PCR primers and methods for the identification of different subgroups of cucurbit Bacteroides fruit spot
A fruit spot fungus and bacterial technology, which is applied in the field of PCR primers for identifying different subgroups of melon bacterial fruit spot fungus, can solve the problem of not being able to distinguish strains of group I and group II, achieve high practical application value, and be easy to operate Ease of use and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
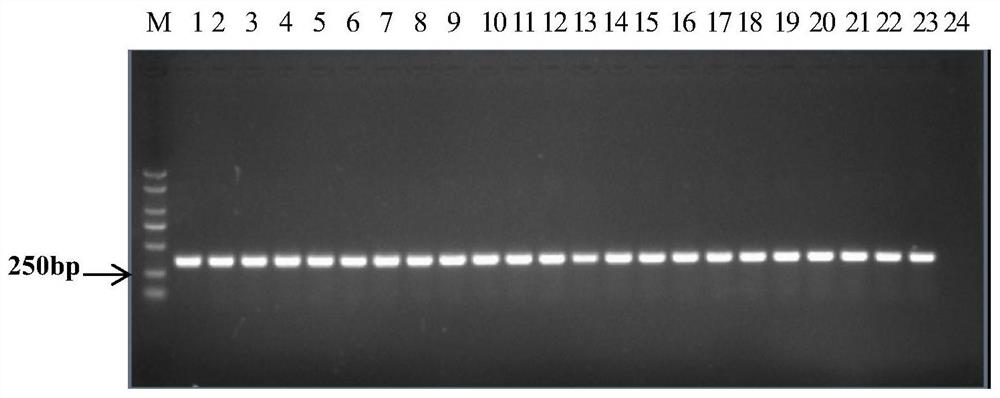
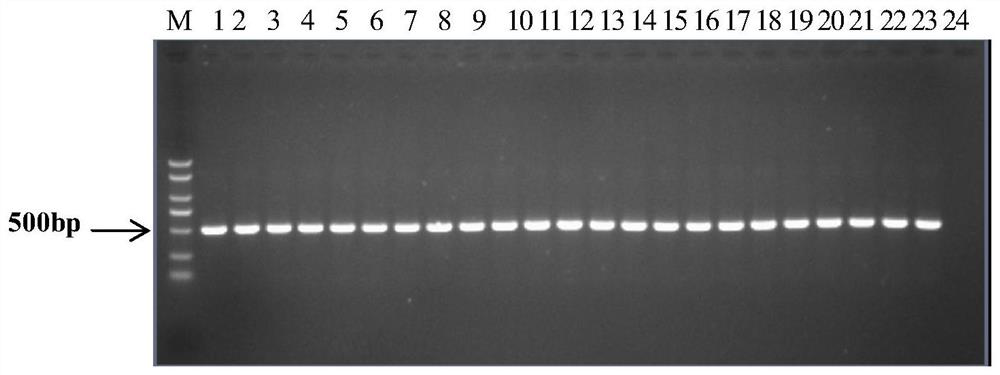
[0062] Embodiment 1. screening distinguishes the specific primers of I and II bacterial strains of cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch
[0063] 1. DNA extraction of melon bacterial fruit spot
[0064] Genomic DNA of group I strains and group II strains of bacterial fruit spot bacteria of melons were extracted respectively, and the adopted strains were as follows:
[0065] Group I strains: Fc247, Fc520, AAC92-300, AAC200-23, Saticoy.B.H, pslb2, pslb15, pslb19, pslb36, pslb37, pslb39, pslb48, pslb55, pslb68, pslb74, pslb88, pslb93, pslb97, pslb998, pslb97, pslb998, pslb101, pslb103, aacw1;
[0066] Group II strains: Aac5, Aac13, Aac14, Fc356, Fc376, Fc380, Fc491, AAC94-95, AAC94-39, AAC94-48, AAC208-27, ATCC29625, pslb27, pslbtw14, pslbtw23, pslbtw26, pslbtw33, pslpsbt pslbtw40, pslbtw41, pslbtw38, pslbtw43.
[0067] Genomic DNA extraction method is as follows:
[0068] Take 50 μl of the bacterium liquid of Phytophthora spp. preserved in glycerin, draw lines on the KB solid medi...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2. One-step identification of different subgroups of melon bacterial fruit spot
[0084] 1. Construction of one-step PCR method
[0085] The present invention constructs the PCR method of one-step amplification detection of different subgroups of melon bacterial fruit spot bacteria, that is, the specific primers of Group I and Group II are placed in a PCR amplification system at the same time, and I can be directly identified by one amplification. Group and Group II strains.
[0086] The reaction system and amplification conditions are as follows:
[0087] PCR reaction system: 25 μl of PCR reaction system is used, and the ratio is as follows: KOD-Plus-Neo 10×PCR buffer 2.5 μl, MgSO 4 (25mM) 1.5μl, dNTPs (2mM) 2.5μl, primers BFB / BFB1 / BFB2 (10mM) 0.5μl each, KODPlus Neo enzyme 0.5μl (1.0U / μl), bacterial solution 0.5μl (10 8 CFU / ml), make up 25 μl with sterilized double distilled water.
[0088] PCR amplification conditions were 94°C for 2min; 94°C for 15sec, 5...
Embodiment 3
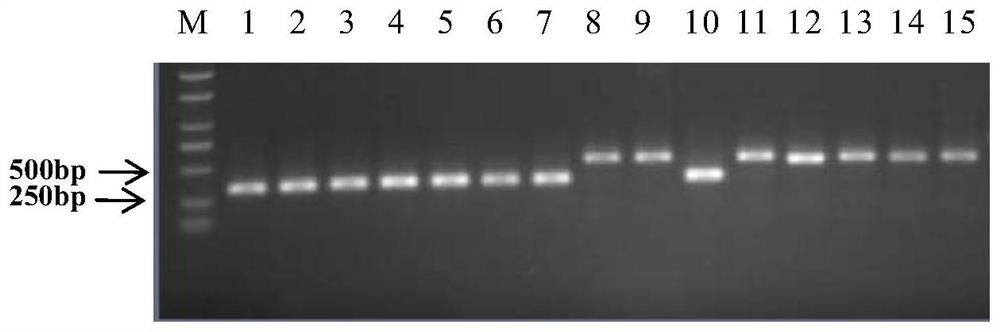
[0094] Example 3. Sensitivity detection of strain-specific primers for group I and group II strains of melon bacterial fruit spot
[0095] 1. Prepare bacterial solution
[0096] Dilute the bacterium solution of Pseudomonas spp. I group strain pslb2 into 8 concentration gradients: 10 8 CFU / ml, 10 7 CFU / ml, 10 6 CFU / ml, 10 5 CFU / ml, 104 CFU / ml, 10 3 CFU / ml, 10 2 CFU / ml, 10 1 CFU / ml.
[0097] Dilute the bacterial solution of Pseudomonas spp. II group strain pslbtw14 into 8 concentration gradients: 10 8 CFU / ml, 10 7 CFU / ml, 10 6 CFU / ml, 10 5 CFU / ml, 10 4 CFU / ml, 10 3 CFU / ml, 10 2 CFU / ml, 10 1 CFU / ml.
[0098] 2. Sensitivity detection
[0099] Using pslb2 bacterial liquid, pslbtw14 bacterial liquid and pslb2+pslbtw14 bacterial liquid (mixing pslb2 and pslbtw14 bacterial liquid according to the volume ratio of 1:1) as templates, and using BFB / BFB1 / BFB2 primer set to carry out PCR, reaction system and amplification Increase condition with embodiment 2 step 1. As a p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com