An insect repellant that can be transported in plants
An antifeedant and plant technology, applied in the field of pesticides, can solve problems such as loss of efficacy and interference effects, and achieve the effects of convenient use and good application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
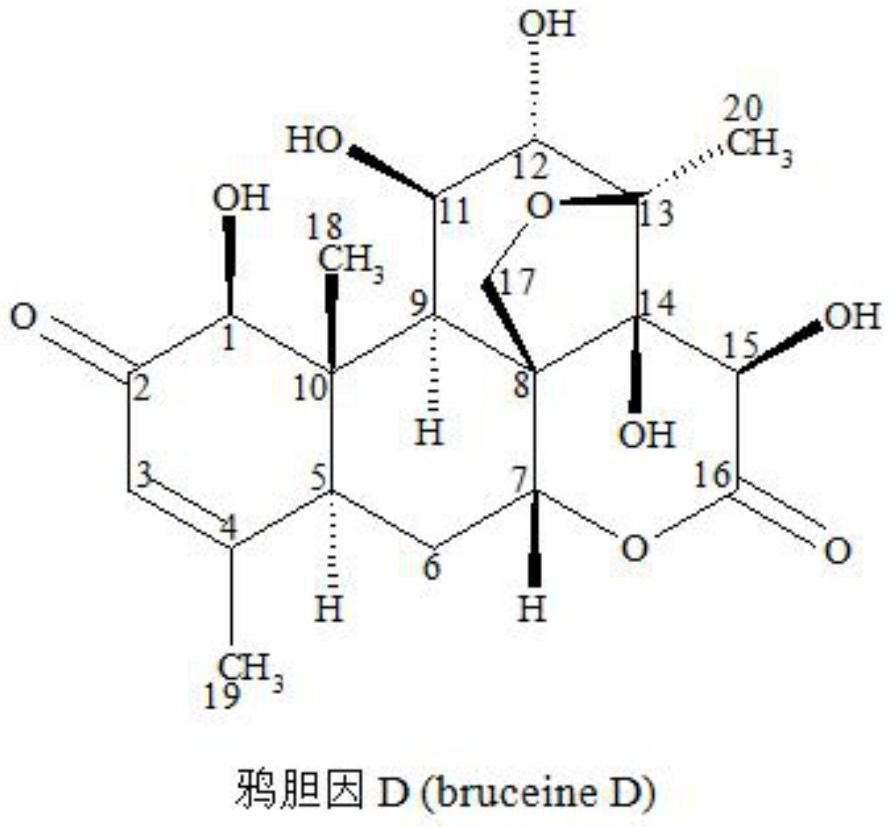
[0044] Example 1: Test the antifeedant activity of Brucea brucein D on several kinds of leaf-eating Lepidoptera larvae that damage vegetables with the classic leaf disc drug-loading method
[0045] 1. Method
[0046] Dissolve Brucea javanica D with methanol, and then apply the prepared drug solution evenly on the surface of a circular cabbage leaf disc with a diameter of 1 cm. The amount of drug applied to each leaf disc is 20 μL. After drying, insert the 2nd instar larvae of the diamondback moth Plutellaxylostella (Linnaeus), repeat each concentration treatment 3 times, and keep it in an environment with a relative humidity of 50% to 70% and a temperature of 25°C to 28°C for 24 hours before counting feeding area to calculate feeding rate and refusal rate.
[0047] Cassava leaves were used to test the antifeedant activity of brucein D on the end-1st instar larvae of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius), and amaranth was used to test the antifeedant activity of brucein D on the end-1...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Brucea javanica D can be sucked into the root of Chinese cabbage through the root from the growth environment of Chinese cabbage, and transported upward to the leaves, so that insects refuse to eat the leaves of Chinese cabbage
[0058]Dissolve brucein D in methanol to make a 10000μg / mL mother solution, and then add 0.5mM CaCl 2 Dilute the stock solution with aqueous solution to 100 μg / mL culture solution. The previously cultivated cabbage seedlings (6-leaf stage, not previously treated with Brucella D) were placed in 0.5mM CaCl 2 After pre-cultivation in aqueous solution for 2 hours, transfer it to the above-mentioned prepared Brucea javanica D culture solution. After 24 hours, take 0.5 g of the top leaves of Chinese cabbage, mash it and dissolve it in 2 mL of methanol. It can be detected by high-performance liquid chromatography. This extract contains brucein D, and the content of brucein D in the top leaves (fresh leaves) of Chinese cabbage reaches 40 μg / ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3: Brucella bruceae D can be sucked into the cabbage root from the growth environment of Chinese cabbage through the root, and transported upwards to the leaves, making Phyllotreta striolata (Fabricius) adults refuse to eat the cabbage leaves
[0060] Dissolve brucein D in methanol to make a 10000μg / mL mother solution, and then add 0.5mM CaCl 2 Dilute the mother liquor with aqueous solution to a 50 μg / mL culture broth. The previously cultivated cabbage seedlings (6-leaf stage, not previously treated with Brucella D) were placed in 0.5mM CaCl 2 After pre-cultivation in aqueous solution for 2 hours, transfer it to the above-mentioned prepared Brucea javanica D culture solution. After 24 hours, insert 50 flea beetle adults into each cage, repeat 4 times, and insert flea beetle adults. After 24 hours, A counts the feeding area, and calculates the average food refusal rate by the formula in Example 1 to be 71%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com