Secondary decoloring method of animal and vegetable oil
A secondary decolorization, animal and vegetable oil technology, applied in the direction of fat oil/fat refining, fat production, etc., can solve the problems such as the decolorization and adsorption function of waste clay is not fully utilized, the adsorption of soap and phospholipids by fresh clay is reduced, and the filter layer channel is easily blocked. To achieve the effect of reducing the number of blowing cakes, improving the secondary utilization rate and good adsorption function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
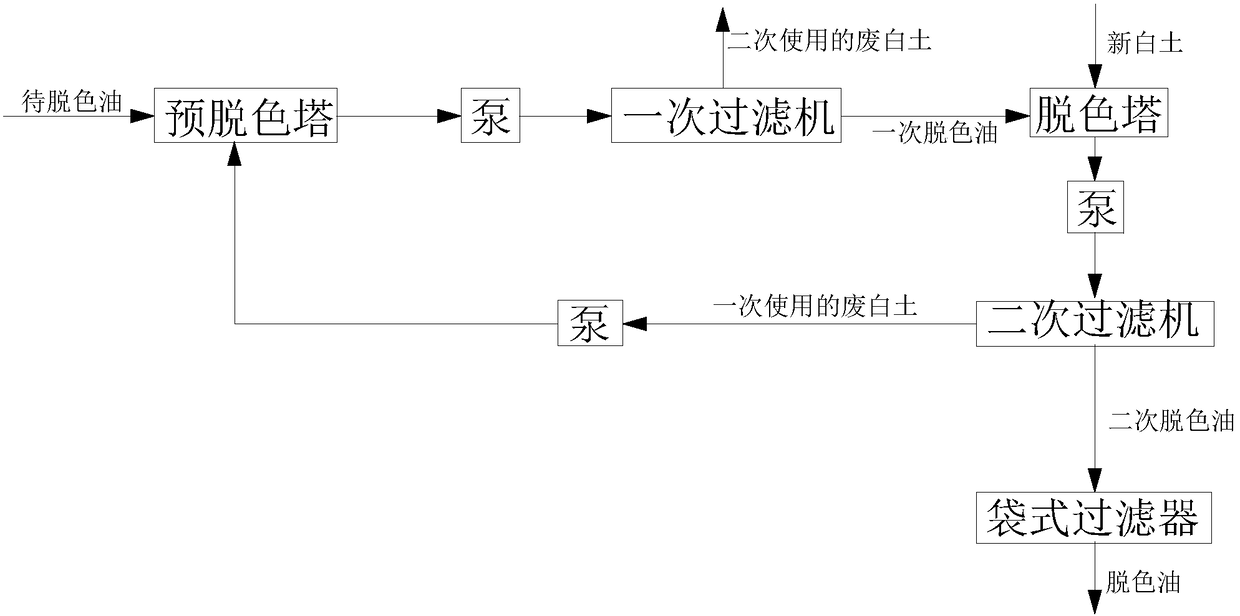
[0037] The secondary decolorization device for animal and vegetable oils includes a pre-decolorization tower, a primary filter, a decolorization tower, a secondary filter, a bag filter, and a pump. Along the flow direction of the material, the pre-bleaching tower, pump, primary filter, decolorizing tower, pump, secondary filter, and bag filter are connected in sequence, and the secondary filter, pump, and pre-bleaching tower are connected in sequence.
[0038] The primary filter is a leaf filter.
[0039]The decolorized oil is mixed with acid, enters the degumming tank and stays for a certain period of time, and then mixes it with the once-used waste clay oil mixture separated by filtration after decolorization, enters the pre-decolorization tower, and vacuums at a temperature of 60-70mbar and a temperature of 105- Stay at 110°C for a certain period of time under steam stirring conditions, and use a decolorization pump to transport the mixture to a primary filter for separatio...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The present embodiment is the secondary decolorization method of neutralizing rapeseed oil, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0043] (1) Neutralized rapeseed oil is heated to a temperature of about 85°C through a heat exchanger, mixed with a certain amount of citric acid, then enters the dry degumming mixer, stays in the mixer for a certain period of time, enters the pre-decolorization tower, and passes through the decolorization tower and The once-used waste clay separated by the secondary filter is mixed, and the mixture is heated to 100-110°C in the pre-bleaching tower, and the vacuum pressure is 65mbar.
[0044] (2) During the initial start-up, the neutralized rapeseed oil enters the oil clay mixer directly from the dry degumming mixer, mixes with fresh clay, and then overflows to the decolorization tower. The initial decolorization clay is added in an amount of 2% oil weight, and is heated and stopped in the bleaching tower After a certain period of tim...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The present embodiment is the secondary decolorization method of crude palm oil, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0052] (1) Crude palm oil is heated to a temperature of about 85°C through a heat exchanger, mixed with a certain amount of citric acid, then enters a dry degumming mixer, stays in the mixer for a certain period of time, enters a pre-decolorization tower, and passes through a decolorization tower and a secondary The once-used waste clay separated by the filter is mixed, and the mixture is heated to 100-110°C in the pre-bleaching tower, and the vacuum pressure is 65mbar.
[0053] (2) The crude palm oil from the dry degumming mixer in the initial driving directly enters the oil clay mixer and is mixed with fresh clay and then overflows to the decolorization tower. Finally, in order to do a comparison experiment, the oil is directly input into the primary filter according to the conventional process, and the oil after the primary filter passes thro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com