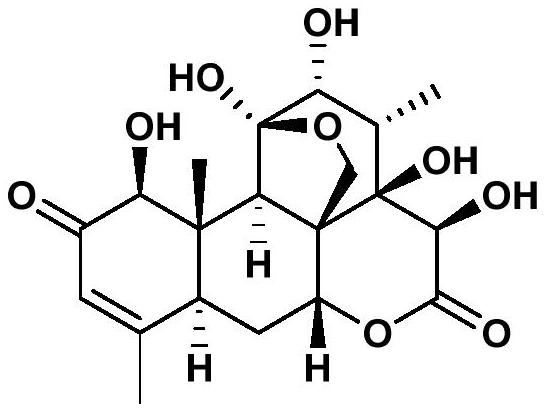
Insect antifeedant 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone transported in plants and its application
A technology of insects and plants, applied in the direction of plant growth regulators, applications, insecticides, etc., can solve the problems of loss of drug efficacy, interference effects, etc., and achieve the effects of environmental friendliness, high antifeedant activity, and convenient use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 113
[0025] Example 113, The plant systemic properties of 21-dihydroeurycomanone and the antifeedant activity after systemic absorption
[0026] Method: Dissolve 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone in methanol, and then make it into a drug solution with a final concentration of 100 μg / mL, and spread it evenly on the surface of a circular cabbage leaf dish with a diameter of 1.2 cm. The dosage is 20 μL, and after the methanol on the surface of the leaf disc is naturally dried, the 3rd instar larvae of the diamondback moth Plutellaxylostella (Linnaeus) are inserted, and each concentration treatment is repeated 3 times at a relative humidity of 50% to 70% and a temperature of 25°C. After keeping in an environment of ~28°C for 24 hours, the feeding area was counted, and the feeding rate and refusal rate were calculated.
[0027] The antifeedant activity of 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone against the last 1st instar larvae of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) was tested with cassava leaves; the antifeedant...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone can be systemically sucked from the growth environment of A. chinensis through the root to the root of A. chinensis, and transported upwards to the leaves, making insects refrain from eating the leaves of A. chinensis
[0035] Method: 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone was dissolved in DMSO to make a 10000μg / mL mother solution, and then 0.5mM CaCl 2 Dilute the stock solution with aqueous solution to 100 μg / mL culture solution. Put the previously cultivated Shanghai green seedlings (6-leaf stage, not treated with 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone before) in 0.5mM CaCl 2 After pre-cultivation in aqueous solution for 2 hours, transfer it to the prepared 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone culture solution mentioned above. After 24 hours, take 0.7 g of the top leaf of Shanghai green, mash it and dissolve it in 2 mL of methanol, and use liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry The instrument can detect that 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone is contained in the leaf extract,...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone can be absorbed from the growth environment of Chinese cabbage through the root to the inside of Chinese cabbage root, and transported upward to the leaves, so that the vegetable aphid Lipaphiserysimi refuses to eat the leaves of Chinese cabbage
[0038] Method: 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone was dissolved in methanol to make a mother solution of 10000μg / mL, and then 0.5mM CaCl 2 Dilute the stock solution with aqueous solution to 100 μg / mL culture solution. The previously cultivated cabbage seedlings (6-leaf stage, not treated with 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone before) were placed in 0.5mM CaCl 2 After pre-cultivation in aqueous solution for 2 hours, transfer to the above-mentioned 13,21-dihydroeurycomanone culture solution prepared above, and 24 hours later, insert the aphid without wings, insert 100 heads in each cage, repeat 4 times, and insert the aphid 24 hours later. Count the number of cabbage aphids inhabited on the control leaves an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com