Method and device for machining laser-induced discharge surface micro-structures
A technology of laser induction and processing device, used in laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of strong corrosion of equipment, affecting the processing accuracy of ECDM, and being unfriendly to the environment, and achieve the effect of improving the speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
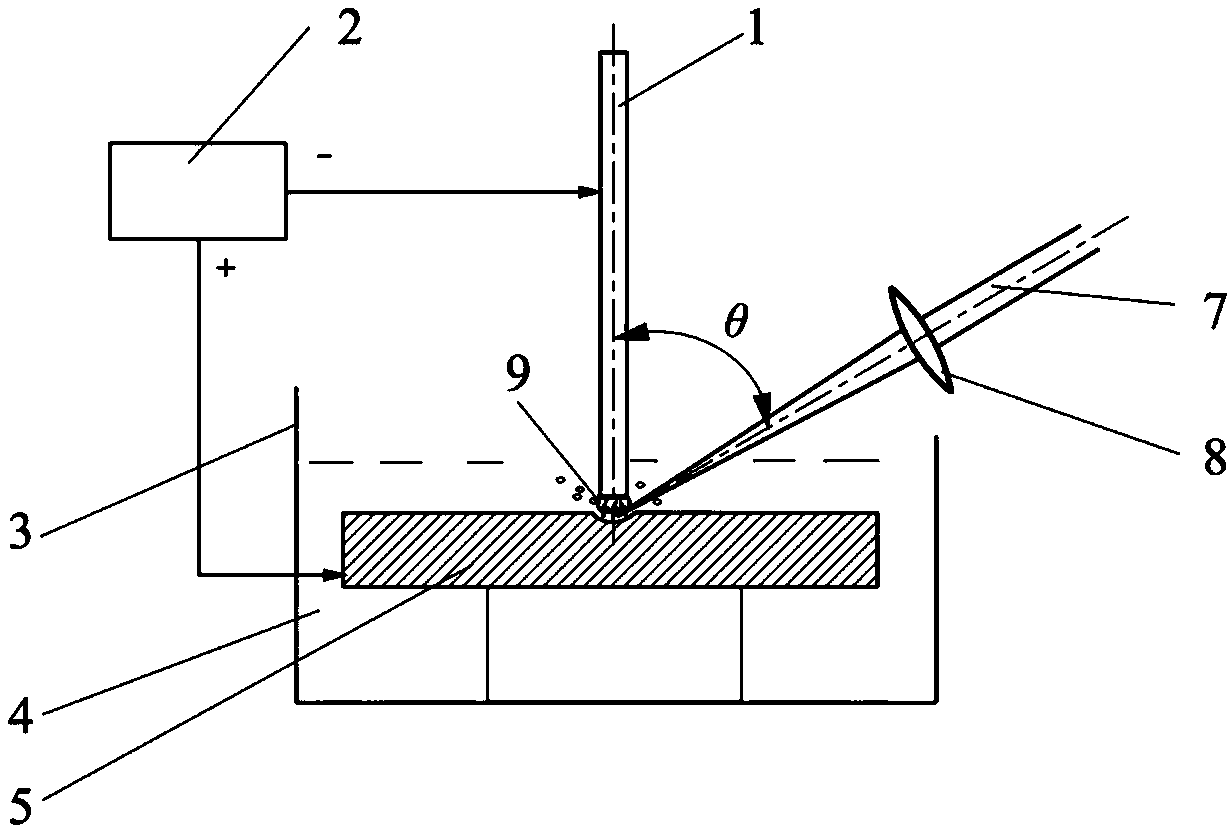
[0044] In this embodiment, the laser-induced discharge surface microstructure processing device such as figure 1 As shown, the working tank 3 contains a liquid working medium 4 , and the workpiece 5 is immersed in the working medium 4 . The microscale tool electrode 1 is connected to the negative pole of the power supply 2 , and the workpiece 5 is connected to the anode of the power supply 2 . A certain gap is maintained between the end surface of one end of the microscale tool electrode 1 and the surface of the workpiece 5 to be processed, the gap is in the range of 0.01 mm to 1.0 mm, and the gap is filled with the working medium 4 .
[0045] The laser light 7 generated by the laser converges in the gap through the focusing lens 8 .
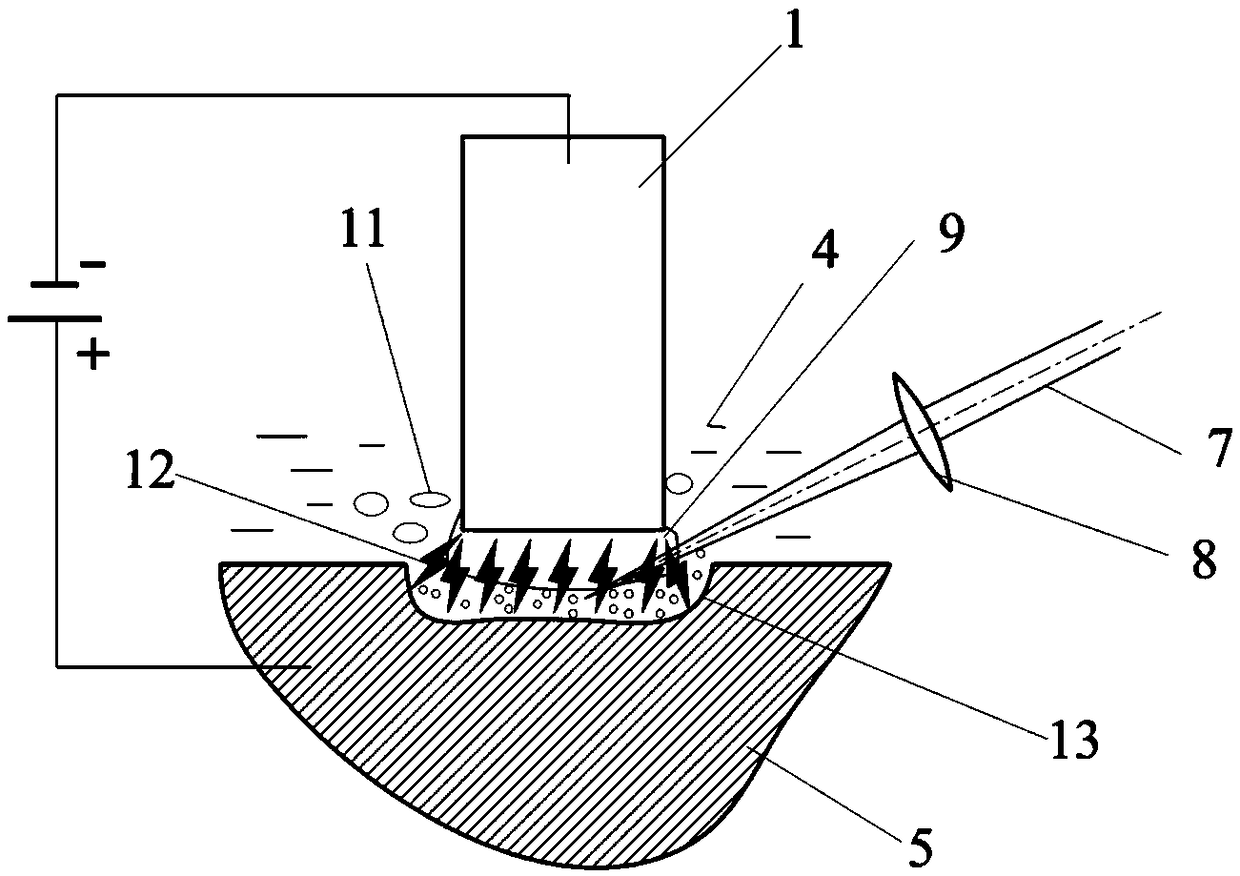
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown, in the working state, the working medium in the gap boils and gasifies under the action of laser energy to generate a large number of bubbles 11, and the bubbles gather at the one end region of the microscal...
Embodiment 2
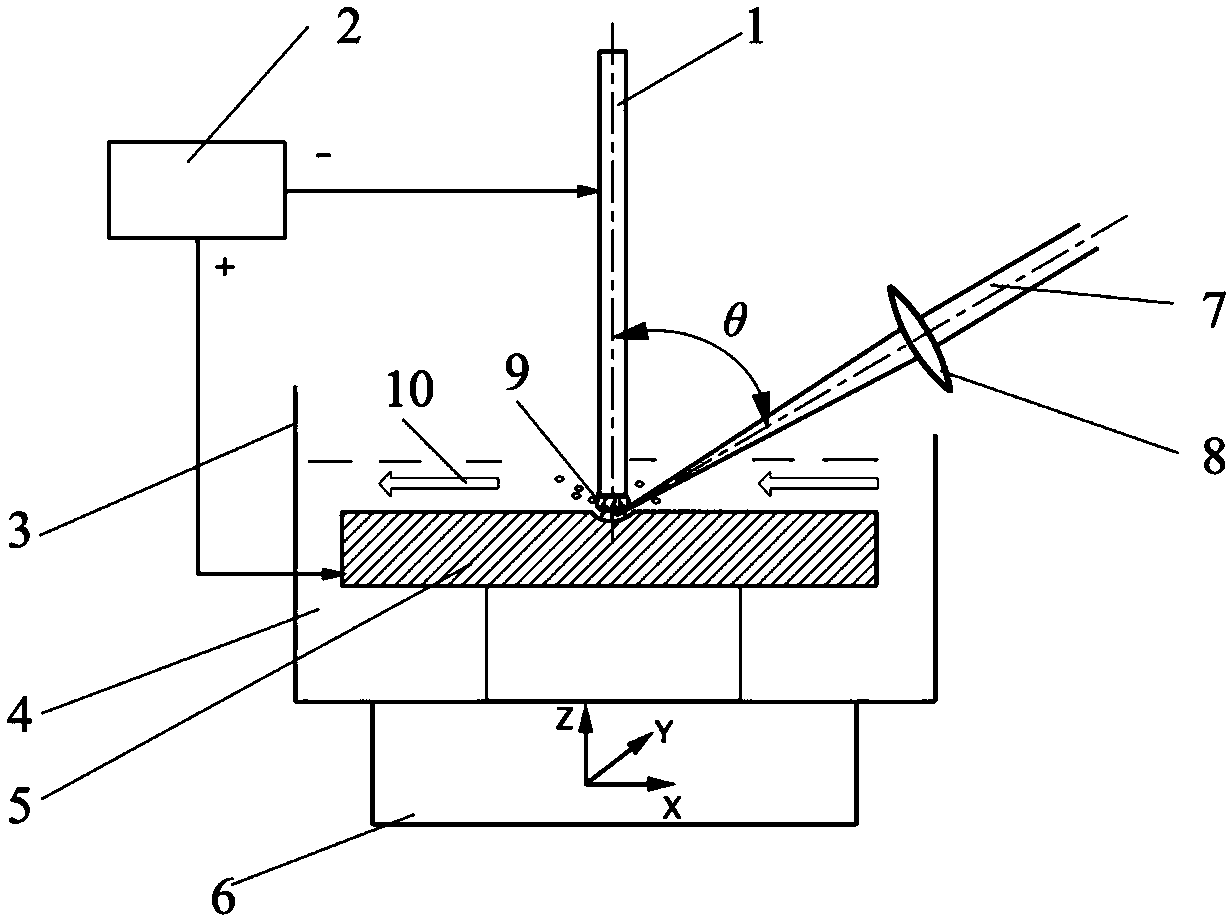
[0049] In this embodiment, the laser-induced discharge surface microstructure processing device such as image 3 As shown, the working tank 3 contains a liquid working medium 4 , and the workpiece 5 is immersed in the working medium 4 . The microscale tool electrode 1 is connected to the negative pole of the power supply 2 , and the workpiece 5 is connected to the anode of the power supply 2 . The working tank 3 is installed on the three-dimensional motion platform 6, and the three-dimensional motion platform 6 moves to drive the workpiece 5 to move. The end surface of one end of the micro-scale tool electrode 1 and the surface of the workpiece 5 to be processed maintain a certain gap, the distance of which is 0.02 mm to 0.5 mm, the gap is filled with the working medium 4, and the working medium 4 flows along the flow direction 10, that is, Flow in from one side of the gap and flow out from the other.
[0050] The laser light 7 generated by the laser converges in the gap thro...
Embodiment 3
[0054] In this embodiment, the structure of the laser-induced discharge surface microstructure processing device is basically the same as that of the laser-induced discharge surface microstructure processing device in Embodiment 2, the difference is as follows Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, the anode of the power supply 2 is connected to the auxiliary anode 23, and the distance between the auxiliary anode 23 and the microscale tool electrode 1 is not greater than 1 mm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com