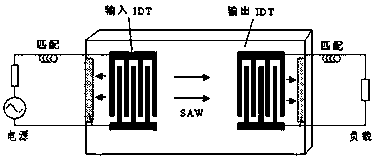
Bonding method for controlling micro-damage at root of wire bonding point of surface acoustic wave device
A surface acoustic wave device and bonding point technology, applied in electrical components, impedance networks, etc., can solve problems such as unavoidable missed detection, low efficiency, and inability to fully detect micro-cracks, reducing cost pressure and quality control pressure, The effect of stable quality and improved bonding reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
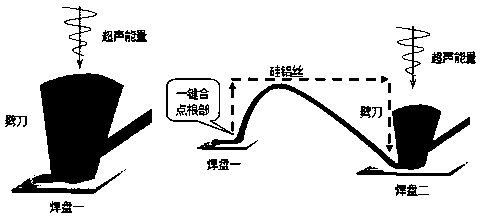
[0021] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the silicon-aluminum wire bonding process. At the first point of the bonding wire on the pad one, the hacker drives the silicon-aluminum wire to complete the arc drawing of the wire according to the path indicated by the arrow, and then bonds the second point on the pad two. Energy only occurs when welding the first and second points.
[0022] Ultrasonic energy consists of ultrasonic power P and ultrasonic duration T. Since ultrasonic vibration is parallel to the welding surface, it is also necessary to apply a downward pressure F perpendicular to the welding surface. The best match between the three parameters can ensure that the bonding point and the welding surface are fused, the molecules of the two materials diffuse to each other to form a firm bond, and at the same time, the micro-damage at ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com