Method for culturing mdck cells
A culture method and cell culture technology, applied in the field of MDCK cell culture, can solve problems such as concerns about serum safety and adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] (Example 1) Preparation and selection of cloned MDCK cells
[0063] (1) Cultivation using serum-containing medium
[0064] Thaw the MDCK cells (ATCC No.CCL-34, Lot 1166395, passage number 53) obtained from ATCC, add Eagle MEM medium (Nissui Pharmaceutical) containing 10% fetal calf serum (hereinafter referred to as FCS) and perform centrifugal washing . Eagle MEM medium containing 10% FCS was added to the pellet to suspend it, and it was cultured in a T75 flask. After the cells cultured at 37°C±1°C for five days were washed with a PBS solution containing 1 mM EDTA-4Na, trypsin was added to detach the cells from the culture vessel. Add Eagle MEM medium containing 10% FCS to neutralize trypsin, and pass in T225 flasks. After culturing the cells at 37°C±1°C for four days, the cells were also passaged in T225 flasks. After cells cultured at 37° C.±1° C. for six days were recovered by trypsin treatment, Eagle MEM medium containing 10% FCS...
Embodiment 2
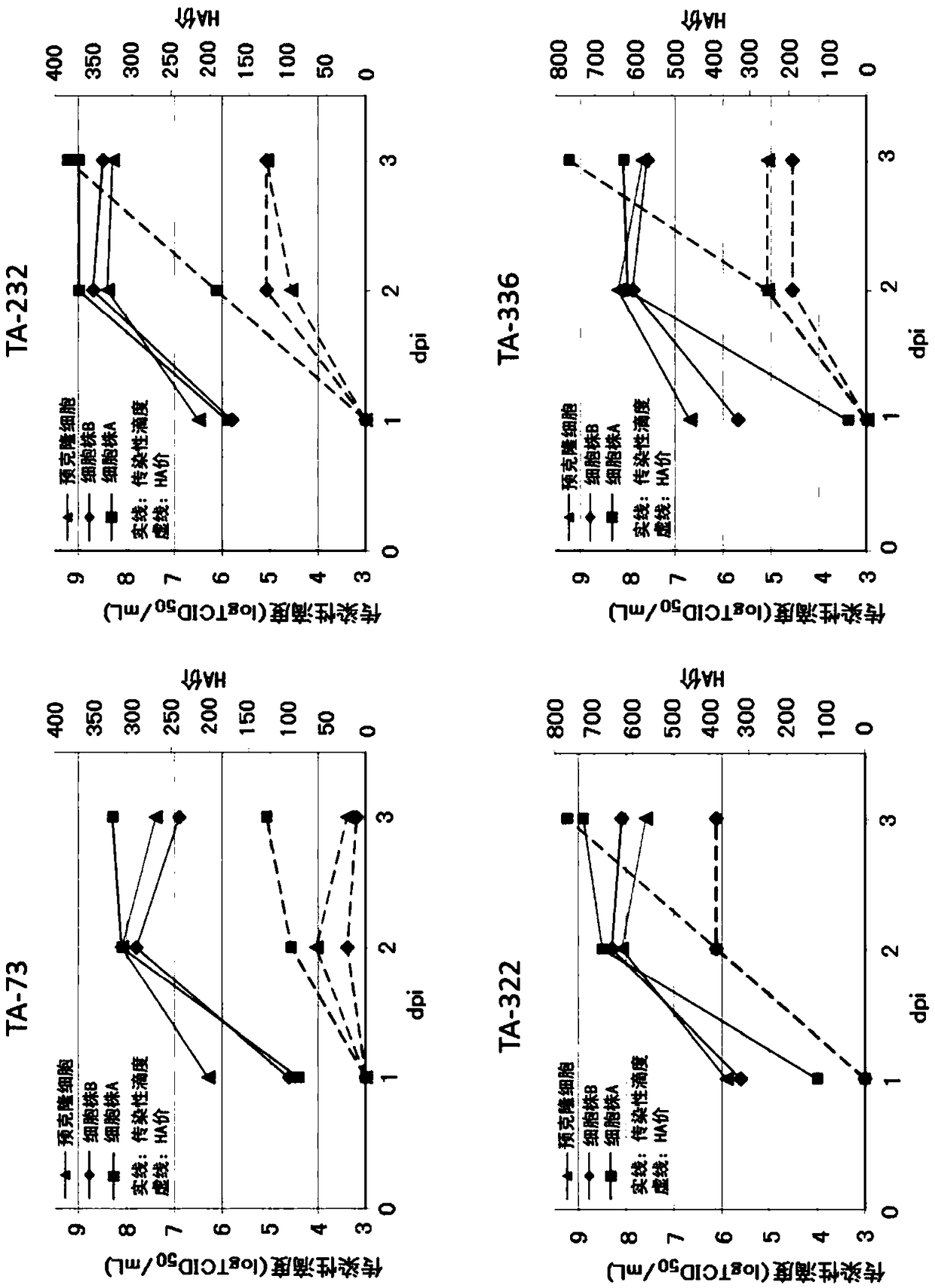
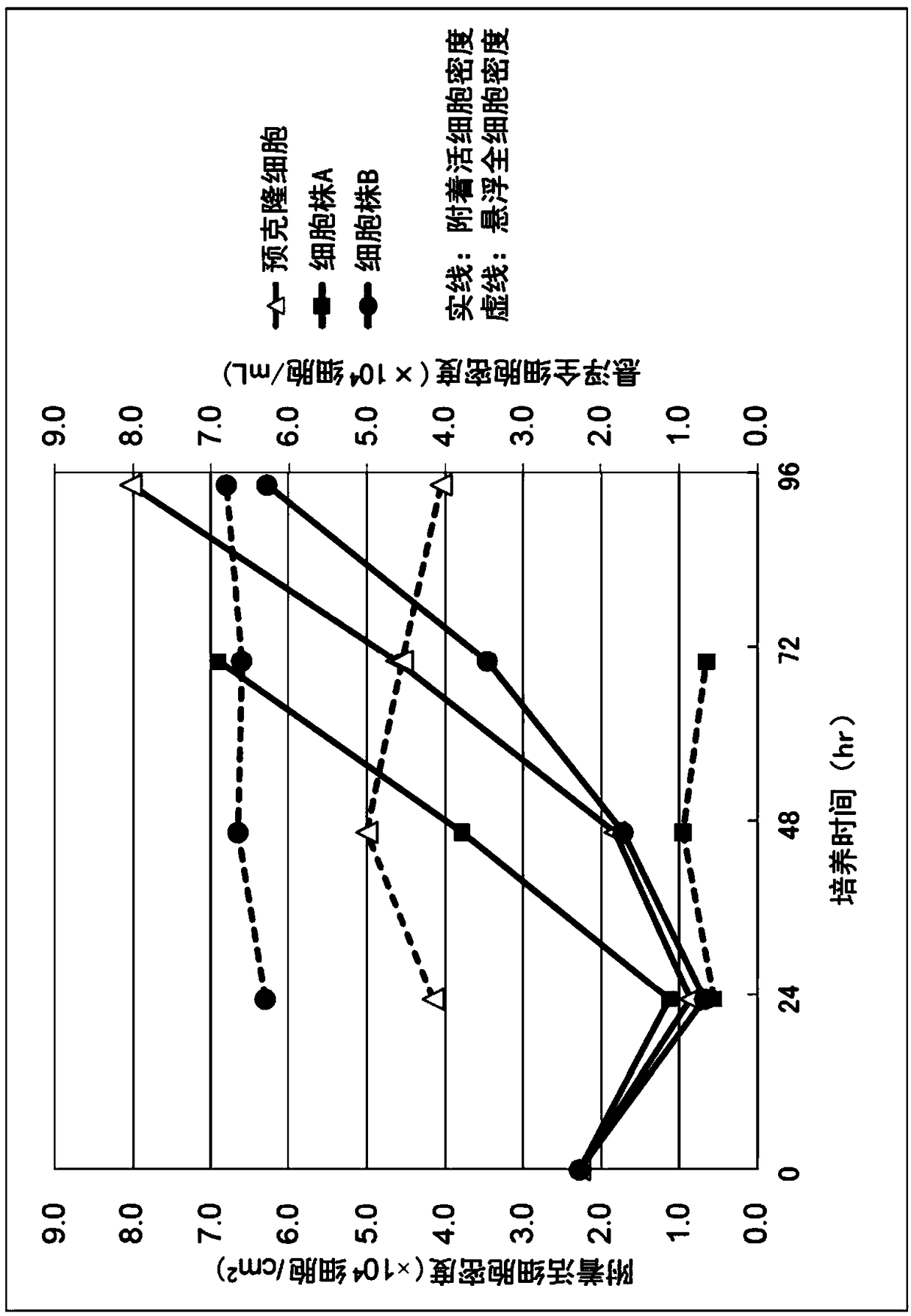
[0098] (embodiment 2) use the cultivation of the clone MDCK cell line of microcarrier
[0099] Cell line A was cultured in serum-free medium OptiPRO SFM (Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with 4 mM glutamine. Cell line B and pre-cloned cells were used as control cells. Cells at 2.3 x 10 4 cells / cm 2 inoculation density. Microcarriers used Cytodex 1 (GE Healthcare Life Sciences) at a density of 3.5 g / L. The culture conditions were as follows: the stirring speed before the 48th hour of culture was 15 rpm, the stirring speed after 48 hours was 30 rpm, the pH was 7.0, the temperature was 37.0° C., and the dissolved oxygen concentration (DO) was 3.00 ppm. Vent through perforated tubes. In addition, a bioreactor with a capacity of 3 L was used as a culture container.
[0100] The number of cells in the culture solution was confirmed by extracting a part of the culture solution and dispersing the cells adhered to the microcarriers using trypsin. For the measurement of the...
Embodiment 3
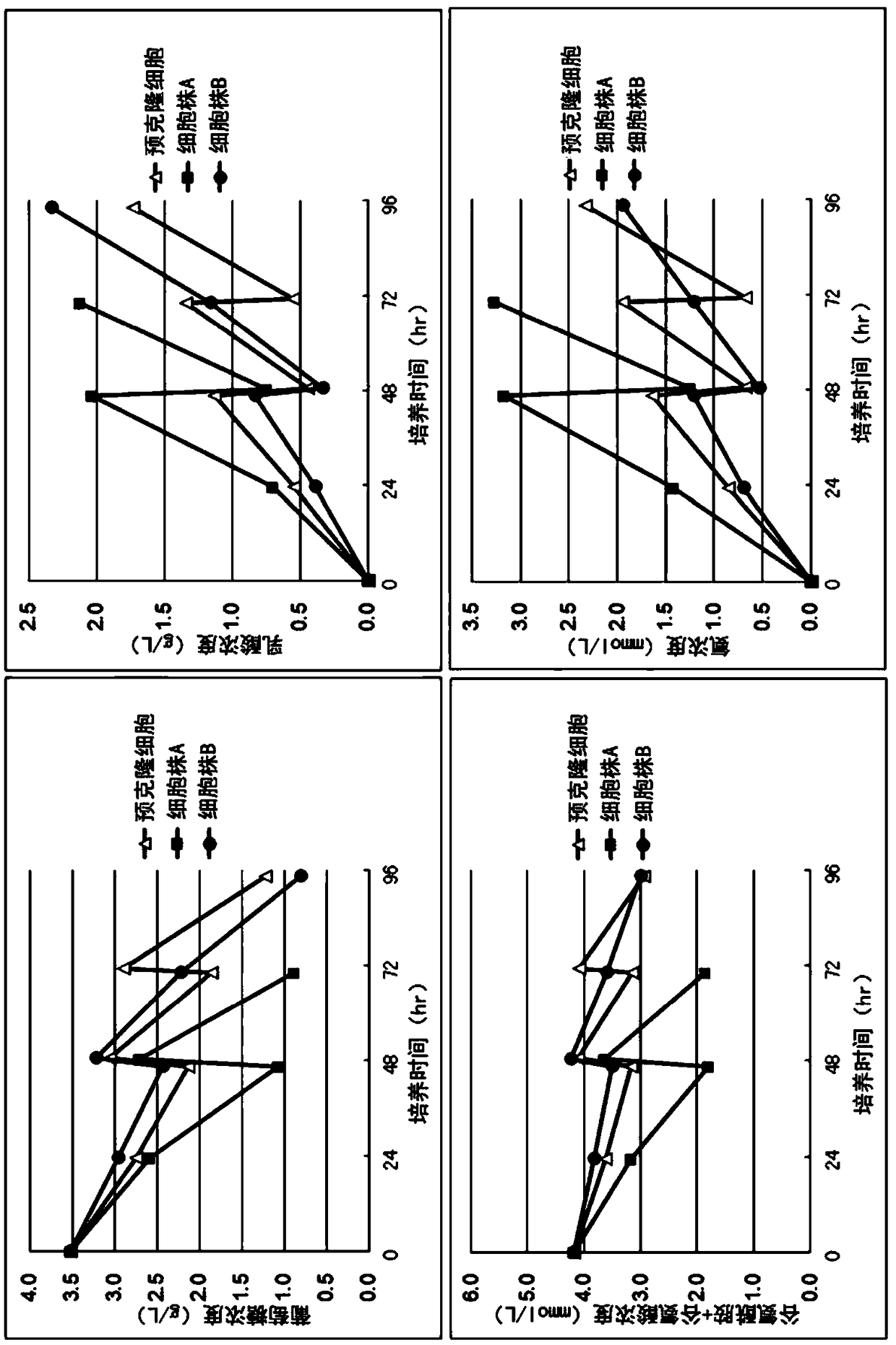
[0110] (Example 3) Confirmation of the expansion rate of the cloned MDCK cell line
[0111] In the same manner as in Example 2, the cell line A was inoculated at the following cell inoculation densities a to d, and cultured. Use precloned cells as controls.
[0112] a: 2.0×10 4 cells / cm 2 (17.6×10 4 cells / mL)
[0113] b: 1.0×10 4 cells / cm 2 (8.8×10 4 cells / mL)
[0114] c: 0.6×10 4 cells / cm 2 (5.3×10 4 cells / mL)
[0115] d: 0.3×10 4 cells / cm2 (2.6×10 4 cells / mL)
[0116] In addition, the culture capacity is 400mL, at 37.0°C, 5% CO 2 In the presence, stirring culture was carried out at 60 rpm. Cytodex 1 was used as microcarrier. The density of the microcarriers is 2.0 g / L.
[0117] The result is as Figure 5 shown. The values near each point in the graph represent the value of the amplification factor at each time point. From this, it can be seen that the expansion rate of the cell line A is higher than that of the pre-cloned cells when about 30 hours to 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com