Method for detecting residual amount of prochloraz of vegetable and fruit
A technology for residues and vegetables and fruits, which is applied in the field of detecting the residues of prochloraz in vegetables and fruits, can solve the problems of large consumption of reagents, glass instruments and time, danger of concentrated sulfuric acid, complicated operation, etc. The effect of improving experimental efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
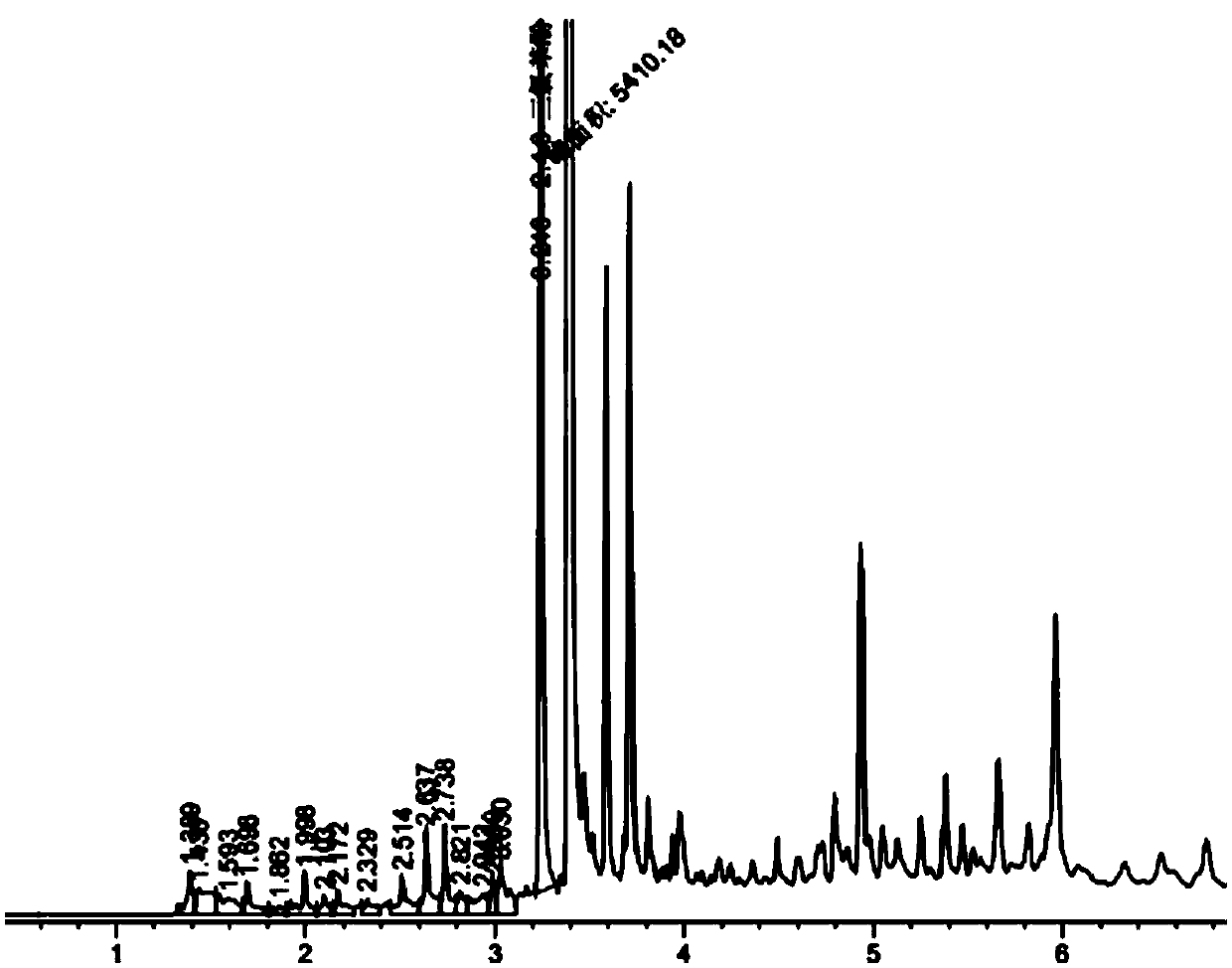
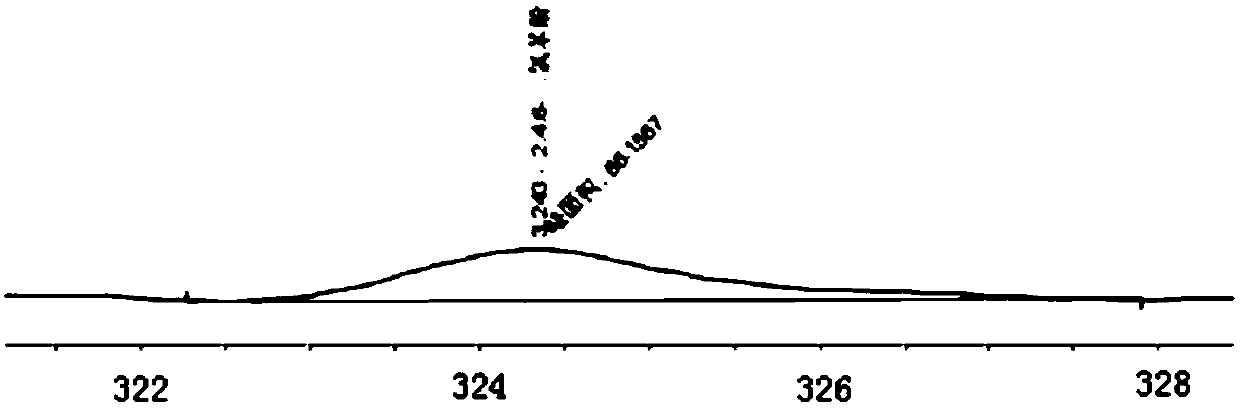
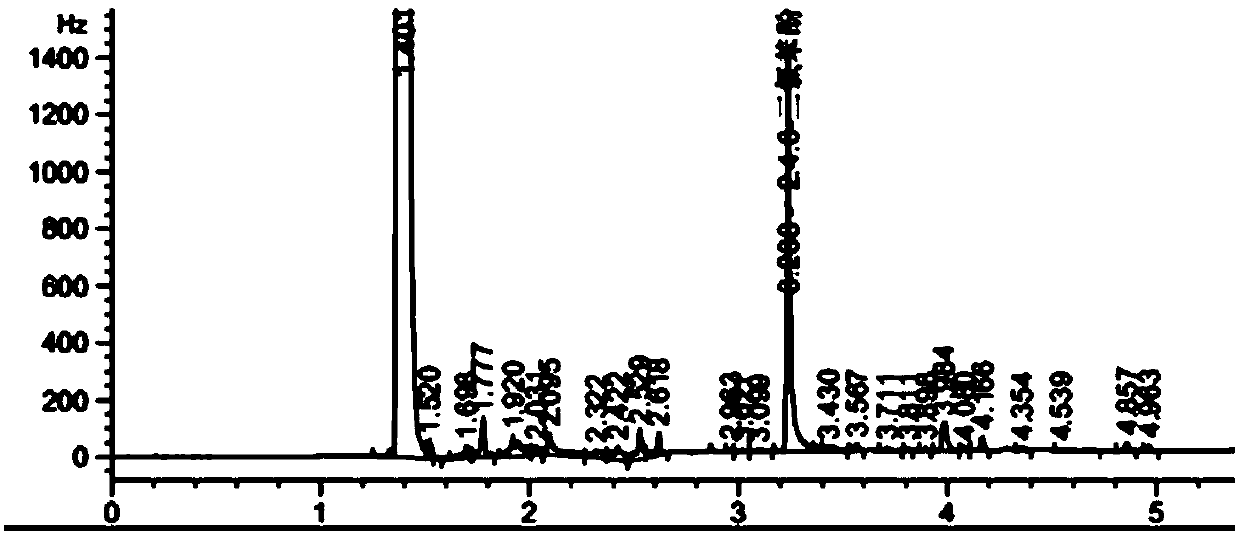
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A method for detecting the residual amount of prochloraz in vegetables and fruits in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0028] Step 1. Homogenization: Select the edible part of the fruits and vegetables to be tested and cut them by diagonal segmentation method, then chop and mix the fruits and vegetables in the diagonal part, and then directly put them into a food processor to mash and homogenate, the obtained The homogenized sample was stored at -20°C to obtain the test to be tested.
[0029] Step 2, extraction: Weigh 40g of the sample to be tested and put it into a homogenizer, add 50ml of acetonitrile solvent, homogenize at a high speed in the homogenizer for 3min, and then filter with filter paper, and collect the filtrate into a 50ml container containing 7g of sodium chloride. In a stopper colorimetric tube, collect 50ml of the filtrate, cover the stopper, shake vigorously for 1min, and let stand at room temperature for 30min to obtain the upper and l...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Step 1. Homogenization: Select the edible part of the fruits and vegetables to be tested and cut them by diagonal segmentation method, then chop and mix the fruits and vegetables in the diagonal part, and then directly put them into a food processor to mash and homogenate, the obtained The homogenized sample was stored at -25°C to obtain the test to be tested.
[0035] Step 2, extraction: Weigh 40g of the sample to be tested and put it into a homogenizer, add 50ml of acetonitrile solvent, homogenize at a high speed in the homogenizer for 3min, and then filter with filter paper, and collect the filtrate into a 50ml container containing 5g of sodium chloride. In a stoppered colorimetric tube, collect 40ml of the filtrate, cover with a stopper, shake vigorously for 1min, and let stand at room temperature for 30min to obtain upper and lower layer separations.
[0036] Step 3, hydrolysis: Accurately draw the above 20ml upper layer solution into a 25ml hydrolysis tube with a ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Step 1. Homogenization: Select the edible part of the fruits and vegetables to be tested and cut them by diagonal segmentation method, then chop and mix the fruits and vegetables in the diagonal part, and then directly put them into a food processor to mash and homogenate, the obtained The homogenized sample was stored at -10°C to obtain the test to be tested.
[0041]Step 2, extraction: Weigh 40g of the sample to be tested and put it into a homogenizer, add 50ml of acetonitrile solvent, homogenize at a high speed in the homogenizer for 3min, and filter with filter paper, and collect the filtrate into a 50ml tool containing 6g of sodium chloride. In a stopper colorimetric tube, collect 40-50ml of the filtrate, cover the stopper, shake vigorously for 1min, and let stand at room temperature for 30min to obtain the upper and lower layer separations.
[0042] Step 3. Hydrolysis: Accurately draw the above 20ml of the upper layer solution into a 25ml hydrolysis tube with a sc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com