Method for preparing cellulose nanoparticles through dialdehyde cellulose
A nanoparticle and cellulose technology, which is applied in the field of cellulose nanoparticle and its preparation, can solve the problems of complex cellulose nanoparticle process and uncontrollable particle size, and achieve the effects of high yield, fast speed and fast response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Preparation of dialdehyde-based fibers
[0021] 1.0 grams of cellulose, 1.65 grams of sodium periodate (NaIO 4 ) and 50ml of deionized water were added to a 250ml flask, and the flask was wrapped with tinfoil for shading, and stirred magnetically at 250rpm at room temperature for 3 days. Ethylene glycol was added to the mixture and stirred for 1 hour to eliminate unreacted sodium periodate; then the contents of the flask were added to a 3500Da dialysis bag and dialyzed in deionized water, and the dialyzed suspension was heated to 80°C and Keep it for 4 hours; then centrifuge it at 14000 rpm for 30 minutes, put it in the upper layer of the refrigerator and let it stand still, and precipitate dialdehyde-based cellulose with an oxidation value of 1.57 (DO=1.57), and the aldehyde group content is 9.69 mmol / g.
Embodiment 2
[0023] 0.16g of dialdehyde-based cellulose, 0.101g of n-hexylamine and 9.0ml of ethanol were added to the reaction flask, stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, and the suspension became a clear solution.
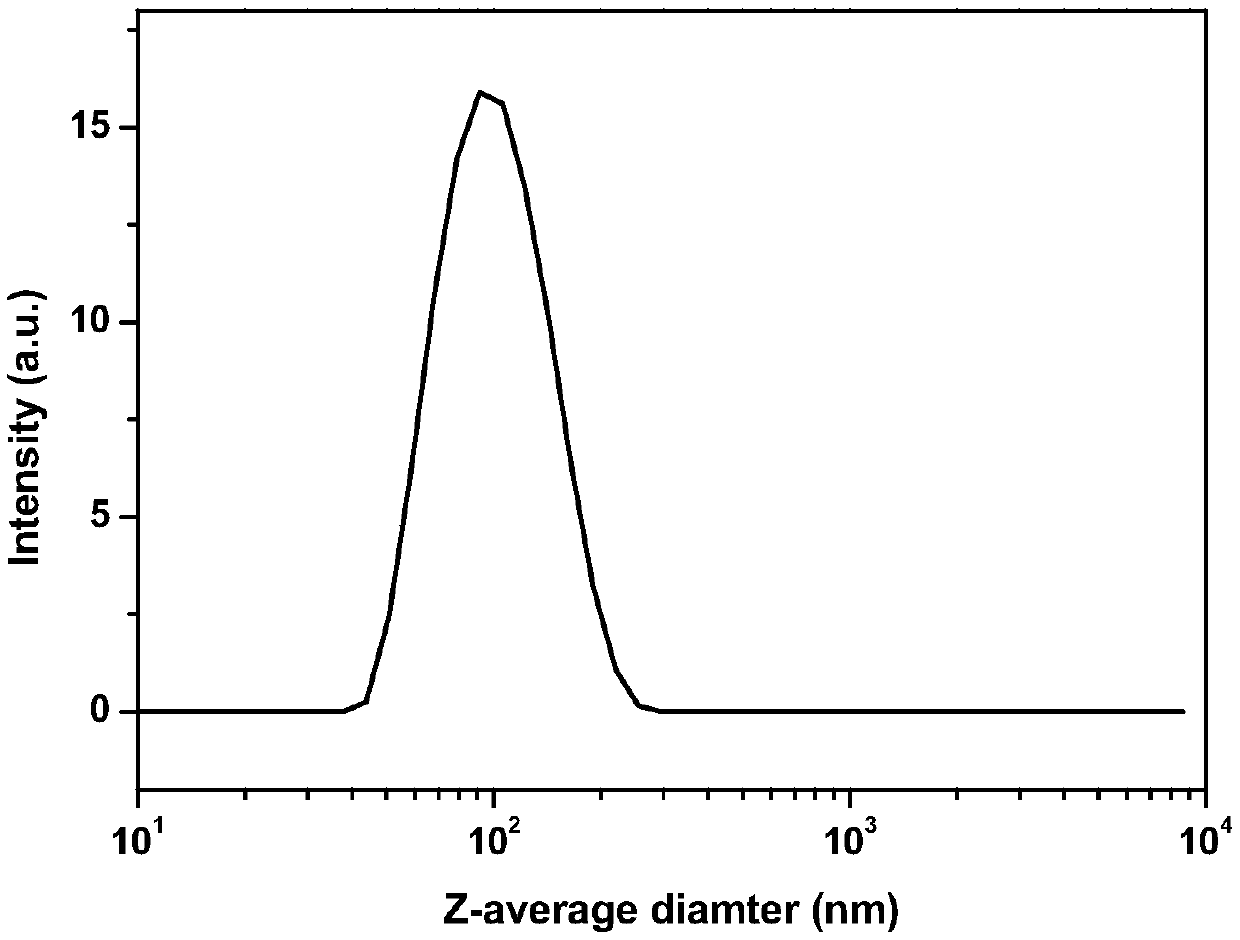
[0024] The obtained clear solution was put into a syringe pump and injected into 132ml deionized water at a speed of 0.2ml / min, wherein the deionized water was stirred at a speed of 800r / min to obtain a cellulose nanoparticle suspension with a concentration of 0.5mg / m1. Obtain the cellulose nanoparticle that particle mean diameter is 100nm, see appendix figure 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0026] 0.16 g of dialdehyde-based cellulose and 0.05 g of n-hexylamine were added to 7.5 ml of ethanol, and the reaction bottle was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, and the suspension became a clear solution.
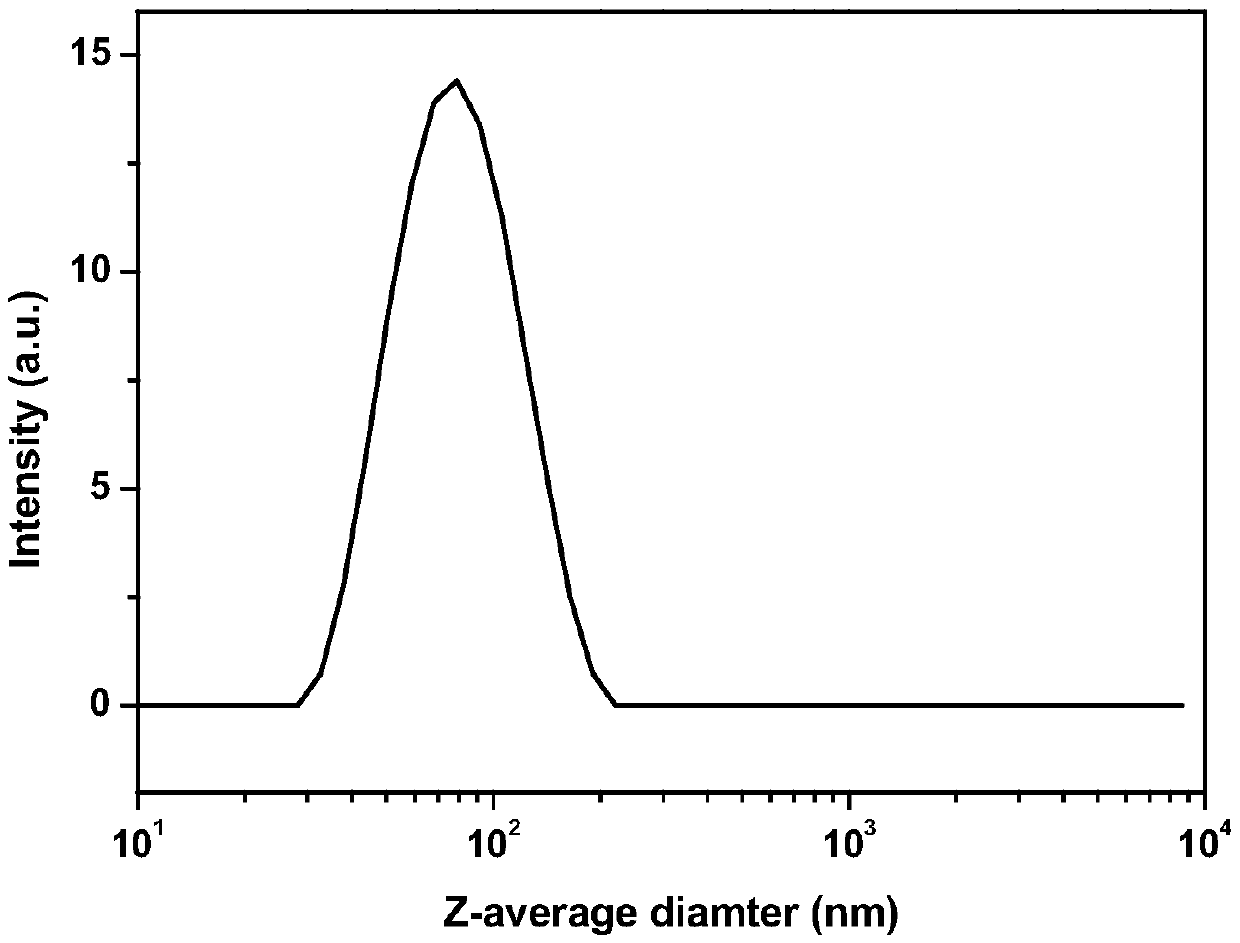
[0027] The obtained clear solution was put into a syringe pump and injected into 75ml of deionized water at a speed of 0.2ml / min, wherein the deionized water was stirred at a speed of 800r / min to obtain a cellulose nanoparticle suspension with a concentration of 1. Obtain the cellulose nanoparticle that particle average diameter is 78nm, see appendix figure 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com