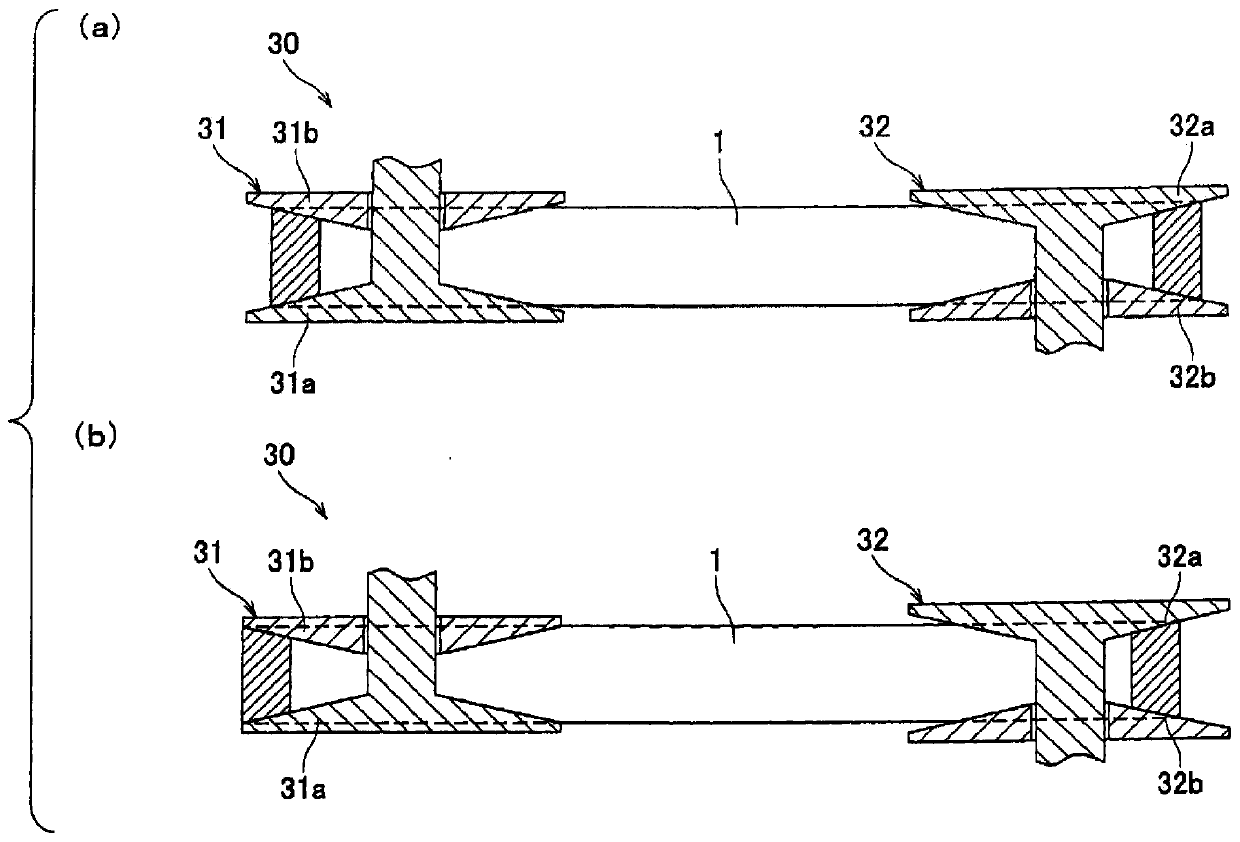
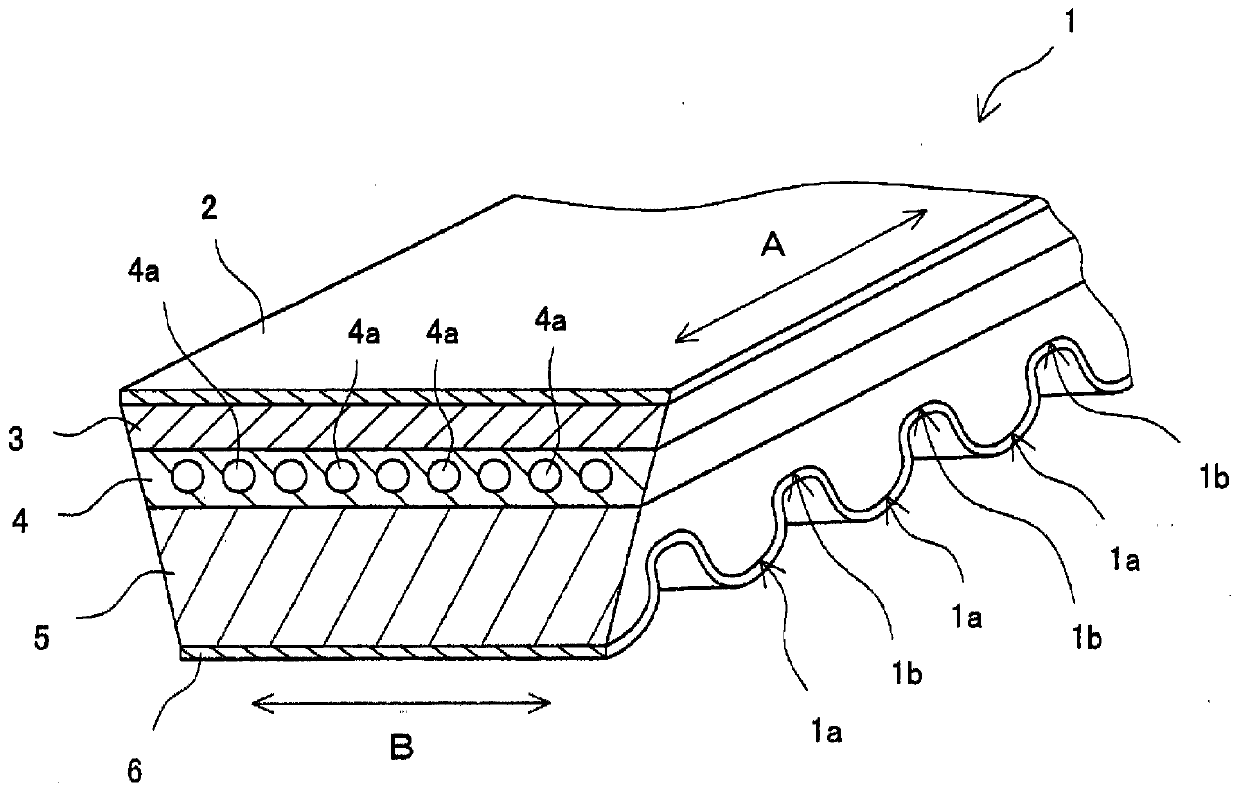
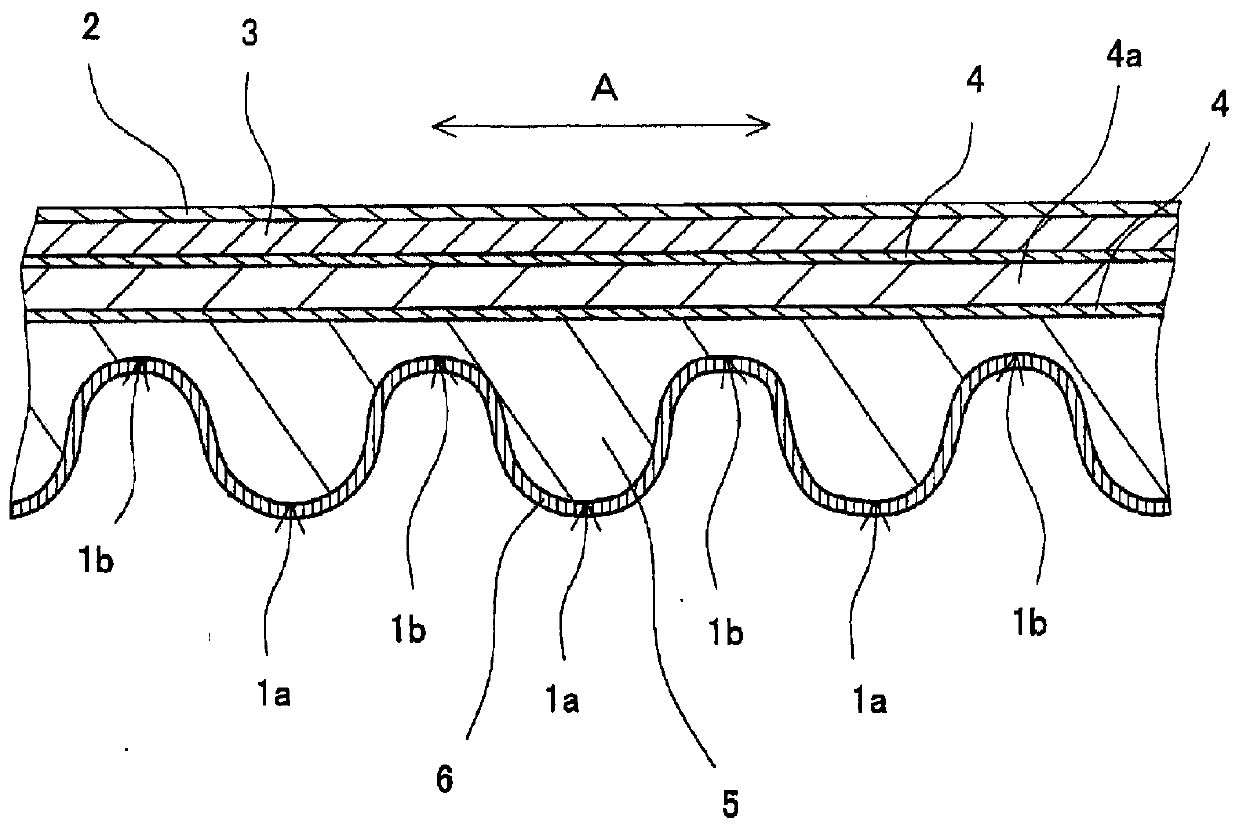
friction belt
A technology of friction transmission belts and mass parts, which is applied in the direction of transmission belts, V-belts, belts/chains/gears, etc., can solve the problems of reduced bending fatigue resistance, durability (reduced life, belt cannot move smoothly, etc.), and achieve inhibition Abrasion, improvement of bending fatigue resistance, effect of suppressing peeling or cracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~8 and comparative example 1~4
[0163] (formation of rubber layer)
[0164] The rubber compositions in Table 1 (adhesive rubber layer) and Table 2 (compressed rubber layer and stretched rubber layer) were respectively kneaded using a known method such as a Banbury mixer, and the kneaded rubber was obtained from calendering. The rolled rubber sheets (sheets for the adhesive rubber layer, sheets for the compressed rubber layer, and sheets for the stretched rubber layer) were produced by passing the rollers. In addition, Table 1 shows the physical properties of the vulcanized rubber for the rubber composition used for the adhesive rubber layer.
[0165] [Table 1]
[0166] Table 1 (adhesive rubber layer)
[0167]
[0168] [Table 2]
[0169] Table 2 (compressed rubber layer and extended rubber layer)
[0170]
[0171] (Adhesive treatment of core wire)
[0172] After immersing the core wire in the first treatment agent (pretreatment liquid) shown in Table 3, heat treatment was performed at 180° C. for 4...
Embodiment 4
[0195] Example 4 is a friction transmission belt in which the amount of carbon black in the adhesive rubber layer is as high as 70 parts by mass. The core wire was slightly peeled off on the side of the belt after running for 24 hours, but it was not a practical problem. In Example 5, the ratio of silica in the adhesive rubber layer was as low as 4 parts by mass relative to 100 parts by mass of carbon black, and the peeling of the core wire was slightly observed on the side of the belt after 24 hours of running, but it was There is no problem practically.
Embodiment 6
[0196] Example 6 is a friction transmission belt containing 10 parts by mass of silica in the outer coating layer. The core wire was slightly peeled off on the side of the belt after running for 24 hours, but it was not a practical problem. Example 8 is a friction transmission belt containing 60 parts by mass of silica in the outer coating layer. The core wire was slightly peeled off on the side of the belt after running for 24 hours, but it was not a practical problem. Considering the results of Examples 6 to 8, it turned out that the peeling of the core wire occurred regardless of whether the amount of silica compounded in the overcoat layer was too small or too large.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com