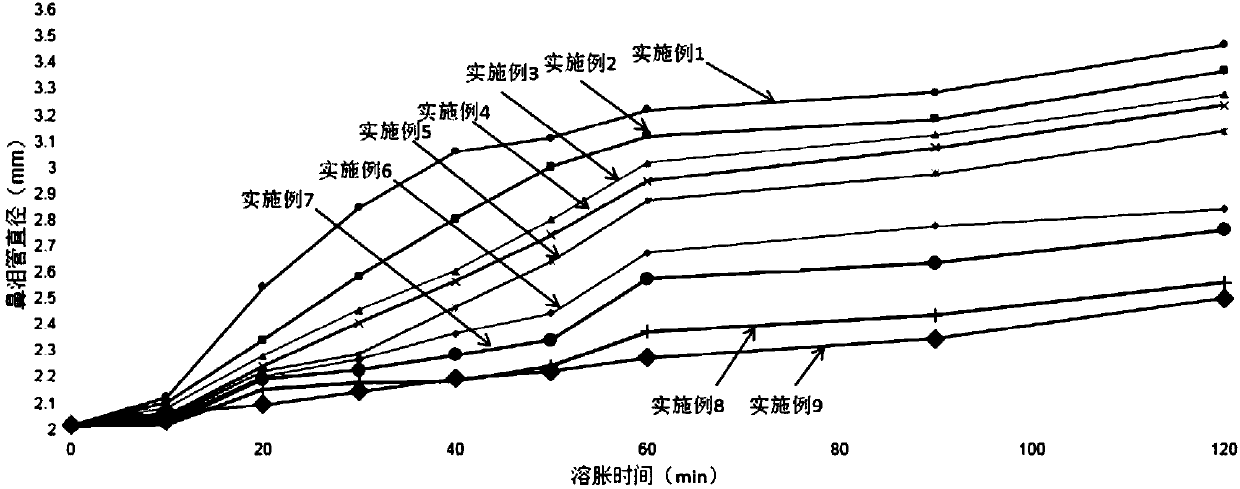
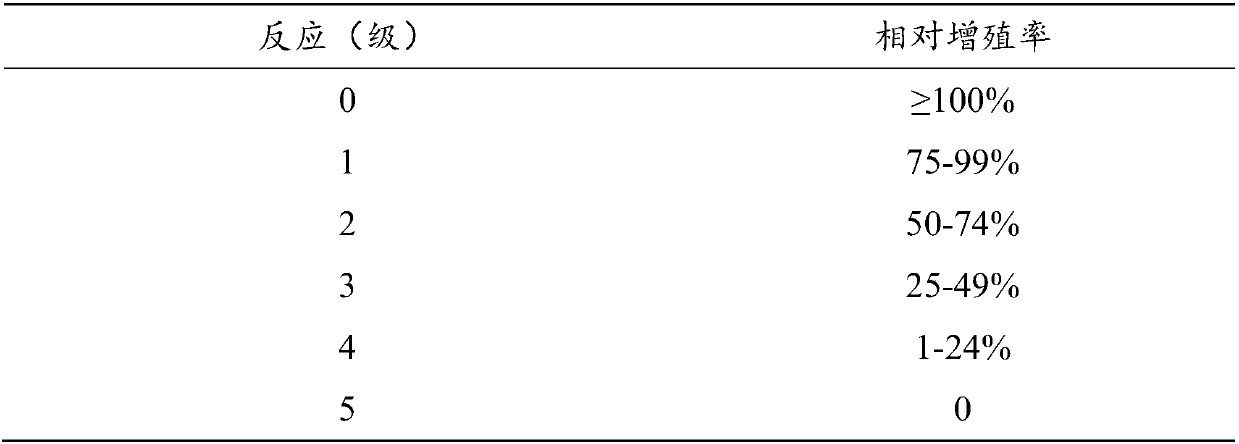
Artificial nasolacrimal duct capable of achieving self-expanding fixation
A nasolacrimal duct and self-expanding technology, which is applied in the human tubular structure device, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of high incidence of shedding, poor biocompatibility, and impossibility of permanent placement, so that it is not easy to fall off , good mechanical properties, easy to operate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] An embodiment of the artificial nasolacrimal duct of the present invention comprises the following preparation raw materials in parts by weight: 40 parts of hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 20 parts of crosslinking agent, 40 parts of water, 5 parts of thermal initiator and 10 parts of catalyst;
[0036] Wherein, the crosslinking agent is polyethylene glycol diacrylate, the thermal initiator is azobisisobutyronitrile, and the catalyst is N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine.
[0037] A kind of artificial nasolacrimal duct prepared by adopting the preparation raw materials of artificial nasolacrimal duct described in the present embodiment, the preparation method of described artificial nasolacrimal duct comprises the following steps:
[0038] (1), mix hydroxyethyl methacrylate, cross-linking agent, water, initiator and catalyst evenly, inject artificial nasolacrimal duct mold;
[0039] (2), the artificial nasolacrimal duct mold containing artificial nasolacrimal duct preparati...
Embodiment 2
[0043] An embodiment of the artificial nasolacrimal duct of the present invention, the difference between the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the ratio of the thermal initiator and the catalyst is different, the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this embodiment The preparation raw materials comprising the following parts by weight: 40 parts of hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 20 parts of crosslinking agent, 40 parts of water, 5 parts of thermal initiator and 5 parts of catalyst;
[0044] Wherein, the crosslinking agent is polyethylene glycol diacrylate, the thermal initiator is azobisisobutyronitrile, and the catalyst is N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine.
[0045] The preparation method of the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this example is the same as that in Example 1.
[0046] The size of the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1 before use
Embodiment 3
[0048]An embodiment of the artificial nasolacrimal duct of the present invention, the difference between the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the ratio of the thermal initiator and the catalyst is different, the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this embodiment Contains the following preparation raw materials in parts by weight: 40 parts of hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 20 parts of crosslinking agent, 40 parts of water, 5 parts of thermal initiator and 15 parts of catalyst;
[0049] Wherein, the crosslinking agent is polyethylene glycol diacrylate, the thermal initiator is azobisisobutyronitrile, and the catalyst is N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine.
[0050] The preparation method of the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this example is the same as that in Example 1.
[0051] The size of the artificial nasolacrimal duct described in this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1 before use
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com