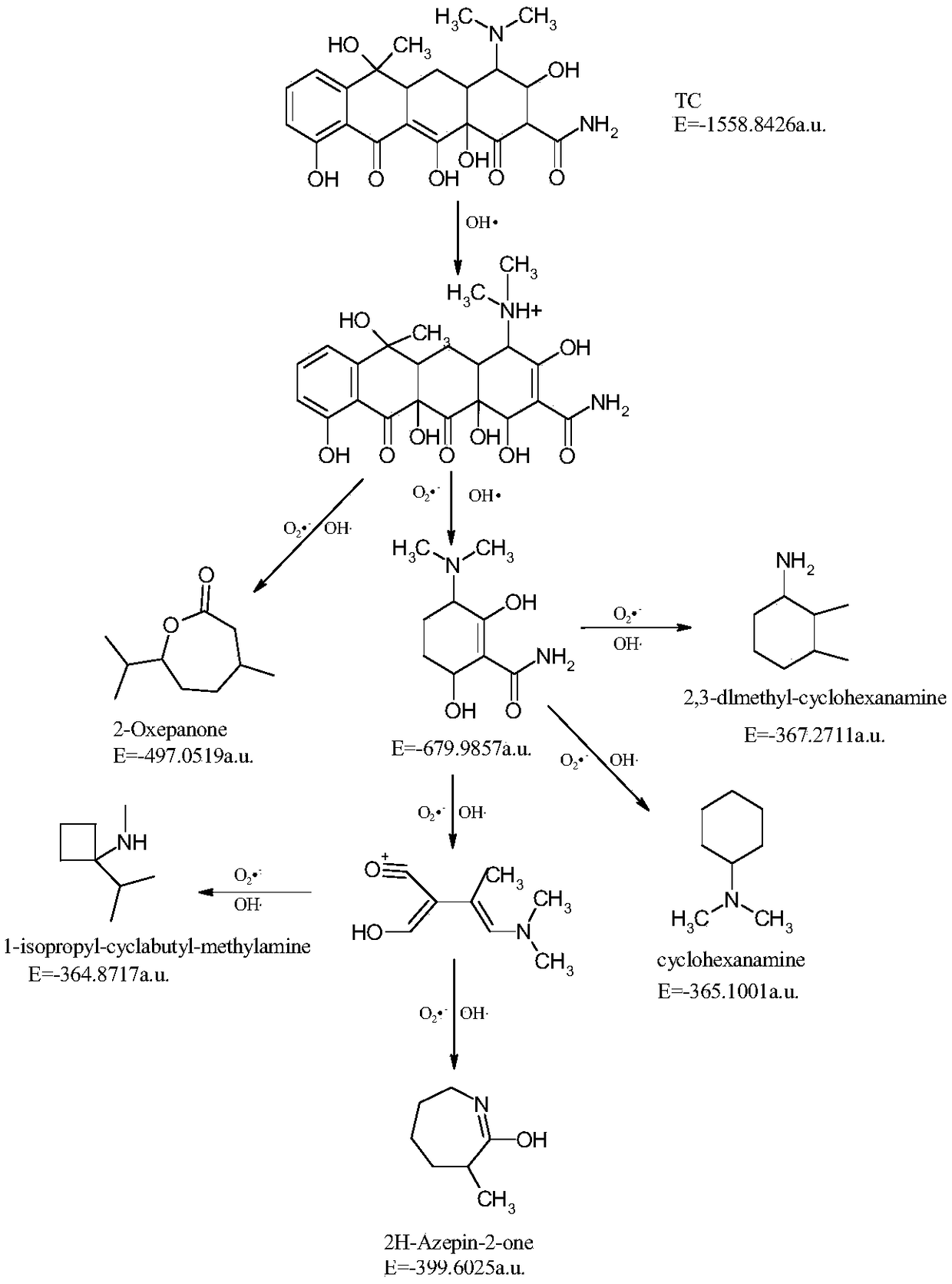
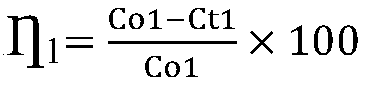Method for treatment of tetracycline antibiotic wastewater by magnesium-aluminum hydrotalcite loaded TiO2 photocatalytic adsorption material
A magnesium-aluminum hydrotalcite and antibiotic wastewater technology, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, special compound water treatment, etc., can solve the problem of tetracycline antibiotic degradation rate and salinity not mentioned, and the treatment effect is vague, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of great practical significance and market competitiveness, low open-loop toxicity and high salinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
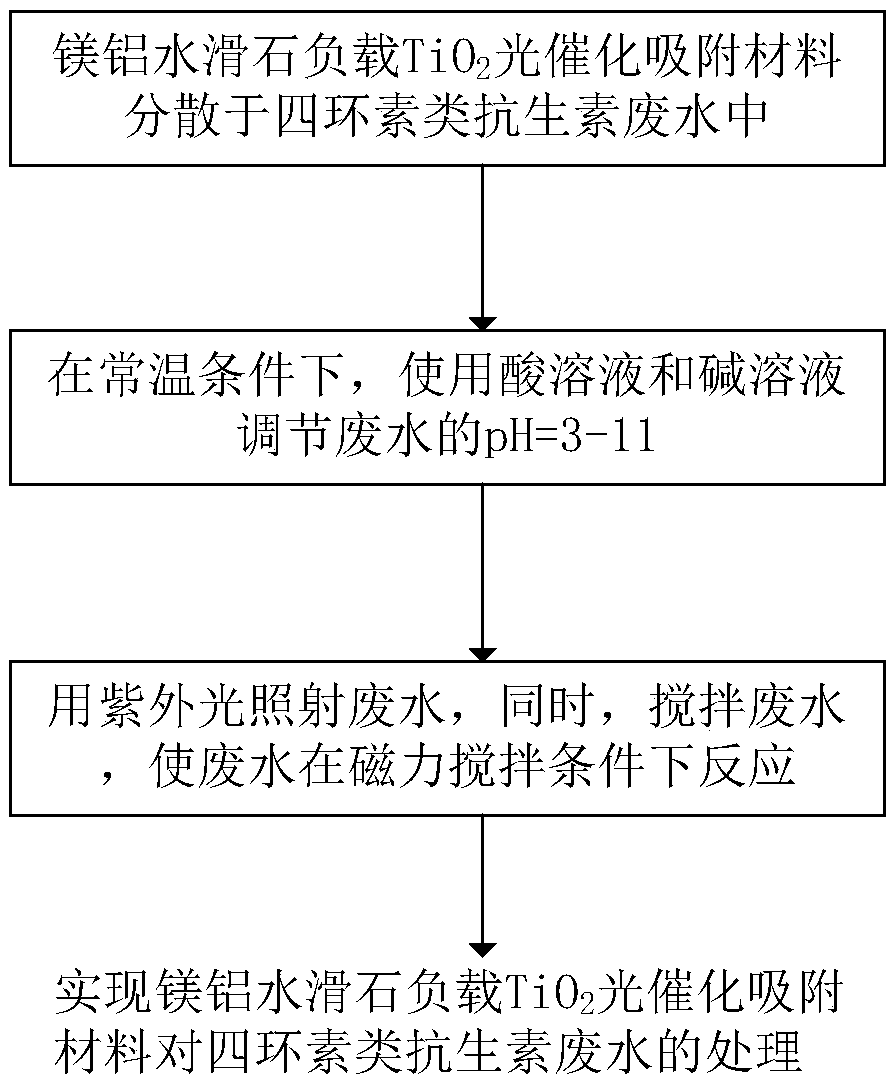
[0034] A magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite supported TiO 2 The method for treating tetracycline antibiotic wastewater with photocatalytic adsorption material, the application steps are:
[0035] Weigh 0.1g of magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite loaded TiO 2 The photocatalytic adsorption material was dispersed in 200mL of 100mgL tetracycline aqueous solution; under normal temperature conditions, the pH of the solution was adjusted to 11 by using acid solution and alkali solution; the reaction was irradiated with 400W ultraviolet light for 120min.
[0036] Use a needle filter to take the supernatant and filter the solid matter, and then use a UV-visible spectrophotometer to test the tetracycline absorbance at 360nm. The converted tetracycline removal rate is 94%, and the salinity is 35%.
Embodiment 2
[0038] A magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite supported TiO 2 The method for treating tetracycline antibiotic wastewater with photocatalytic adsorption material, the application steps are:
[0039] Weigh 0.1g of magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite loaded TiO 2 The photocatalytic adsorption material was dispersed in 200mL of 50mgL tetracycline aqueous solution; under normal temperature conditions, the pH of the solution was adjusted to 11 with acid solution and alkali solution; 500W power of ultraviolet light was used to react for 180min.
[0040] Use a needle filter to take the supernatant and filter the solid matter, and then use a UV-visible spectrophotometer to test the tetracycline absorbance at 360nm. The converted tetracycline removal rate is 94.3%, and the mineralization degree is 40%.
Embodiment 3
[0042] A magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite supported TiO 2 The method for treating tetracycline antibiotic wastewater with photocatalytic adsorption material, the application steps are:
[0043] Weigh 0.1g of magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite loaded TiO 2 The photocatalytic adsorption material was dispersed in 200mL of 50mgL tetracycline aqueous solution; under normal temperature conditions, acid solution and alkali solution were used to adjust the pH of the solution to 7; 400W power of ultraviolet light was used to react for 120min.
[0044] Use a needle filter to take the supernatant and filter the solids, and then use a UV-visible spectrophotometer to test the tetracycline absorbance at 360nm. The converted tetracycline removal rate is 92%, and the salinity is 40%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com