Reading method and device of memory unit
A technology for storing cells and reading voltage, applied in the field of memory, can solve problems such as large changes in current, increased reading difficulty, and increased design complexity of current comparators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
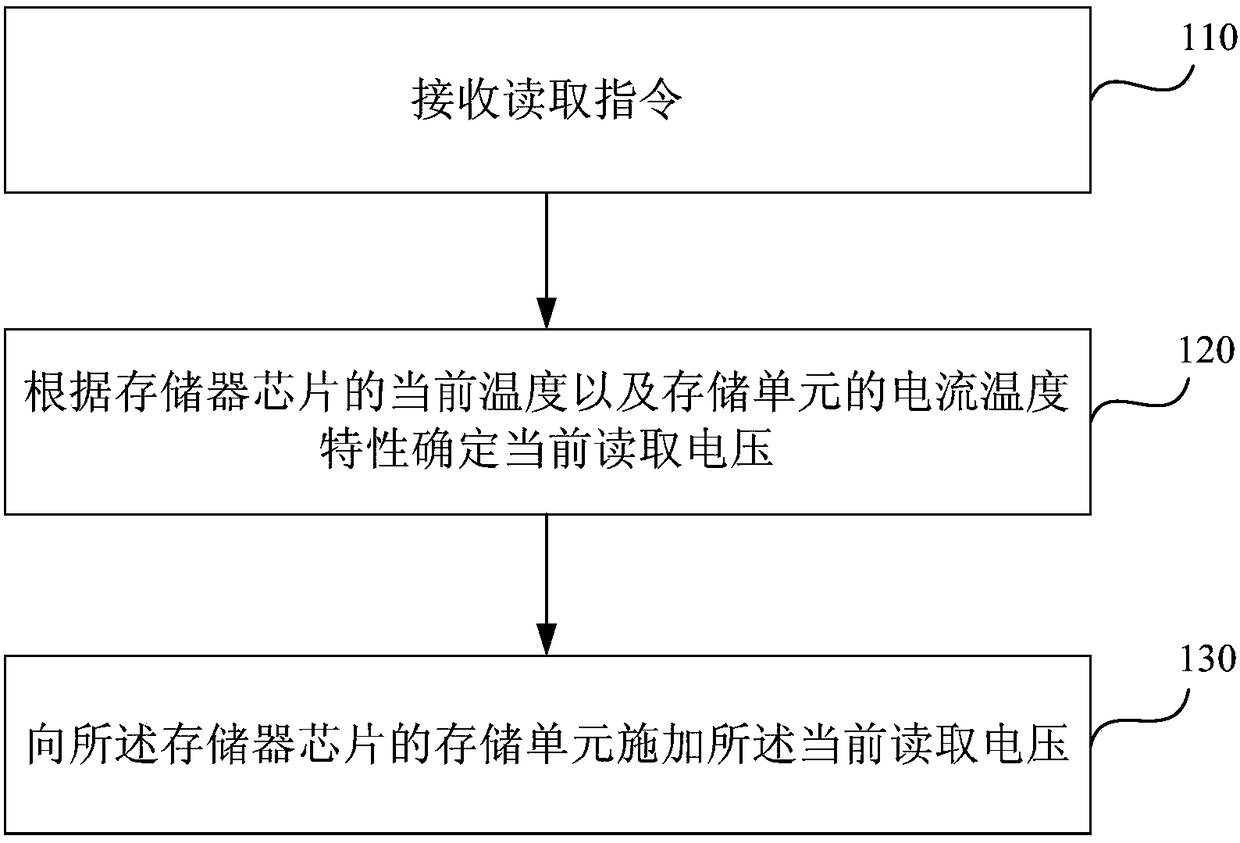
[0045] figure 2 It is a flow chart of a method for reading a storage unit provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This embodiment is applicable to the case of performing a reading operation on a storage unit of a memory chip when the temperature of the memory chip often changes. see figure 2 The method for reading the storage unit provided in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0046] Step 110, receiving a read instruction.
[0047] By writing program codes, the flash memory can be controlled to perform three major operations, namely, read operation, write operation (that is, programming operation) and erase operation; among them, the principle of read operation is to apply a read operation to the gate of the storage unit. Voltage, at this time, a current will be generated in the memory cell, compare this current with the reference current, and finally obtain whether the current state of the memory cell is an erased state or a programmed...
Embodiment 2
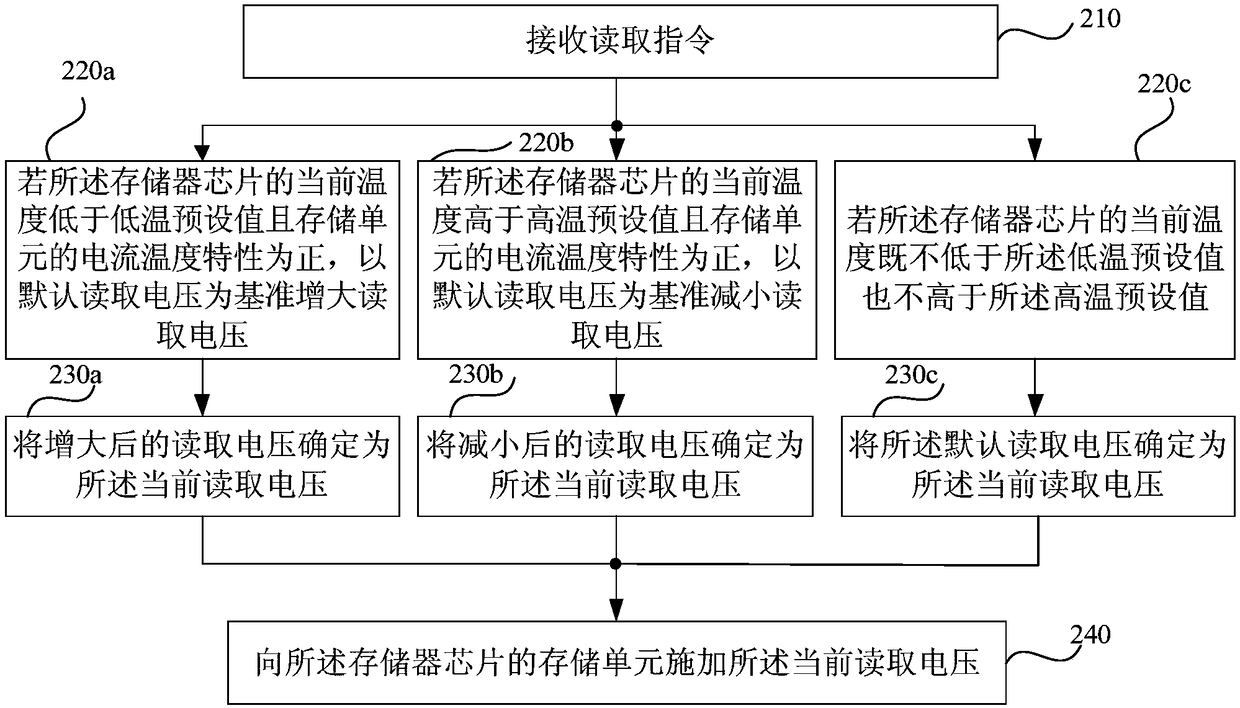
[0057] image 3 It is a flow chart of a method for reading a storage unit provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This embodiment is further optimized on the basis of Embodiment 1. The advantage of optimization is that when the temperature of the memory chip is higher than the high temperature preset value Or when the temperature is lower than the low temperature preset value, a reading voltage matching the temperature is determined to ensure reading performance. Typically, this embodiment takes a memory cell with a positive temperature characteristic as an example, that is, when the same read voltage is applied, the current flowing through the memory cell increases as the temperature increases and decreases as the temperature decreases. For details, please refer to image 3 , the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0058] 210. Receive a read instruction.
[0059] 220a. If the current temperature of the memory chip is lower than the low temperatur...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Figure 4 It is a schematic structural diagram of a reading device for a storage unit provided in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and the device specifically includes:
[0076] receiving module 310, determining module 320 and applying module 330;
[0077] Wherein, the receiving module 310 is used to receive the read instruction; the determination module 320 is used to determine the current read voltage according to the current temperature of the memory chip and the current temperature characteristics of the storage unit; the application module 330 is used to apply to the memory chip The memory cell applies the current read voltage.
[0078] Further, the device may further include: a detection module, configured to detect the current temperature of the memory chip through a temperature sensor before determining the current read voltage according to the current temperature of the memory chip and the current-temperature characteristic of the storage unit.
[0079]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com