Load commutation inverter drive electrically excited synchronous motor rapid parking method
A technology of synchronous motor and electric excitation, applied in the direction of the stopping device, etc., to achieve the effect of fast stopping, short stopping time, and short stopping time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0020] The fast stopping method of the electric excitation synchronous motor driven by the load commutation inverter in this embodiment, the fast stopping method belongs to the electric braking method, and the fast stopping method includes when the motor speed is high and when the motor speed is low The fast parking methods of these two states are:
[0021] When the motor speed is high, use the LCI starting device, adopt the method of feedback braking, and feed back the kinetic energy of the motor to the grid to make the motor stop quickly; the full name of LCI is load commutation inverter;
[0022] When the motor speed is low, the method of energy consumption braking is adopted to consume energy in the motor winding, so that the motor stops quickly.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0023] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the fast stopping method of the electric excitation synchronous motor driven by the load commutation inverter in this embodiment, when the motor speed is high, the LCI starting device is used and the feedback braking method is used to stop the motor The method of feeding the kinetic energy of the kinetic energy back into the power grid makes the process of stopping the motor quickly. In the case of a high motor speed, the motor speed is relatively high after the excitation current of the motor with a high speed and a medium speed is increased, and the speed obtained by increasing the motor terminal voltage is relatively low. high,
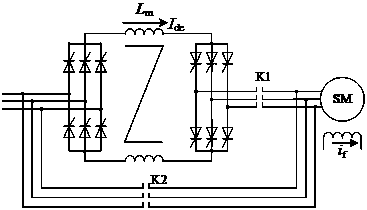
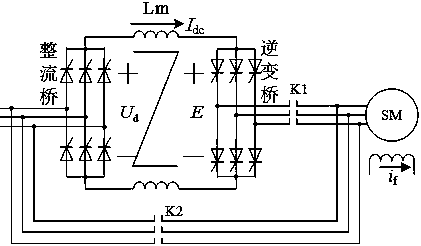
[0024] First, when booting the device with LCI:
[0025] Then the LCI drive device works in the electric running state, and the directions of the voltages and currents are as follows: image 3 Shown: the rectifier works in the "rectification state" (firing angle αd =2.34U 2 cosα, DC bus current Su...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] The difference from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is that the fast stopping method of the load commutation inverter driving the electric excitation synchronous motor in this embodiment adopts the energy-consumption braking method when the motor speed is low, and the Energy is consumed in the motor windings, and the process of making the motor stop quickly is that when the motor is at a low-to-medium speed, the energy consumption braking method is used to stop the motor quickly. In order to avoid the instantaneous short-circuit current being too large when the three-phase winding is short-circuited, first De-excitation, so that the motor terminal voltage drops to 0; then gradually build up the excitation, closed-loop adjustment of the short-circuit current, adjust the braking torque, so that the motor stops quickly.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com