(Hf,Ta)Fe2 magnetic phase transition alloy with zero thermal expansion effect in wide temperature range and applications thereof
A zero thermal expansion, magnetic phase change technology, applied in the field of magnetic phase change alloys, to achieve the effect of small thermal expansion coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
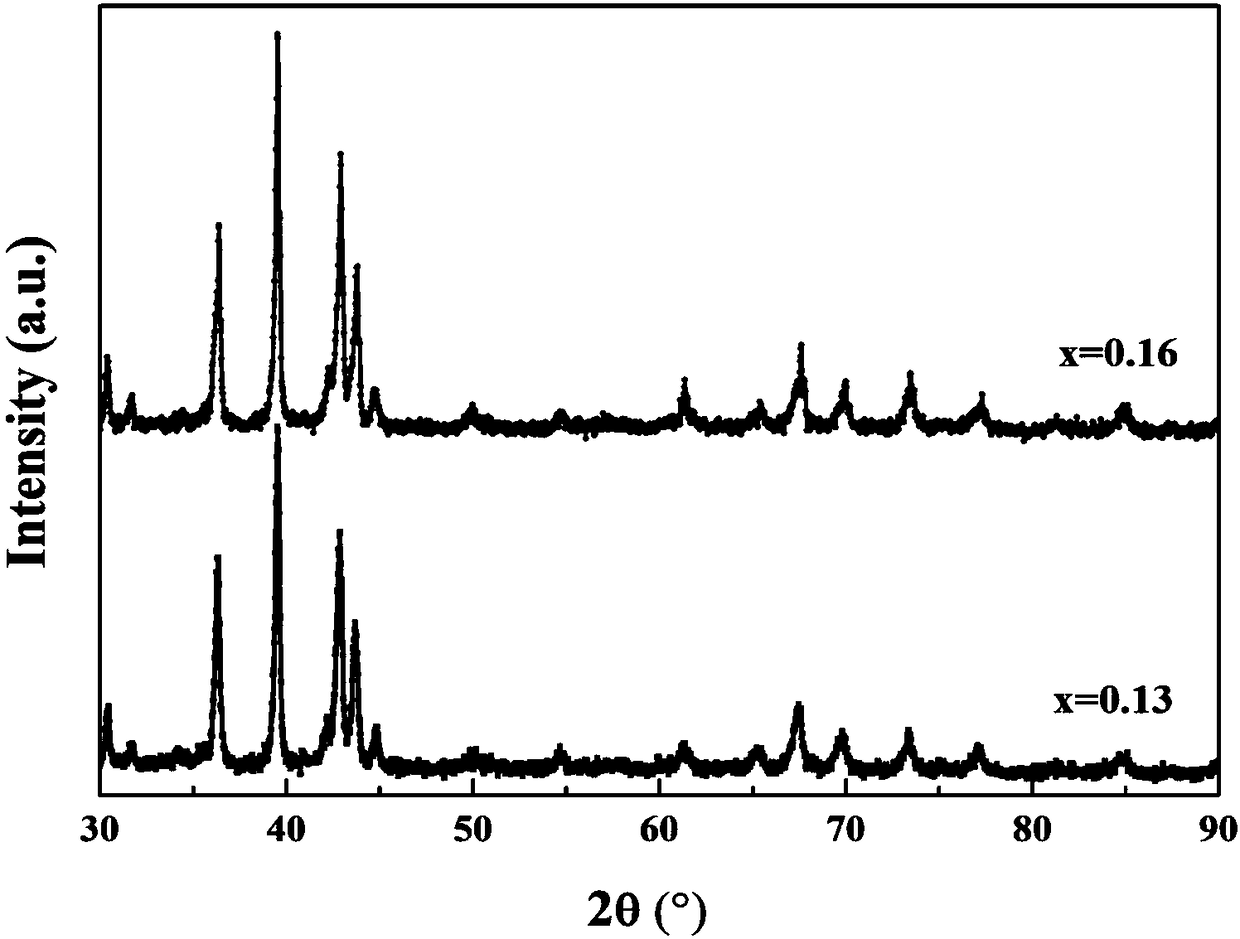
[0024] The phase structure of the alloy was characterized by X-ray Diffraction (XRD). figure 1 Yes (Hf 1-x , Ta x )Fe 2 The room temperature XRD diffraction data of alloys (x=0.13 and 0.16) can be seen as a single MgZn 2 Type structure hexagonal phase, no other impurity phase exists.
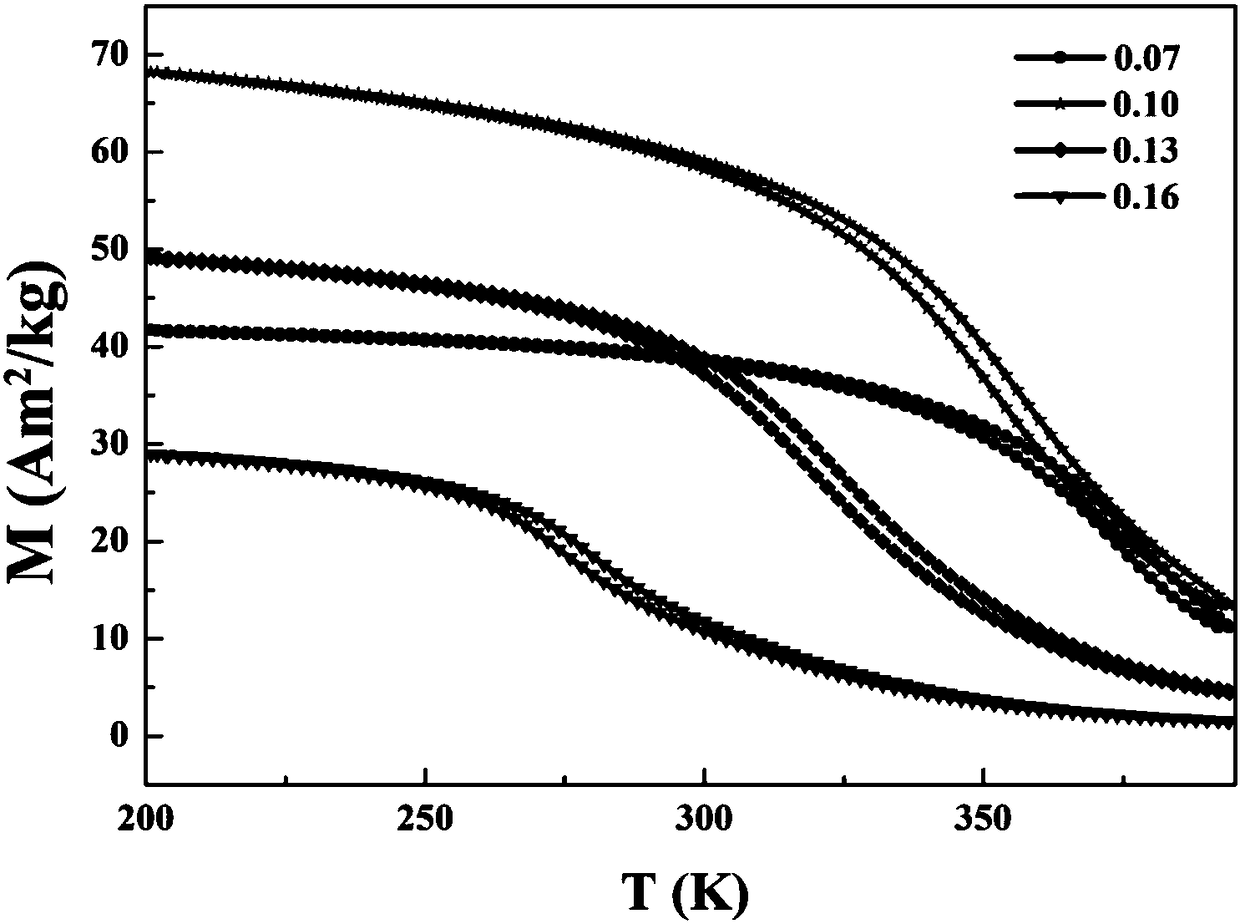
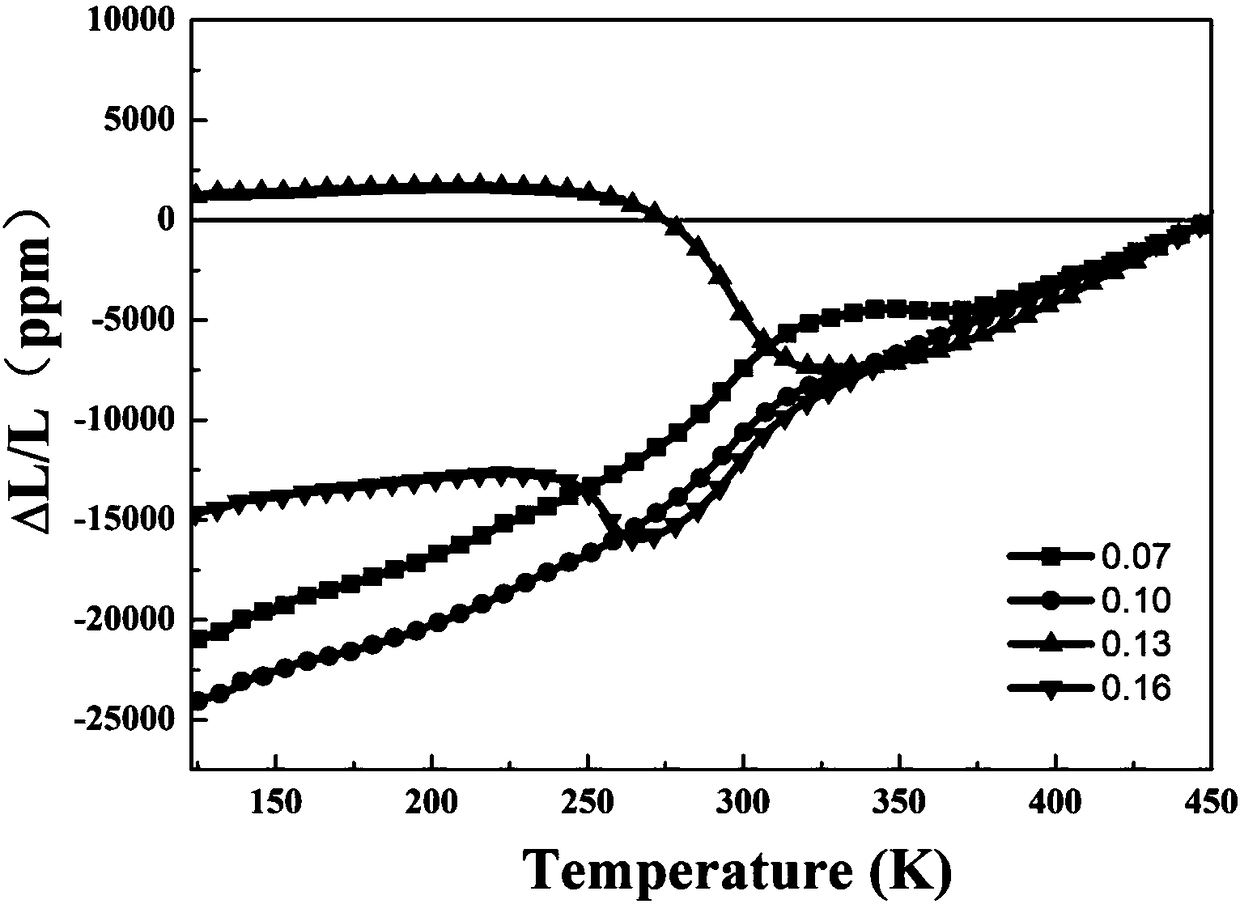
[0025] Measured by the Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS) (Hf 1-x , Ta x )Fe 2 Alloy (x=0.07,0.10,0.13,0.16) isothermal magnetization curves. figure 2 is the 0.1 T field (Hf 1-x , Ta x )Fe 2 Plot of magnetization as a function of temperature for alloys (x=0.07,0.10,0.13,0.16). It can be found that with the increase of Ta content, the phase transition temperature of the system decreases gradually. x = 0.07 and x=0.10 samples have magnetization jumps around 360K and 350K, and the corresponding heating and cooling curves basically coincide, which indicates that the system only undergoes magnetic phase transitions and no structural phase transitions. x = 0.13 and x=0.16, the ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com