Trichoderma asperellum and application thereof in lead-polluted soil repairing
A technology for Trichoderma aculeatus and polluted soil, which is applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms and ecological restoration, can solve the problems of consuming large energy or chemical products, restoring the adverse effects of soil physical and chemical properties of polluted soil, and high finished products, and achieves excellent tolerance and adsorption capacity. , broad heavy metal tolerance, reducing the effect of stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Isolation and identification of bacterial strains
[0028] 1. Isolation of strains:
[0029] Select 10g of soil collected from a polluted area of a lead storage battery factory in Shandong and put it in a triangular flask. Under sterile conditions, add 90ml of sterile water, shake fully to fully elute the microorganisms from the soil, then let it stand for 20 minutes, and absorb the supernatant Dilute 100 times with sterile water; take 1ml of the supernatant and evenly spread it on a solid plate (Martin's medium) with a lead concentration of 100mg / L. 100-1500mg / L Martin's medium, 30 ℃ gradient acclimatization culture; the colony with the strongest resistance to lead was selected, and the single colony was continuously purified by plate streak separation method, and the best resistance was screened. Lead-competent strains were used as test strains for further study.
[0030] 2. Identification of strains:
[0031] (1) Morphological identification:
[0032...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: Determination of tolerance of Trichoderma asperellum to other heavy metals
[0046] Trichoderma asperellum (Trichoderma asperellum) screened and isolated in Example 1 was inoculated on the glucose-peptone medium containing heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn), and the concentration of heavy metals was gradually increased until the bacterial strain could not grow normally. This concentration was The minimum inhibitory concentration, the results are shown in Table 1.
[0047] Table 1: Minimal inhibitory concentrations of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn against strains
[0048]
[0049] As can be seen from Table 1, Trichoderma asperellum of the present invention has a very good tolerance to the heavy metal Pd, and at the same time, it also has a certain tolerance to heavy metals such as Cd, Cu, and Zn.
Embodiment 3
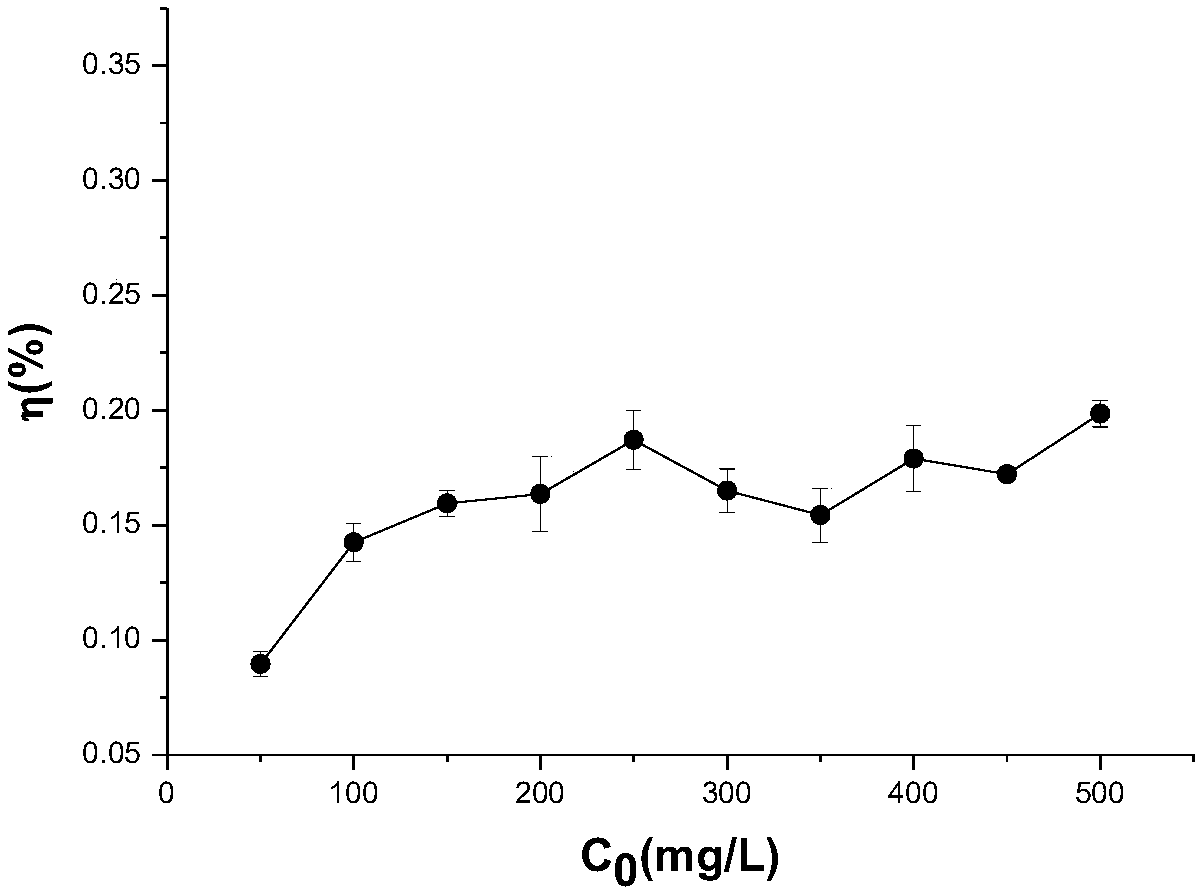
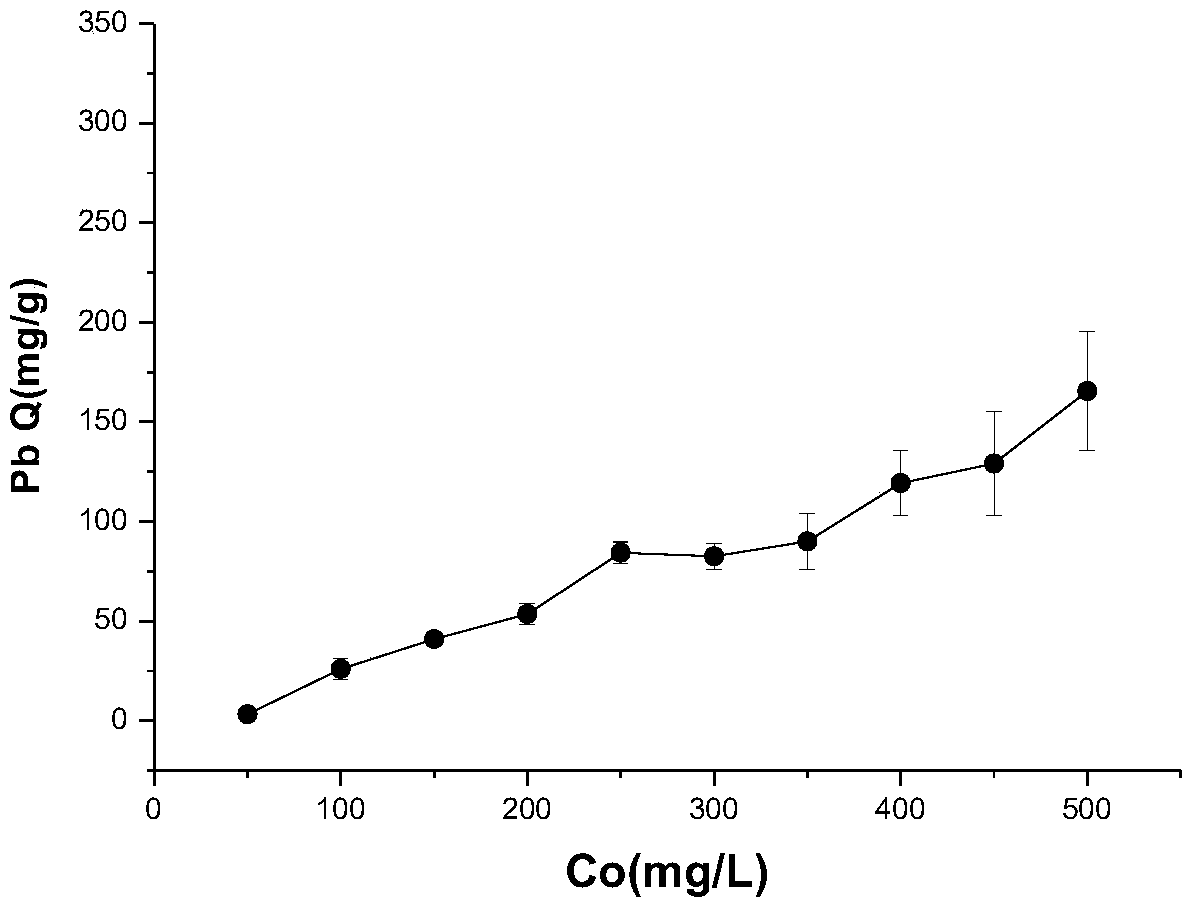
[0050] Embodiment 3: Determination of removal and adsorption capacity of Trichoderma asperellum to lead ion
[0051] In 100ml lead solution, the lead concentrations are 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500mgL -1 Add the Trichoderma asperellum (Trichoderma asperellum) that 0.2g embodiment 1 screens and separates respectively in the Erlenmeyer flask of 0.2g, at 150rpm min -1 , Shake at a constant temperature at 30°C for 24 hours, filter the solution after the shaking is completed, and measure the lead content in the solution.
[0052] The removal rate and adsorption capacity of Trichoderma aculeatus to lead ions were calculated according to the following formula.
[0053] Removal rate (η%) = (C 0 -C E )*100% / C 0 ;
[0054] Adsorption capacity (Q) = (C 0 -C E )*V / 1000W;
[0055] In the formula: the adsorption capacity of Q-microbes to lead (mg / g); C 0 -Initial concentration of lead ions (mg / L); C E - lead concentration (mg / L) when the adsorption reaches equil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com