Cycloidal-pin gear speed reducer
A technology of pin wheel reducer and cycloidal wheel, which is applied in the direction of gear transmission, belt/chain/gear, transmission parts, etc., which can solve the problems of easy failure of parts, scrapping of the whole reducer, and increase of production cost. , to achieve the effect of prolonging life, easy fastening and dismounting, and reducing friction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
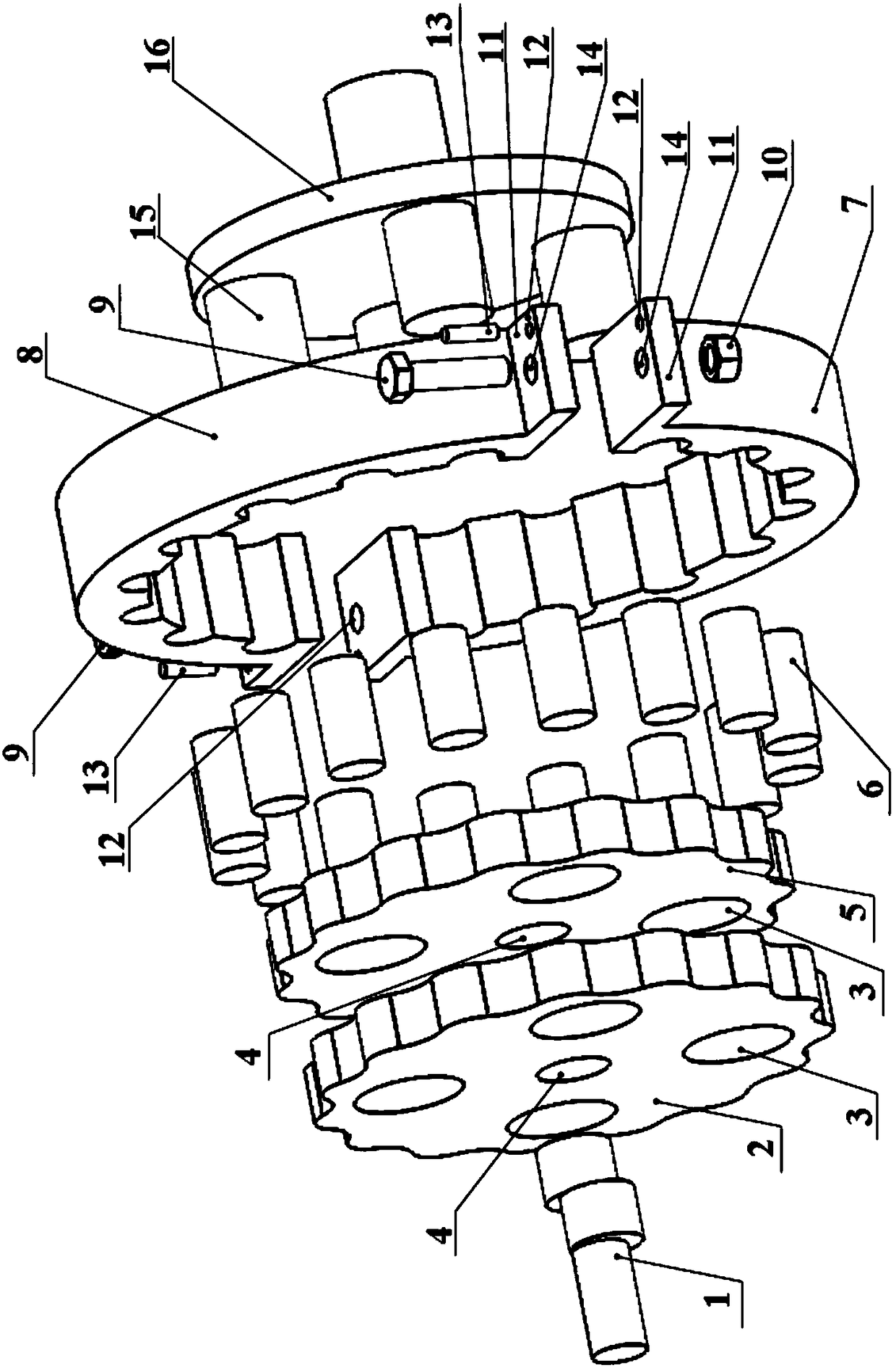
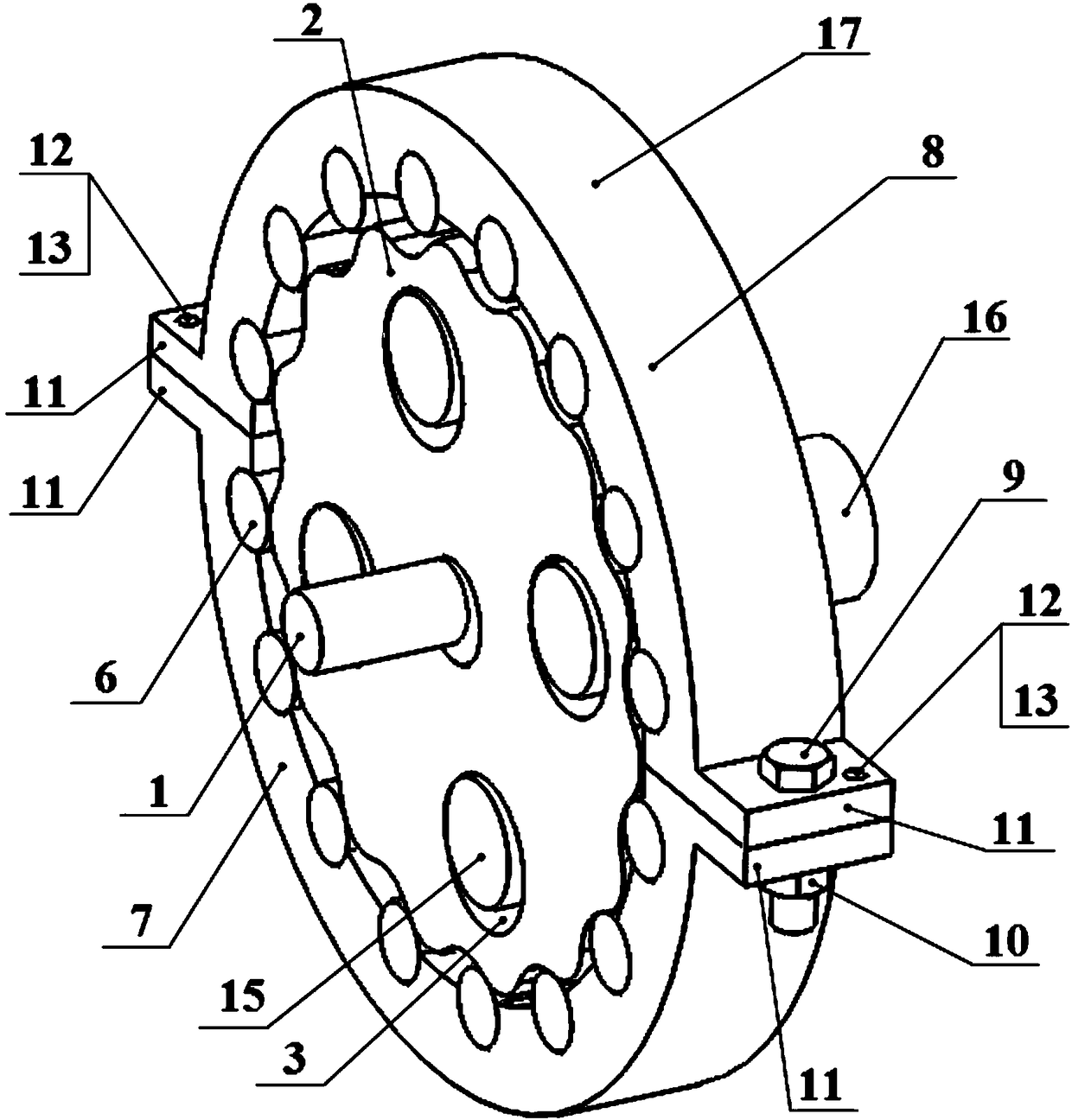
[0028] A cycloid reducer of this embodiment, such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, it includes input shaft 1, cycloid wheel A2, pin hole 3, center hole 4, cycloid wheel B5, needle roller 6, sub pin wheel A7, sub pin wheel B8, fastening bolt 9, fastening nut 10, Boss 11, positioning pin hole 12, positioning pin 13, through hole 14, bearing pin 15, output disc 16. Described needle wheel 17 is split type, and it is that two completely identical sub-pin wheels A7 and sub-pin wheel B8 are spliced to form complete pin-wheel structure by circumferential angle of 180 °; The wheel 17 meshes with the cycloid wheel B5 through the needle roller 6, and the mating surface between the two sub-pin wheels is perpendicular to the cross section of the pin wheel. The fixing mechanism for realizing the splicing and splitting of the sub-pin wheels is that the outer sides of the arc end faces of the two sub-pin wheels are provided with bosses 11, and there are through holes 14 at the positions ...
Embodiment 2
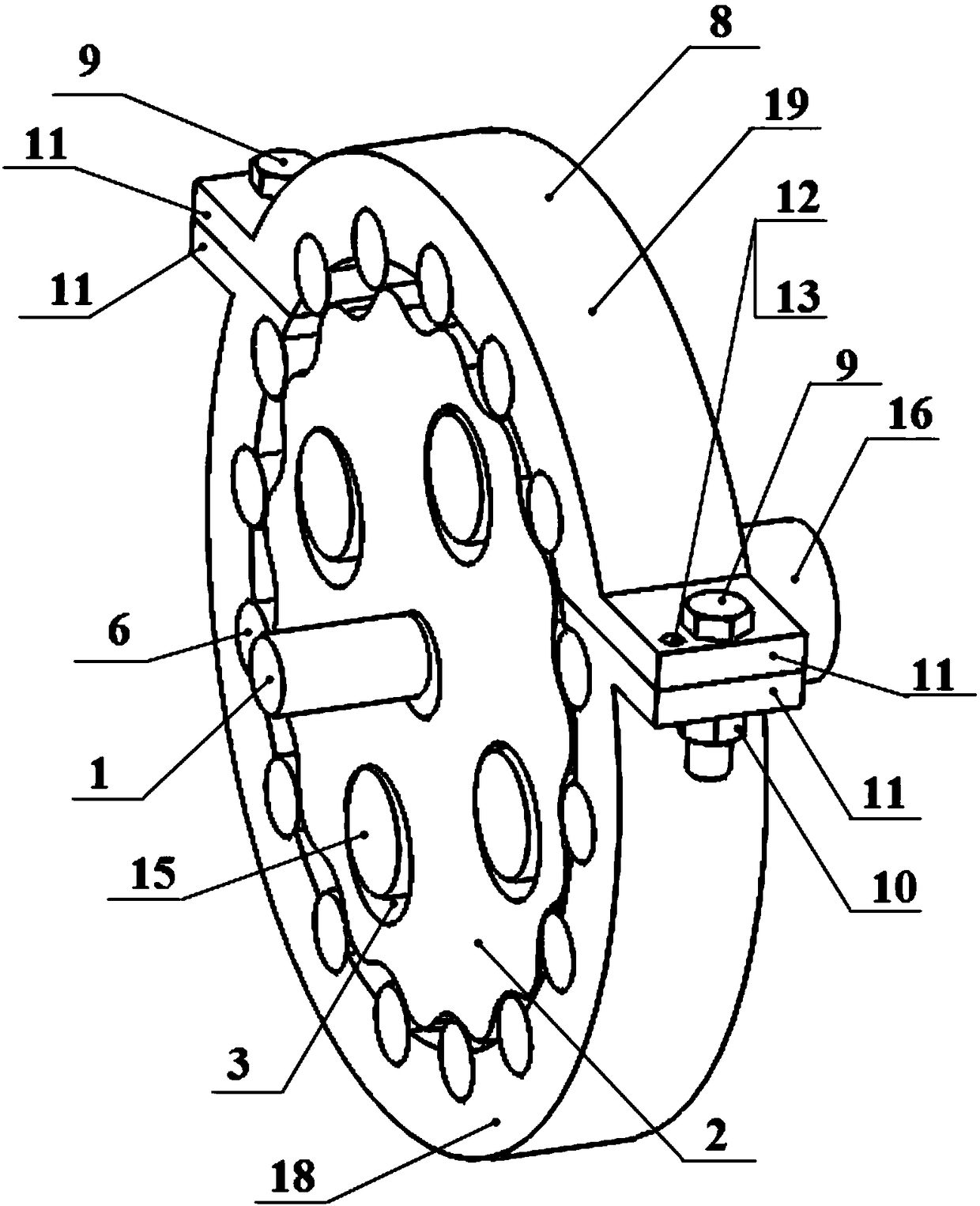
[0032] Such as image 3 As shown, the needle wheel 17 of the present embodiment is composed of two arc-shaped sub-pin wheels C18 and sub-pin wheels D19 splicing to form a complete pin-wheel structure; the circumferential angles of the two sub-pin wheels are respectively 60° and 120°; the pin wheel 17 meshes with the cycloid wheel B5 through the needle roller 6; the mating surface between the sub-pin wheels is perpendicular to the cross section of the pin wheel, and other fixed mechanisms that realize the splicing and splitting of the sub-pin wheels, The positioning, connection and fastening methods and the working principle of the reducer are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The decomposition structure of the pin wheel in this embodiment is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the sub-pin wheel adopts the cone surface positioning method, and its connection relationship is as follows: a convex cone 20 is provided on the lower surface of the boss 11 of the sub-pin wheel A7, and a convex cone 20 is provided on the corresponding position of the boss 11 of the other sub-pin wheel B8. A concave cone 21 is provided, and the two sub-pin wheels are butted together, and the conical surfaces between the convex cone 20 and the concave cone 21 cooperate with each other to realize the positioning of the two sub-pin wheels. The working principles of other fixing mechanisms, connection and fastening methods and speed reducers for realizing the splicing and dismantling of the sub-pin wheels are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com