Method for determining enzyme-inhibiting activity of aminopeptidase N inhibitor and application
A technique for measuring enzyme activity and aminopeptidase, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, and measuring devices. Accurate, little impact on detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Example 1: Screening for suitable cell carriers.
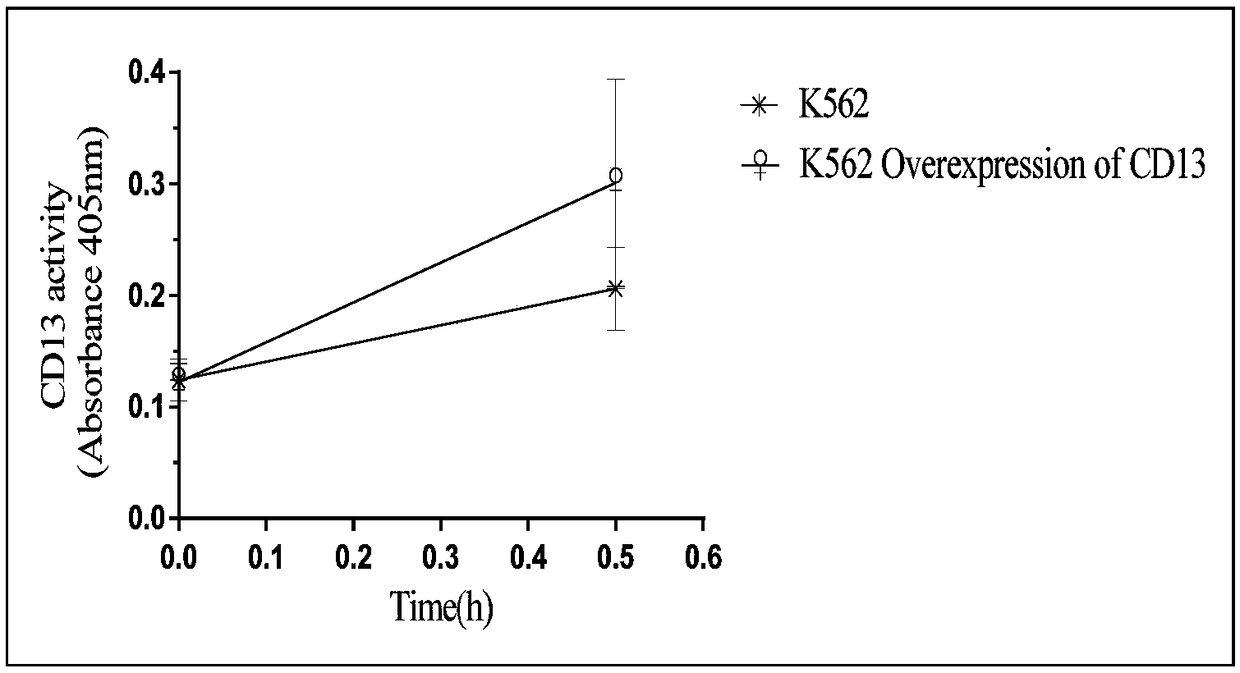
[0072] In order to improve the accuracy of enzyme activity determination, the present invention investigates the construction of vector cells for protein expression, including K562, PLC, MCF7, A549, and EA.hy926. Count the cells in the logarithmic growth phase after washing, and use 1×10 5 The number of each well was inoculated in a 96-well plate, and the CD13 substrate was added to 1.6mM. Each cell was paralleled to three wells, and the absorbance of the cells was measured at 0h, 0.5h, 1h, and 1.5h, respectively. The results are shown in Table 1:
[0073] Table 1 Luminescence ability of CD13 substrates catalyzed by different cells
[0074]
[0075] It can be seen from the results in Table 1 that K562 cells have the weakest catalytic ability to CD13 substrates, and as an enzyme activity detection tool, they have the least impact on the color development results. The types and quantities of K562 cell membrane surfac...
Embodiment 2
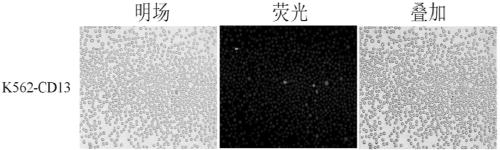
[0076] Example 2: Using the method of the present invention to establish a K562 monoclonal cell line overexpressing CD13.
[0077] 1. Resuspend K562 cells with complete culture medium, inoculate K562 cells in a 96-well plate, 5×10 3 per well, with a volume of 80 μL.
[0078] 2. The stock solution of recombinant lentivirus LV-CD13 is 2×10 8 TU / mL, diluted with ENi.S so that the MOI was 40, 10 μL of recombinant lentivirus LV-CD13 dilution was added to each well, and 10 μL of Polybrene was added as a virus infection auxiliary agent, and cultured overnight.
[0079] 3. Replace the fresh culture medium on the second day to continue the culture, and change the fresh culture medium again on the third day until three days after the recombinant lentivirus LV-CD13 infection, add puromycin to screen the virus-infected K562 cells, and treat the control group cells 2 weeks later. When all the cells died, the culture medium with a concentration of 1.0 mg / mL of puromycin was replaced, and ...
Embodiment 3
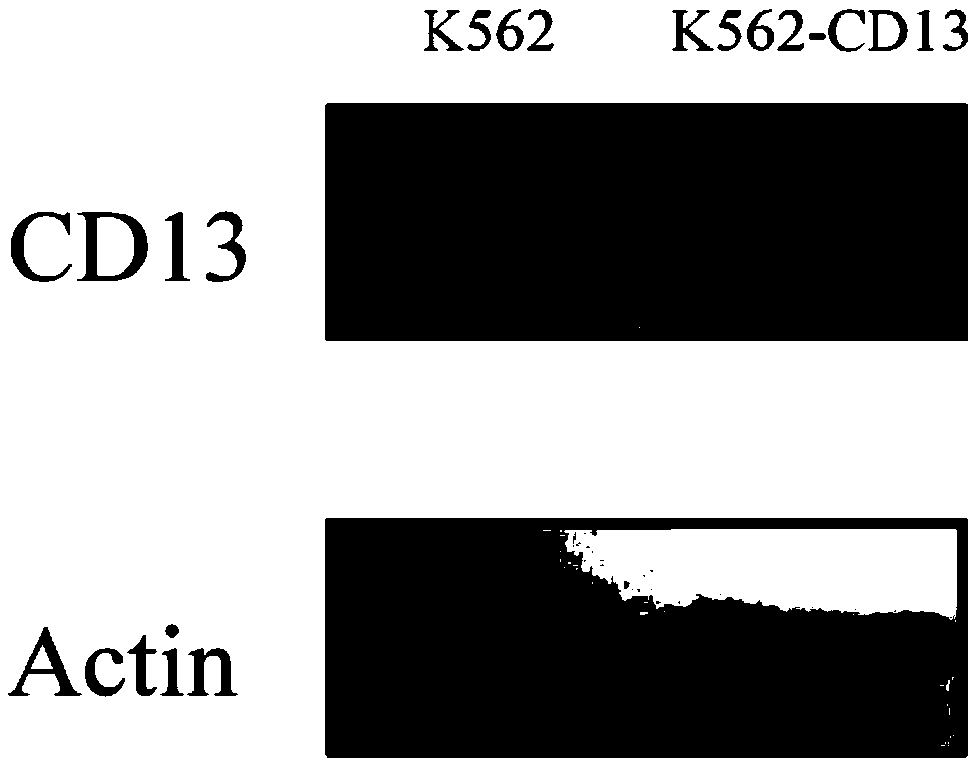
[0082] Example 3: Using the method of the present invention to detect the expression level of CD13 by Western Blotting.
[0083] 1. Resuspend K562 and K562-CD13 cells, resuspend K562-CD13 cells and K562 cells, transfer to a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 1000rpm to remove the supernatant, put on an ice box, add protein lysate, and freeze-thaw fully Cells were lysed, centrifuged at 12000rpm for 15min at 4°C, and the supernatant was taken. Take 5 μL of the supernatant to determine the protein concentration by Bradford method, add the remaining supernatant to an equal volume of 2×loading buffer, heat and boil at 100°C for 5 min to denature the protein. Store at -70°C.
[0084] 2. Add 20 μL, 40 μL, 60 μL, 80 μL, and 100 μL of BSA (1 μg / ml) to 5 test tubes, make up to 1 ml with pure water, and adjust to zero with 1 ml of pure water at the same time, take 50 μL of the lysed whole-cell protein solution, and make up with pure water When the volume reaches 1ml, add 1.4ml of Coomassie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com