Patents
Literature
71 results about "Systemic absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Systemic absorption. Uptake to the blood and transport via the blood of a substance to an organ or compartment in the body distant from the site of absorption. (You must log in first to edit the definition.)
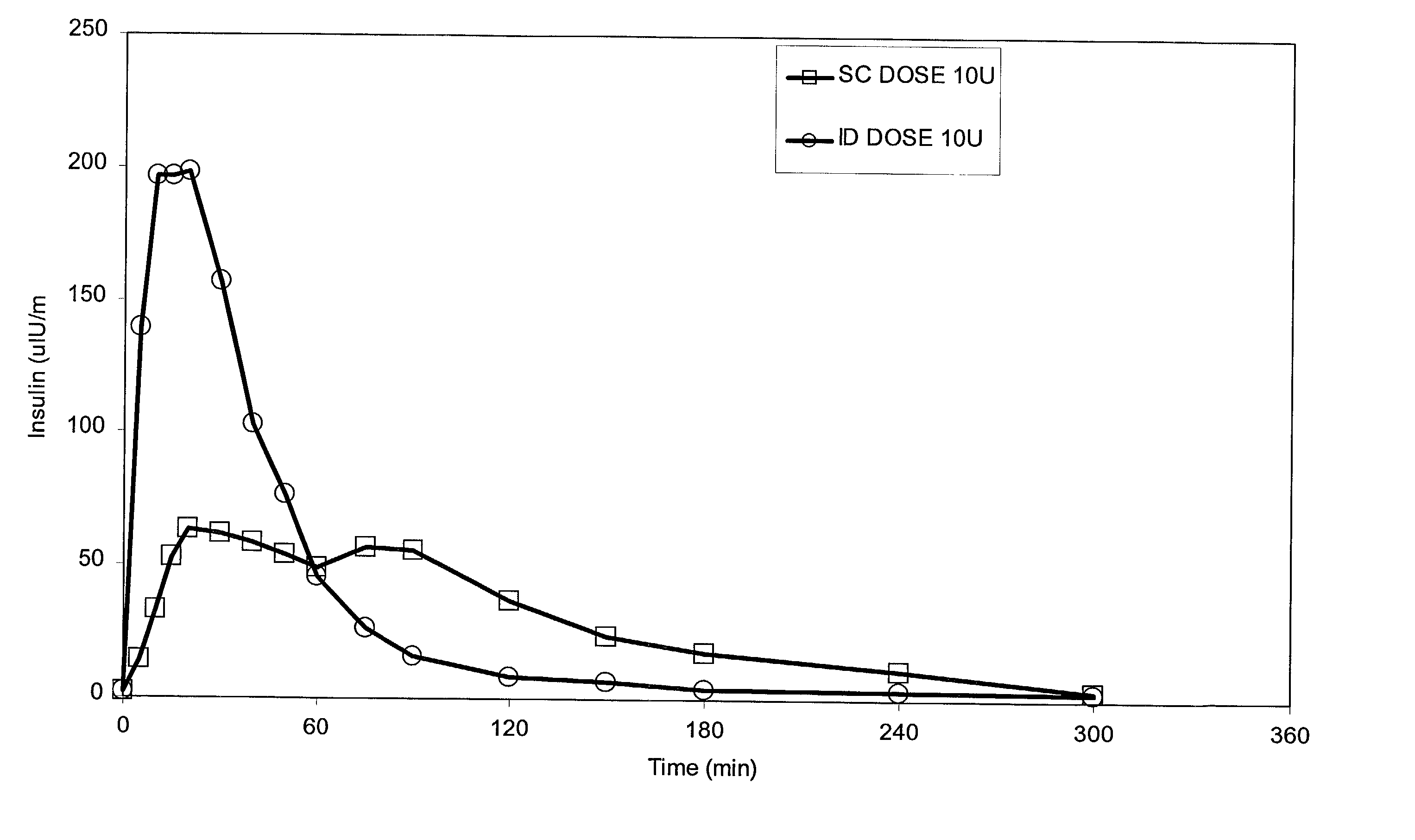
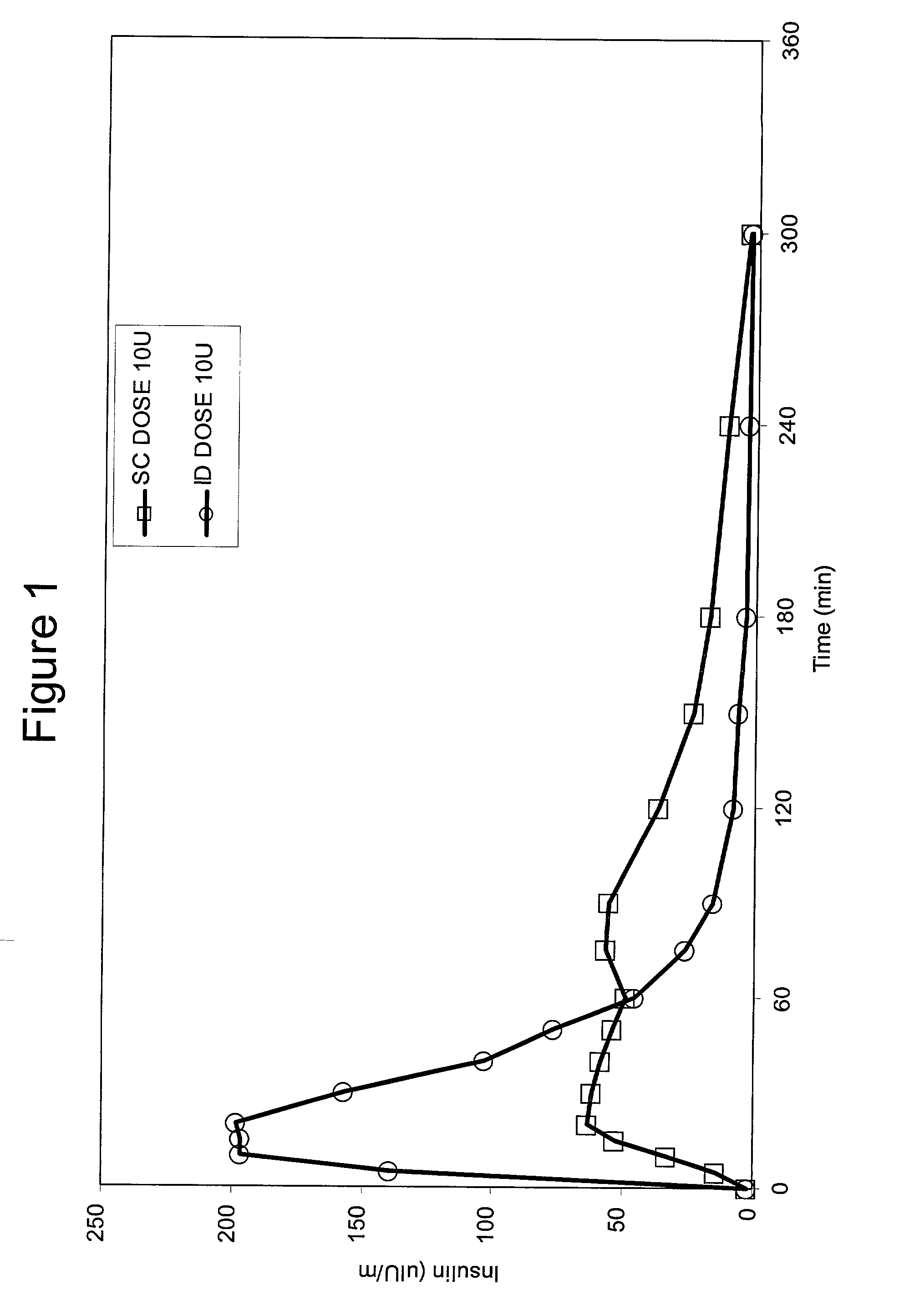
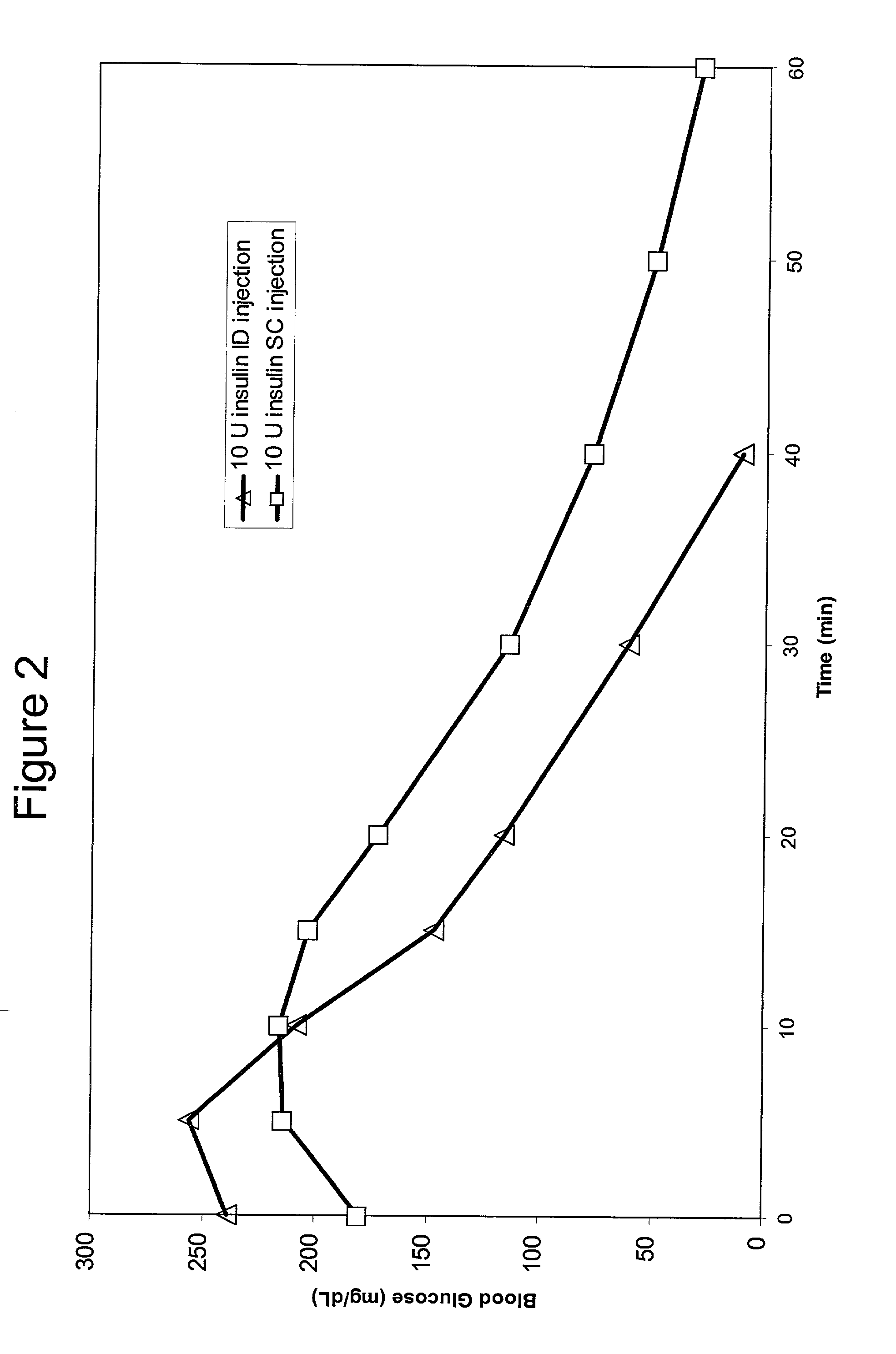
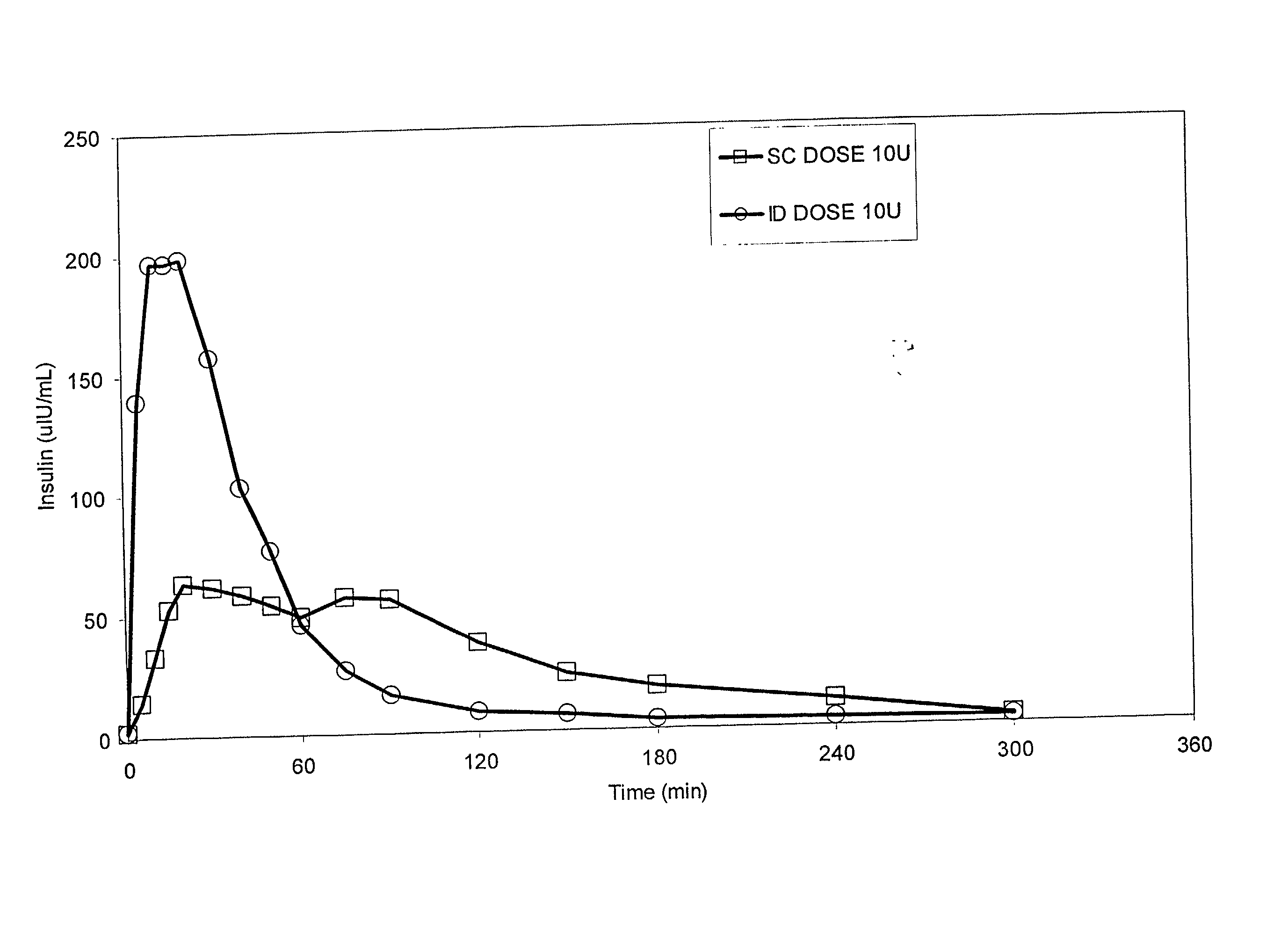
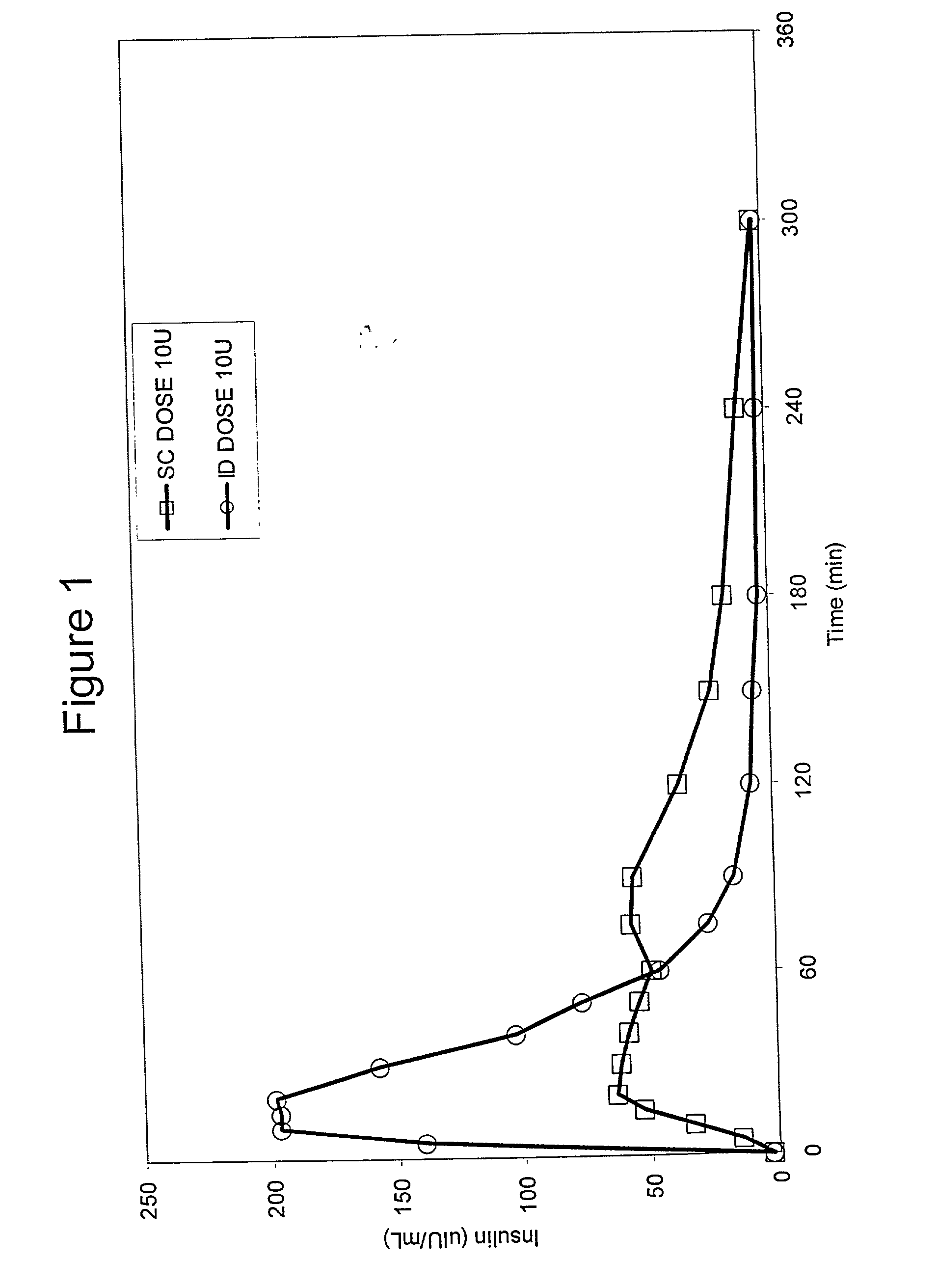
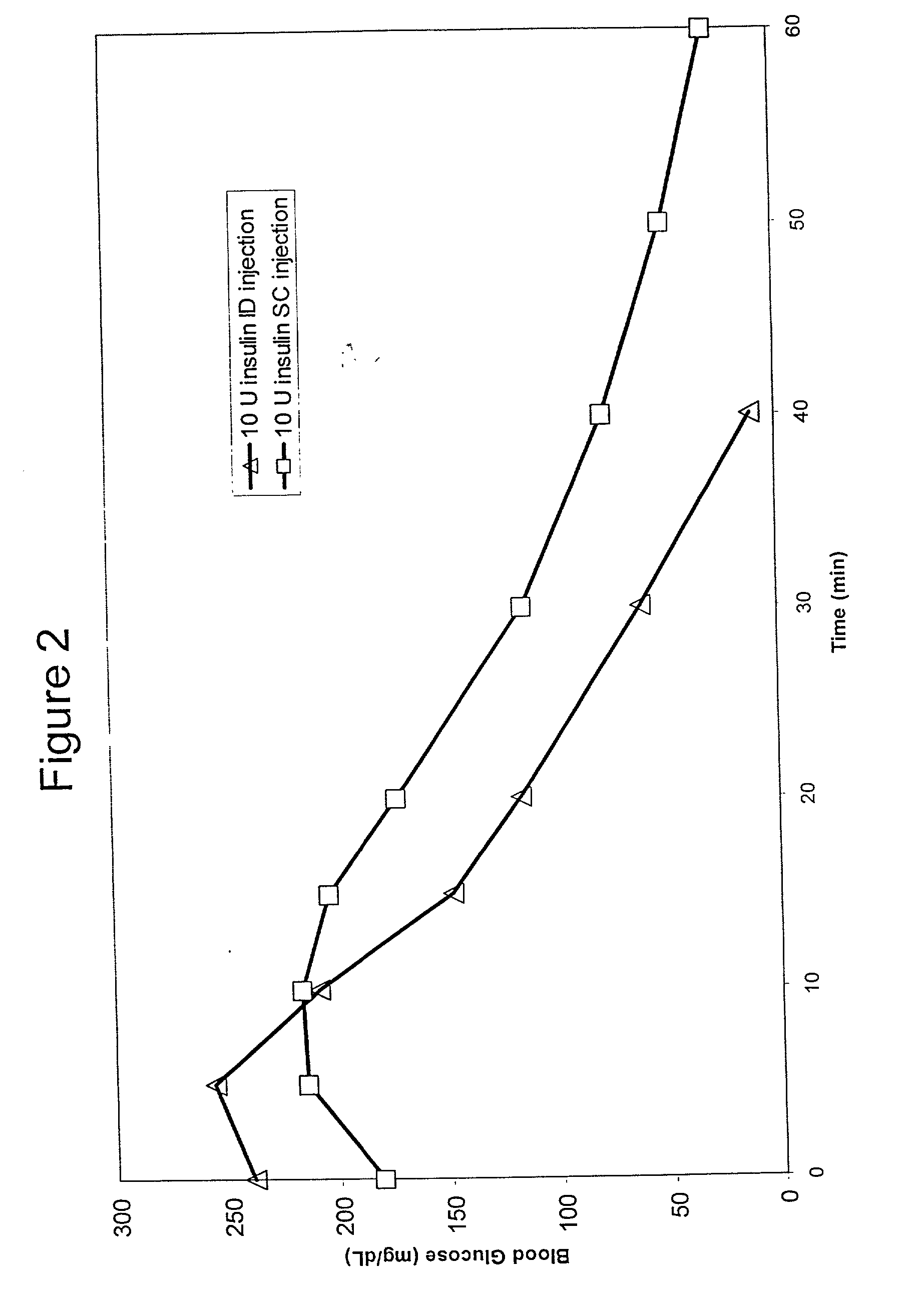
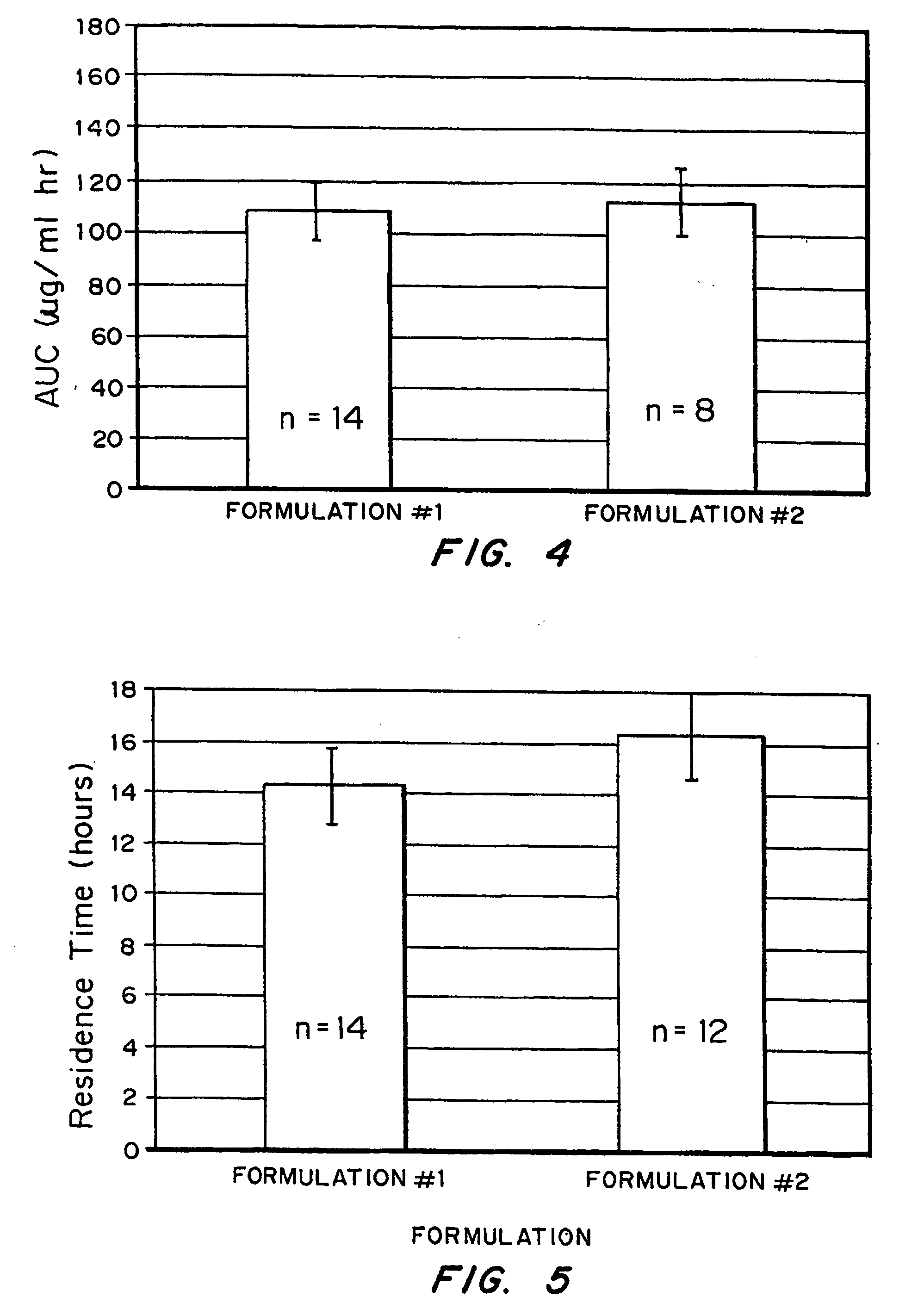
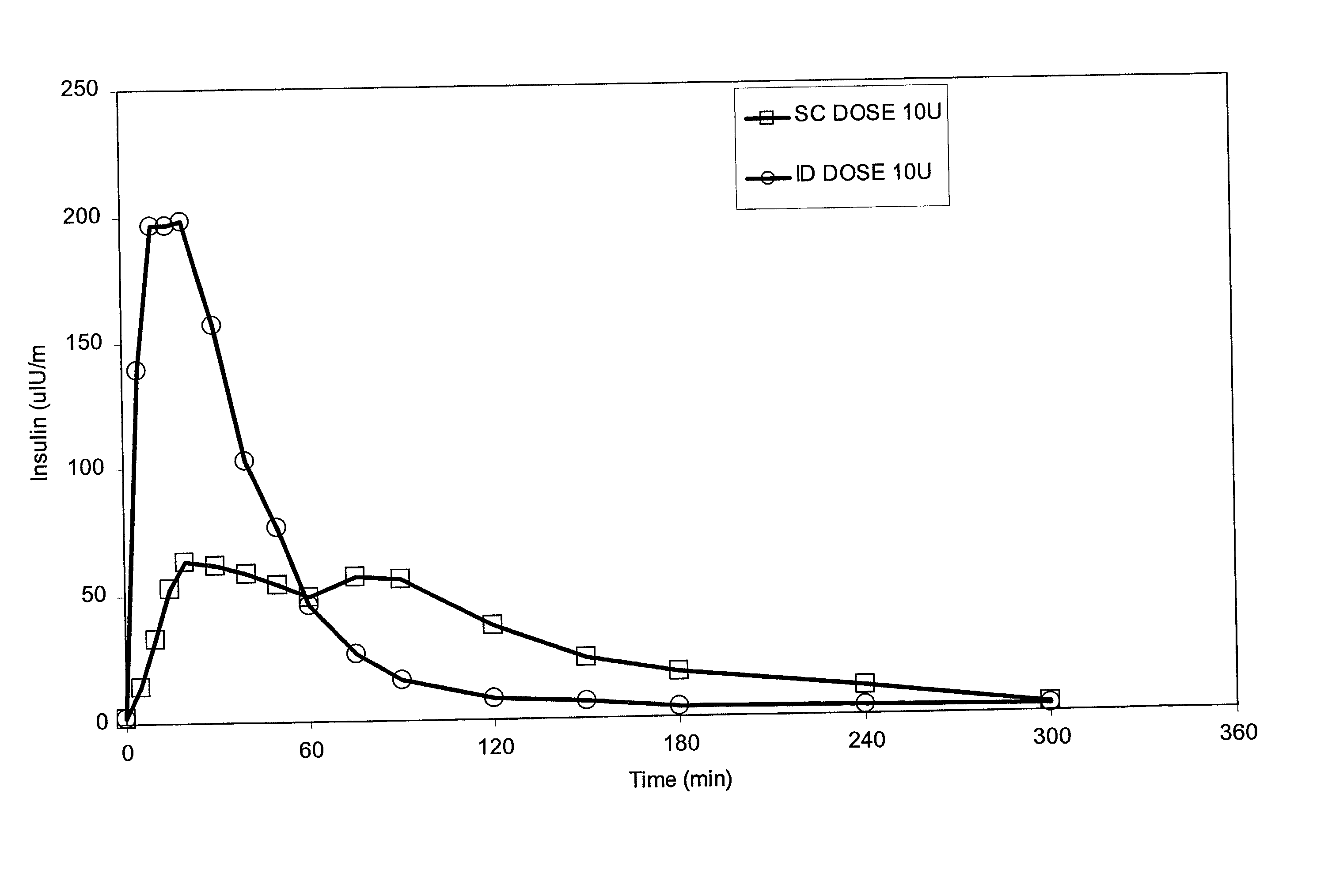
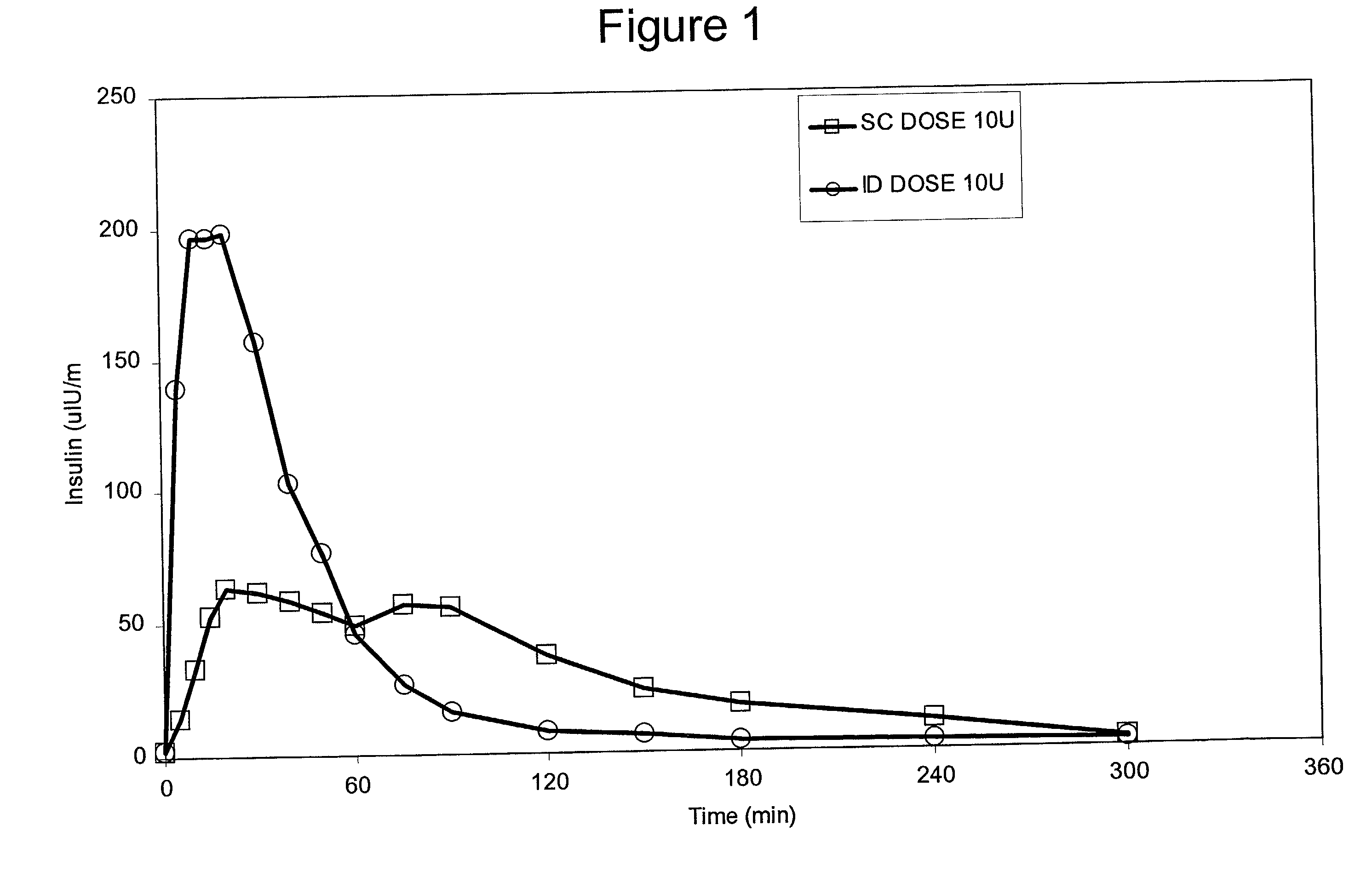
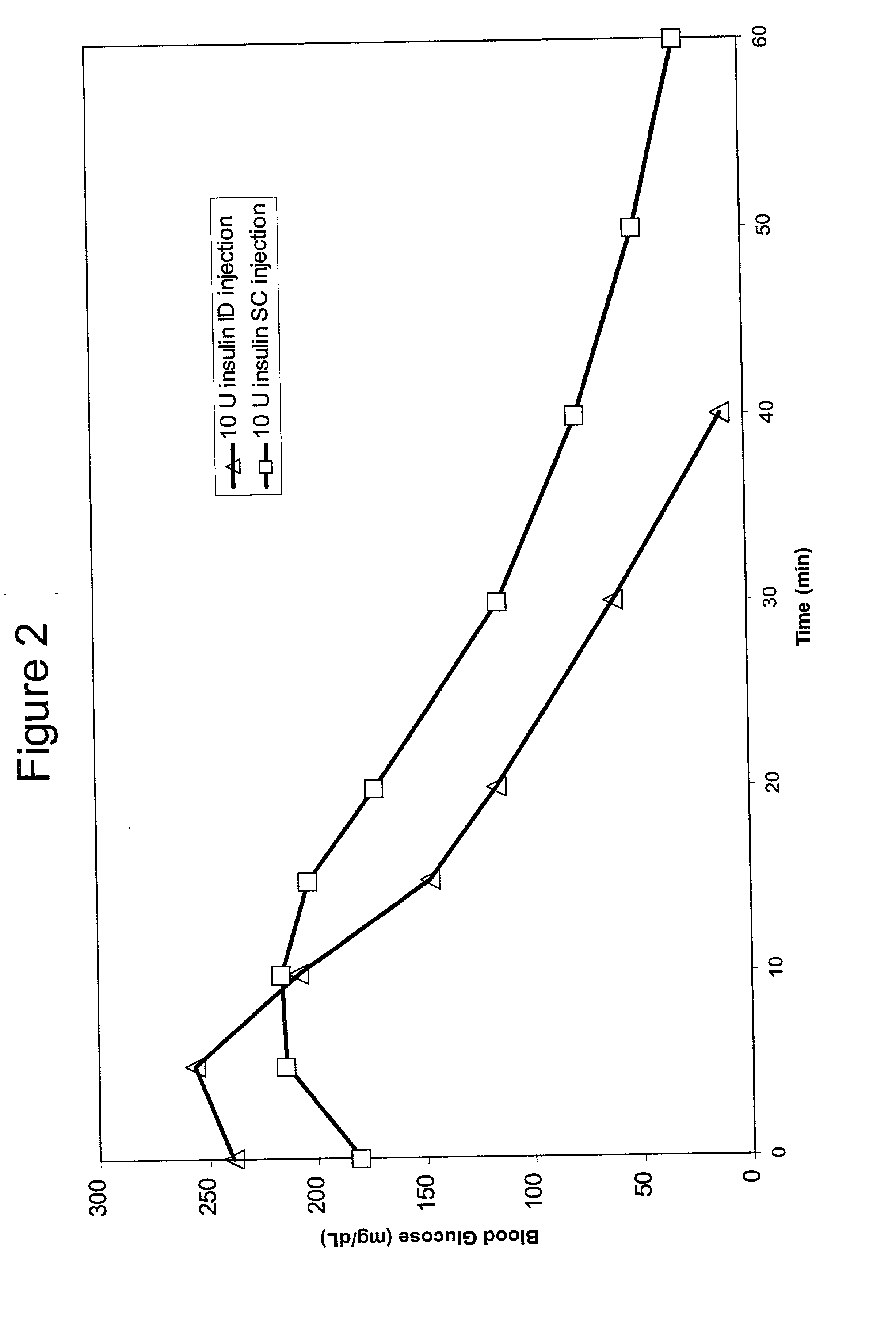
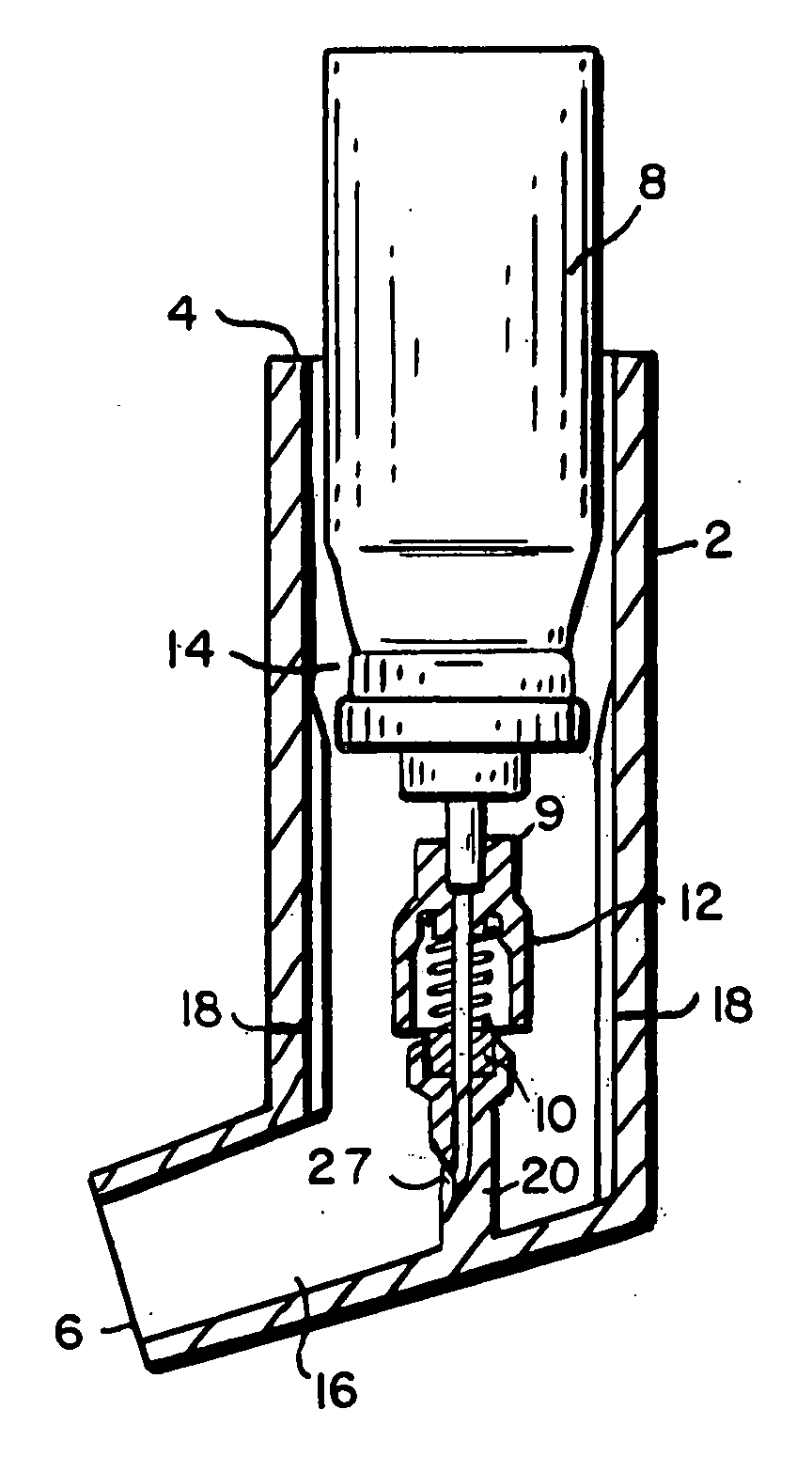
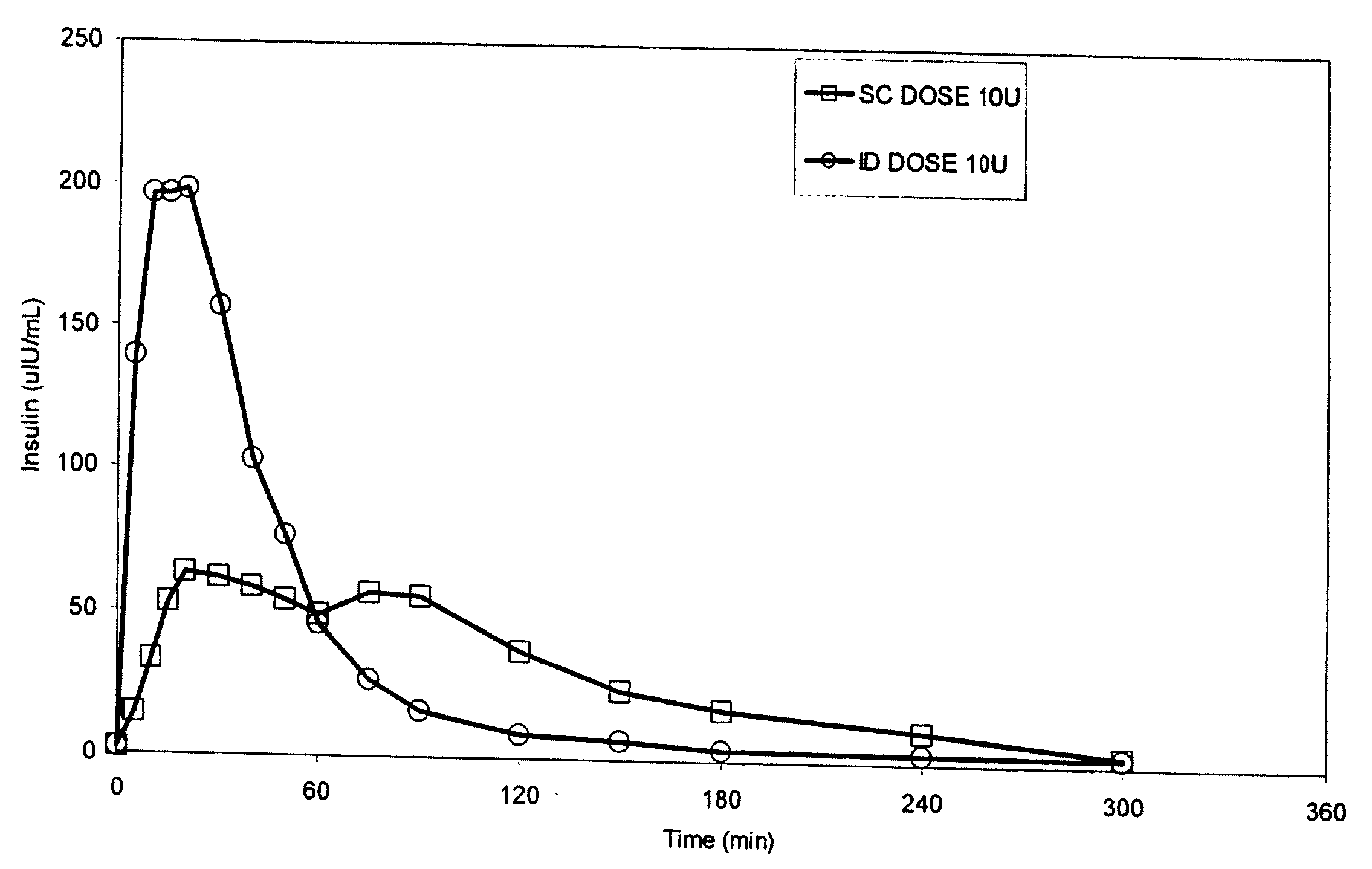
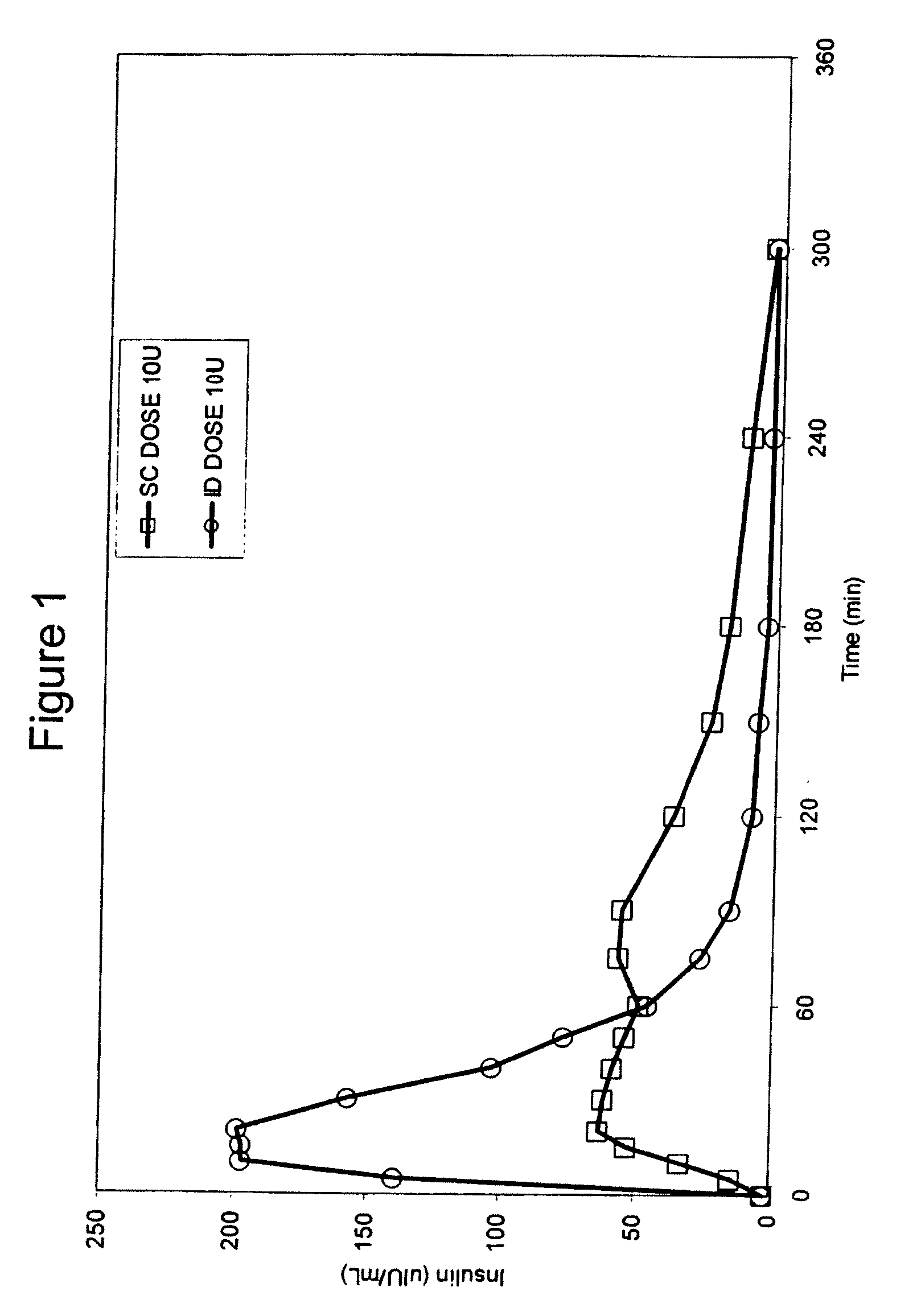
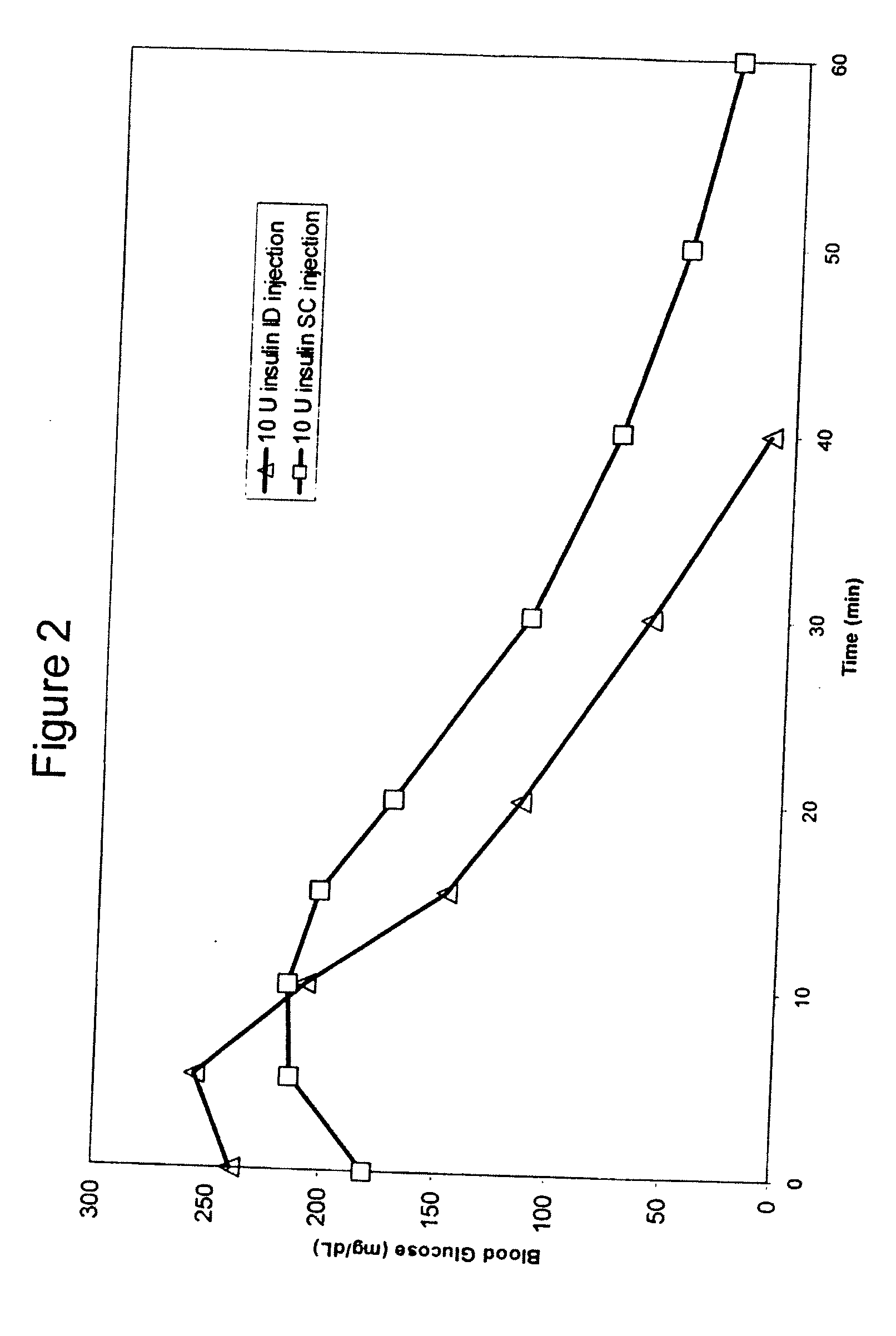
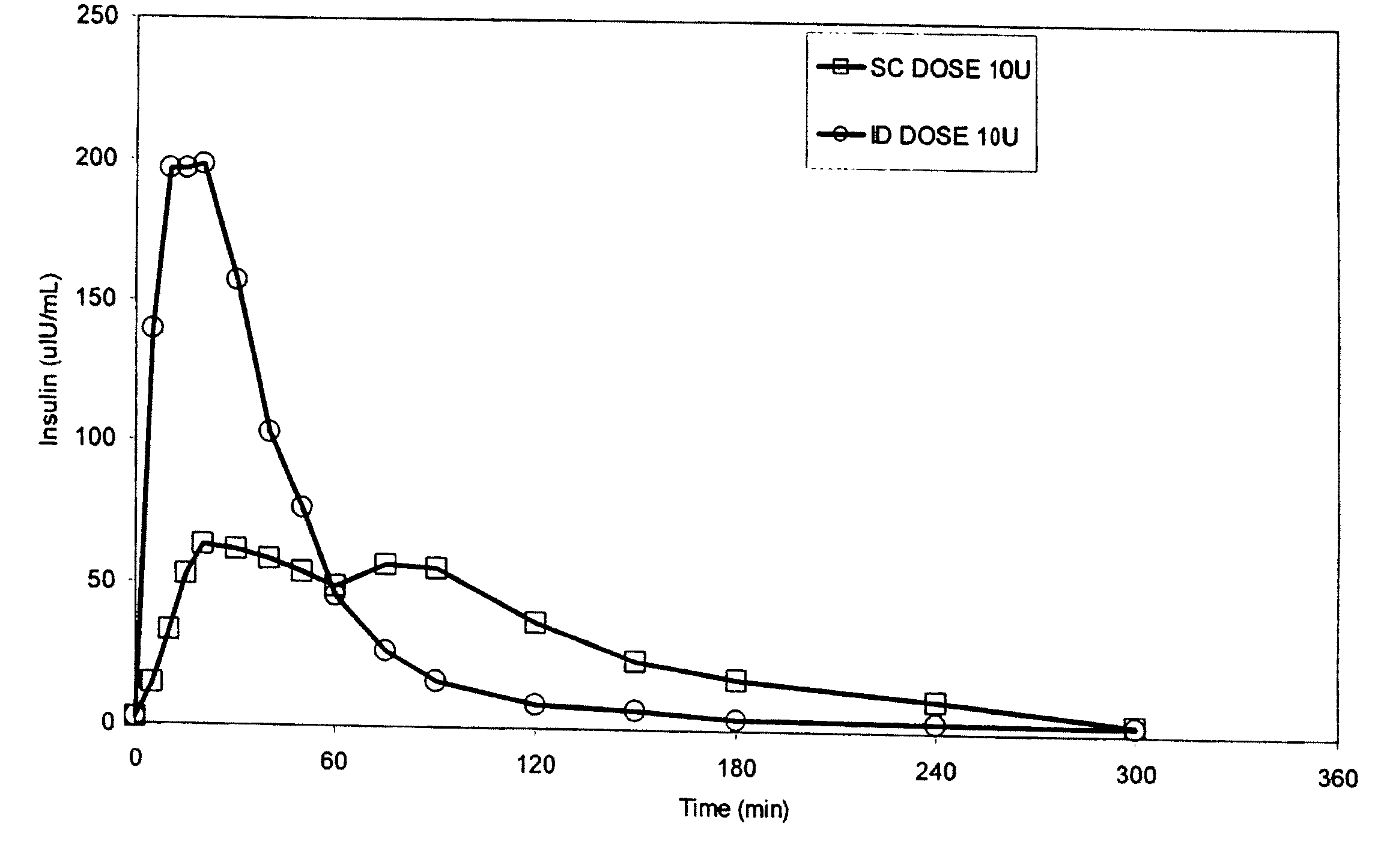
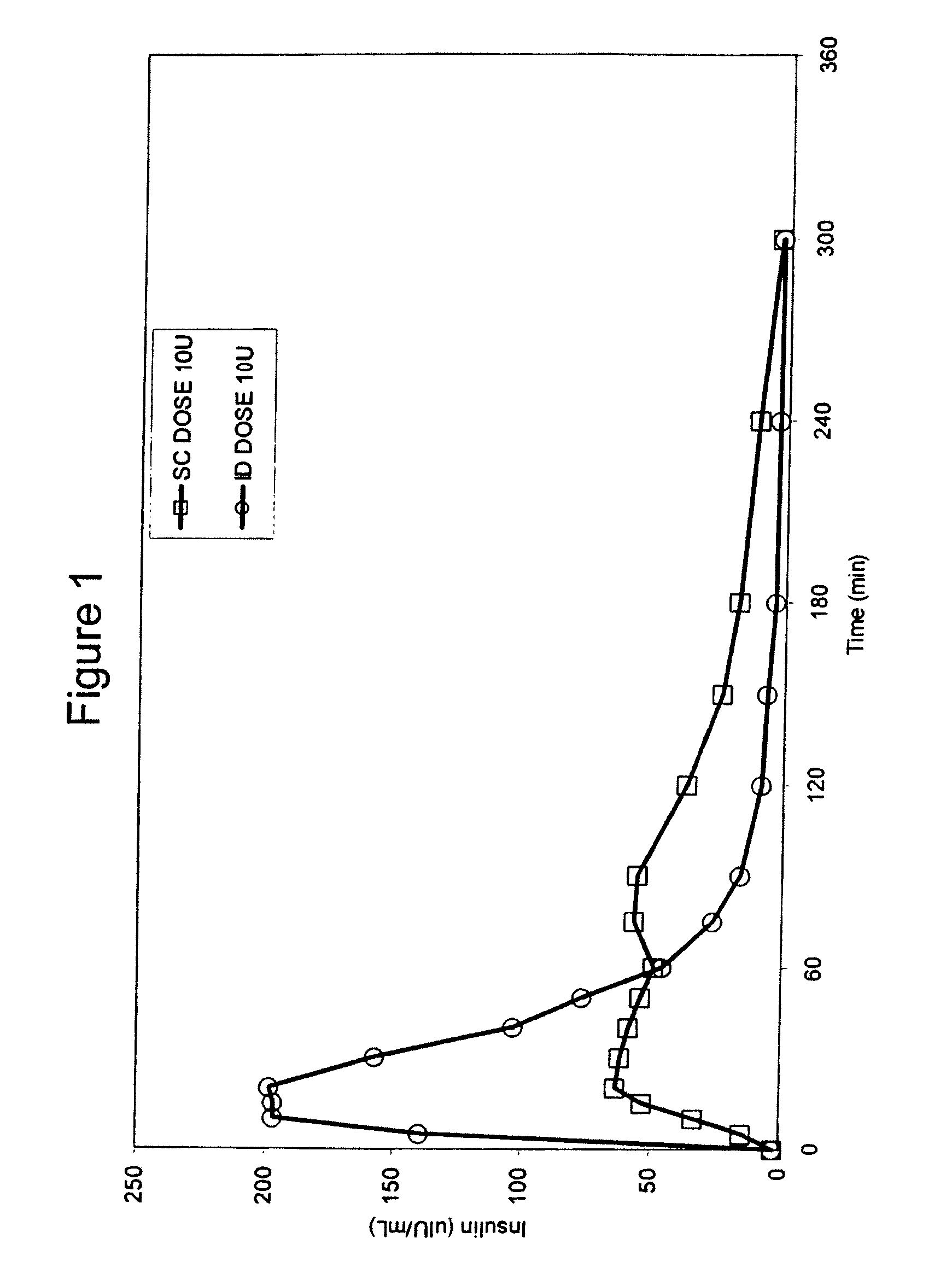
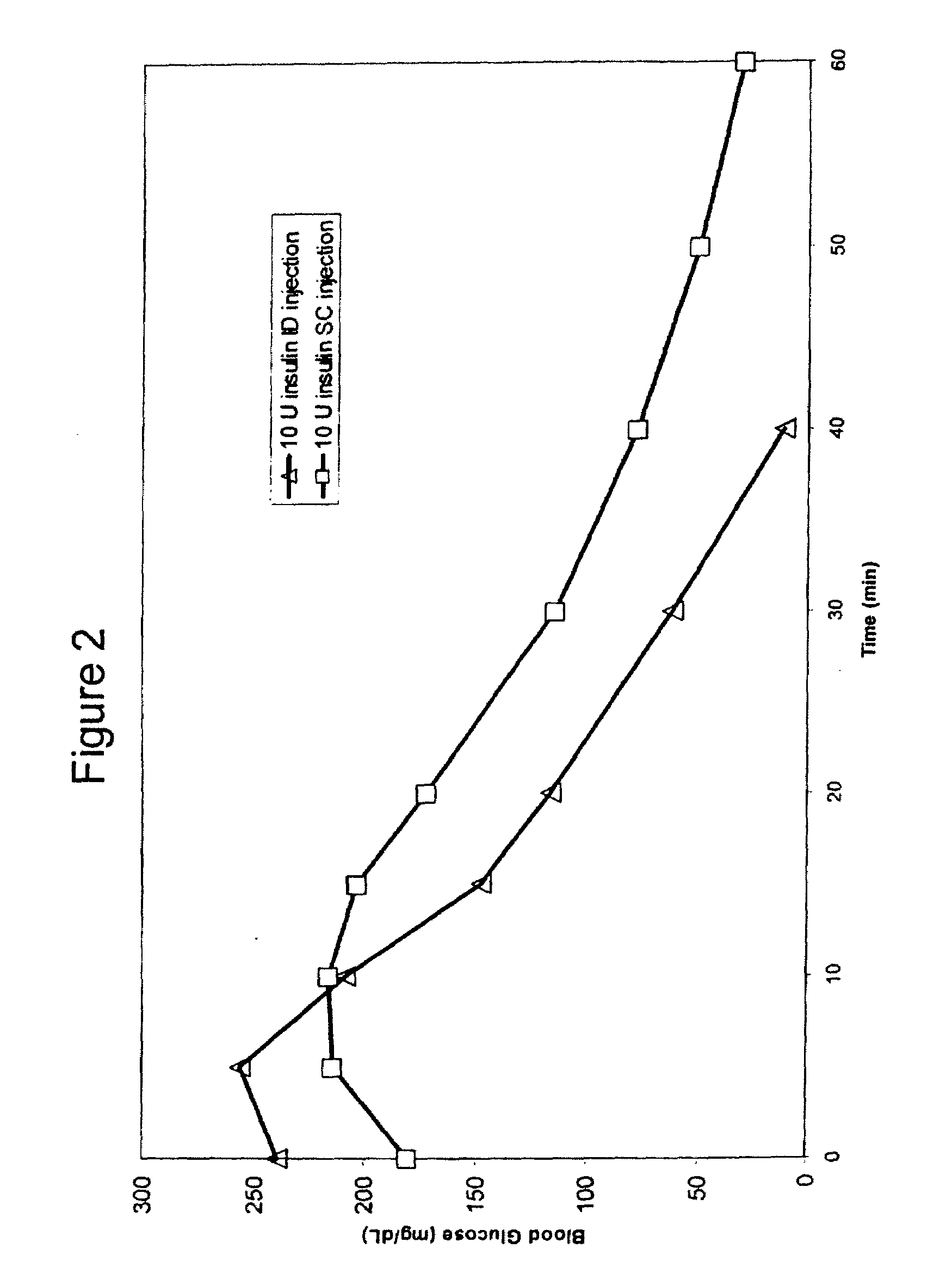
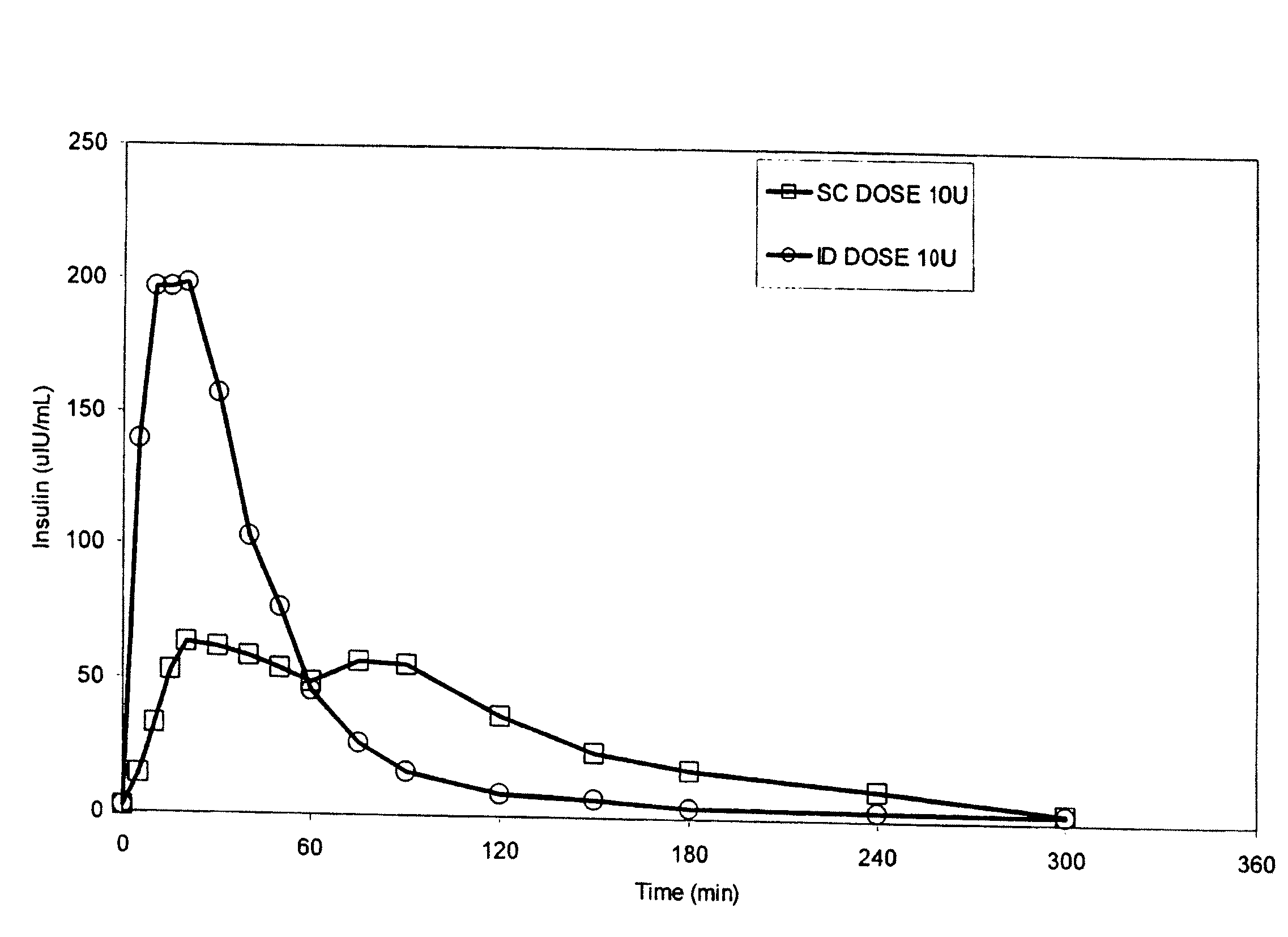
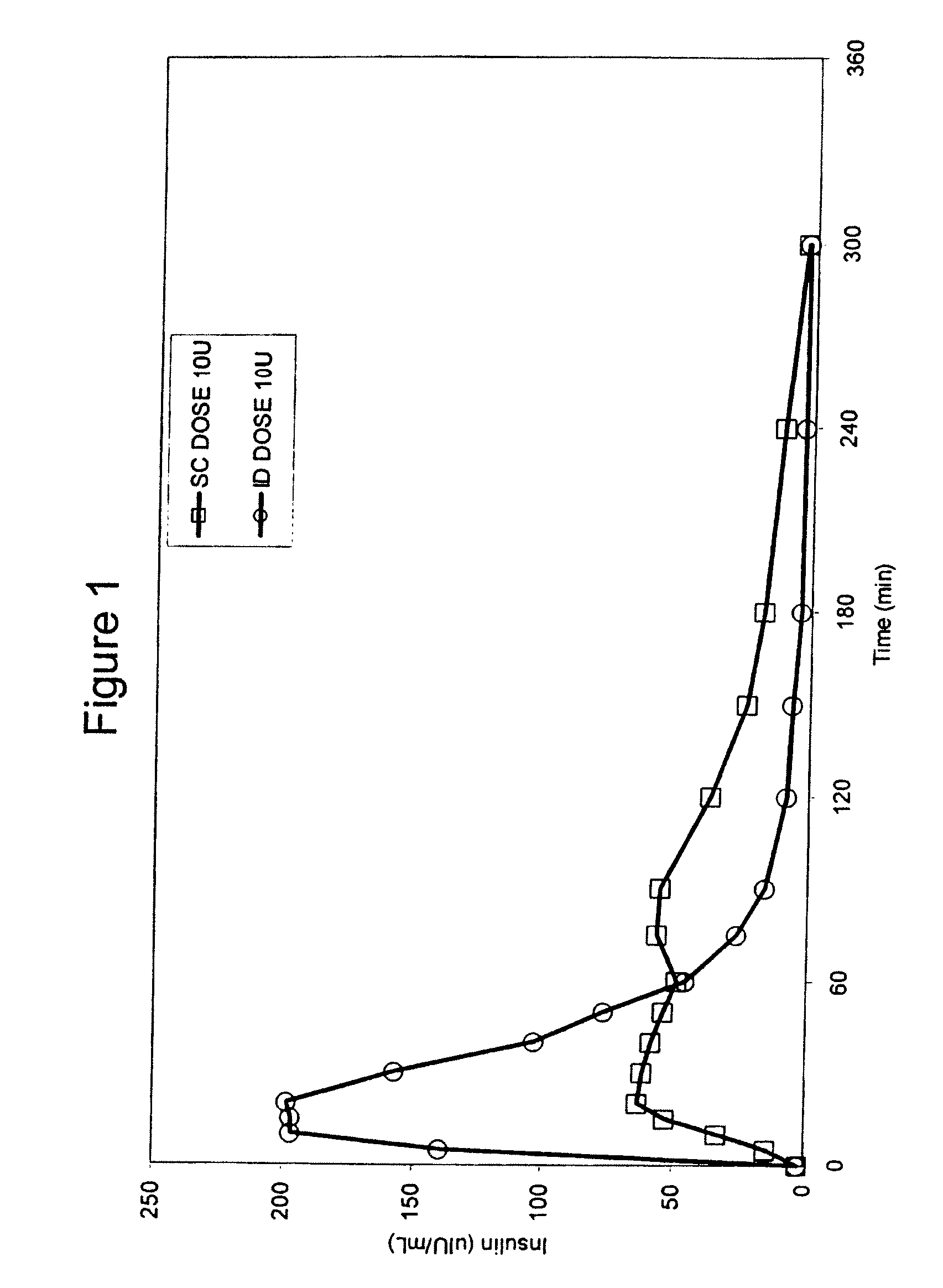
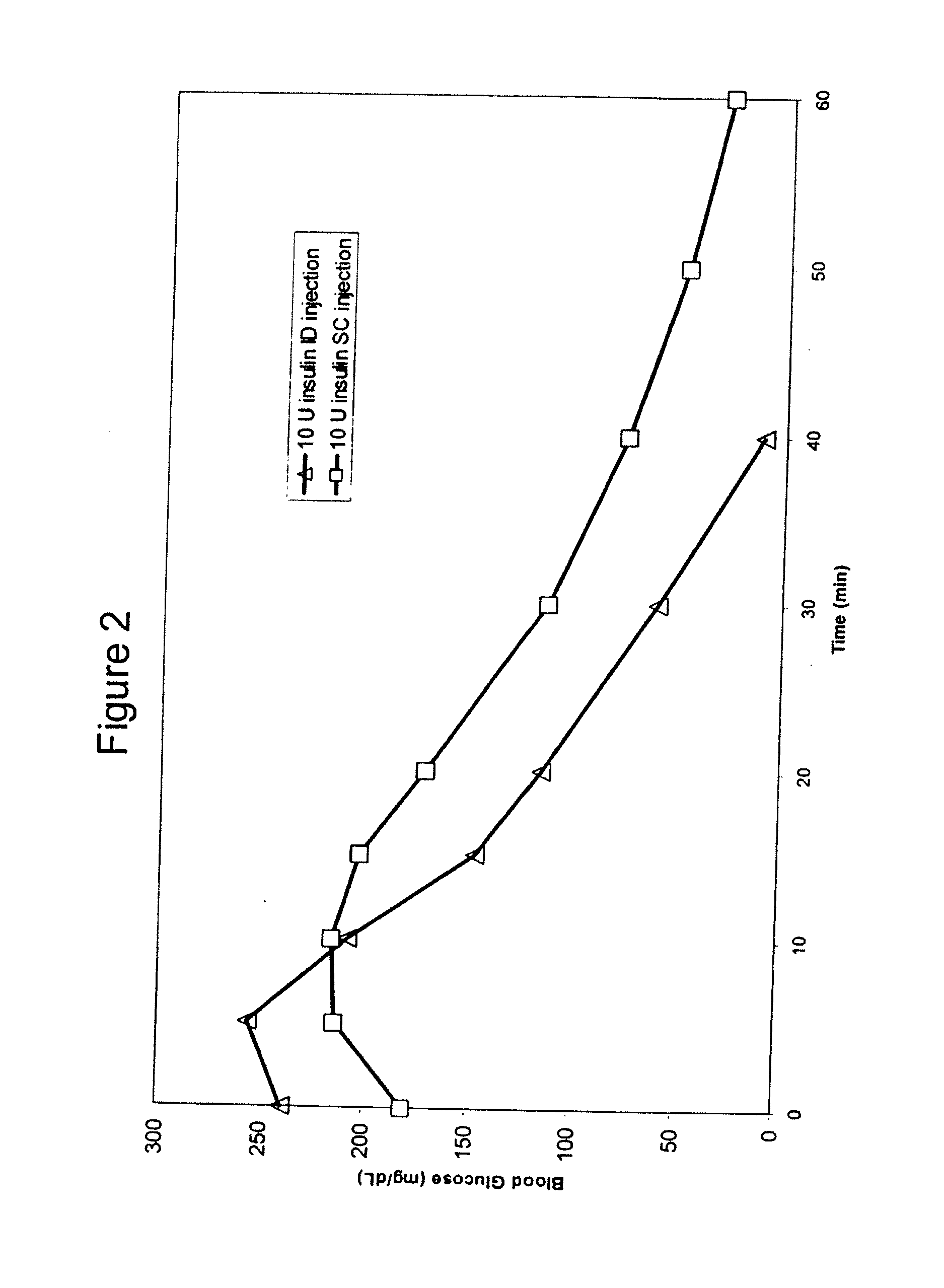
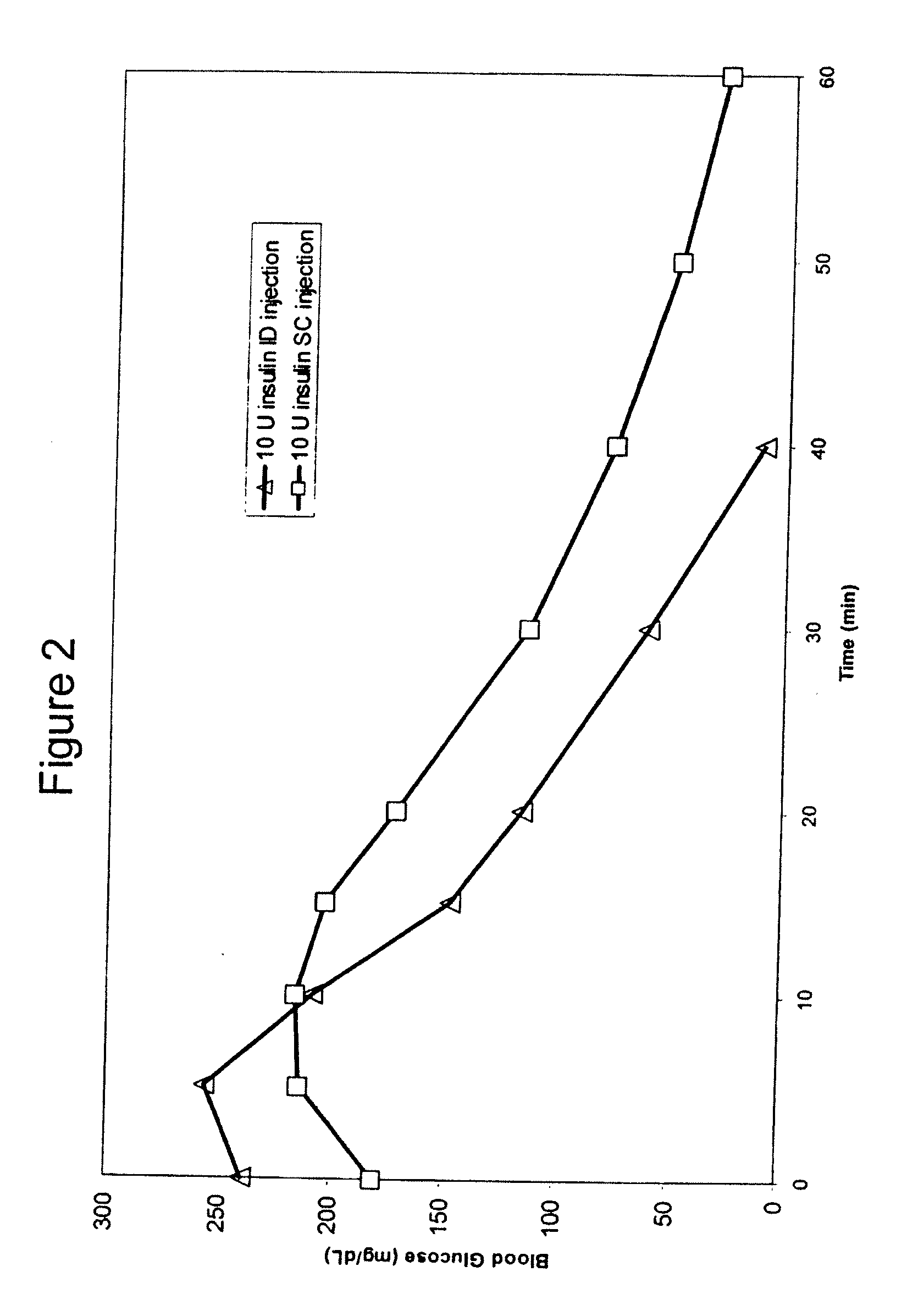
Intradermal delivery of substances
InactiveUS20040073160A1Increase uptakeRapid uptake rateJet injection syringesPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyGrowth hormone
A method for administration of a substance into the dermis of a mammal is disclosed. The method involves administration into the dermis by injection which results in improved systemic absorption relative to that obtained upon subcutaneous administration of the substance. The substance administered may be a growth hormone, a low molecular weight heparin or a dopamine receptor agonist.
Owner:PHARMACIA CORP
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption
InactiveUS20030100885A1Increase uptakeRapid onsetOrganic active ingredientsAmpoule syringesWhole bodySystemic absorption
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
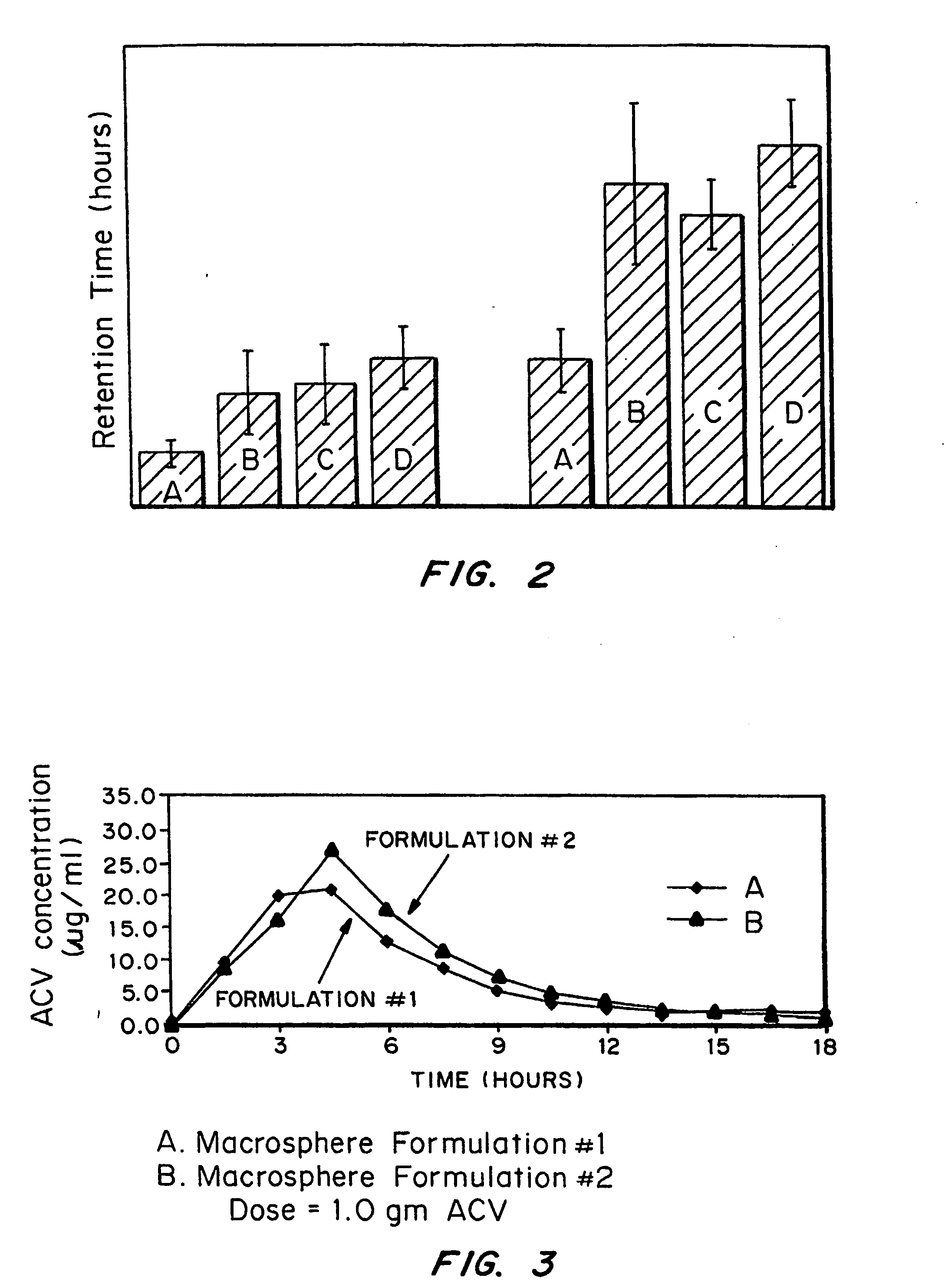
Bioadhesive drug delivery system with enhanced gastric retention
InactiveUS20050064027A1Prolonged gastric retention timeHigh retention rateBiocideCosmetic preparationsWhole bodyRetention time
Bioadhesive macrosphere delivery systems (“BDDS”) having prolonged gastric retention time due to bioadhesion rather than physical density or size are described. In general, the macrospheres have diameters that are greater than 200 microns, more preferably greater than 500 microns. The bioadhesive macrospheres are released in the stomach where they reside in close proximity to the gastric mucosa for a prolonged period of time. Increased residence of BDDS in the upper GI can lead to increased systemic absorption of drug in the preferred site of systemic absorption, namely the upper GI tract (upper to mid-jejunum). The BDDS may be engineered either as a capsule with drug delivery controlled by a diffusion-limited membrane or degradable shell, or as a solid matrix system with drug delivery controlled by a combination of diffusion and polymer degradation kinetics.
Owner:SPHERICS
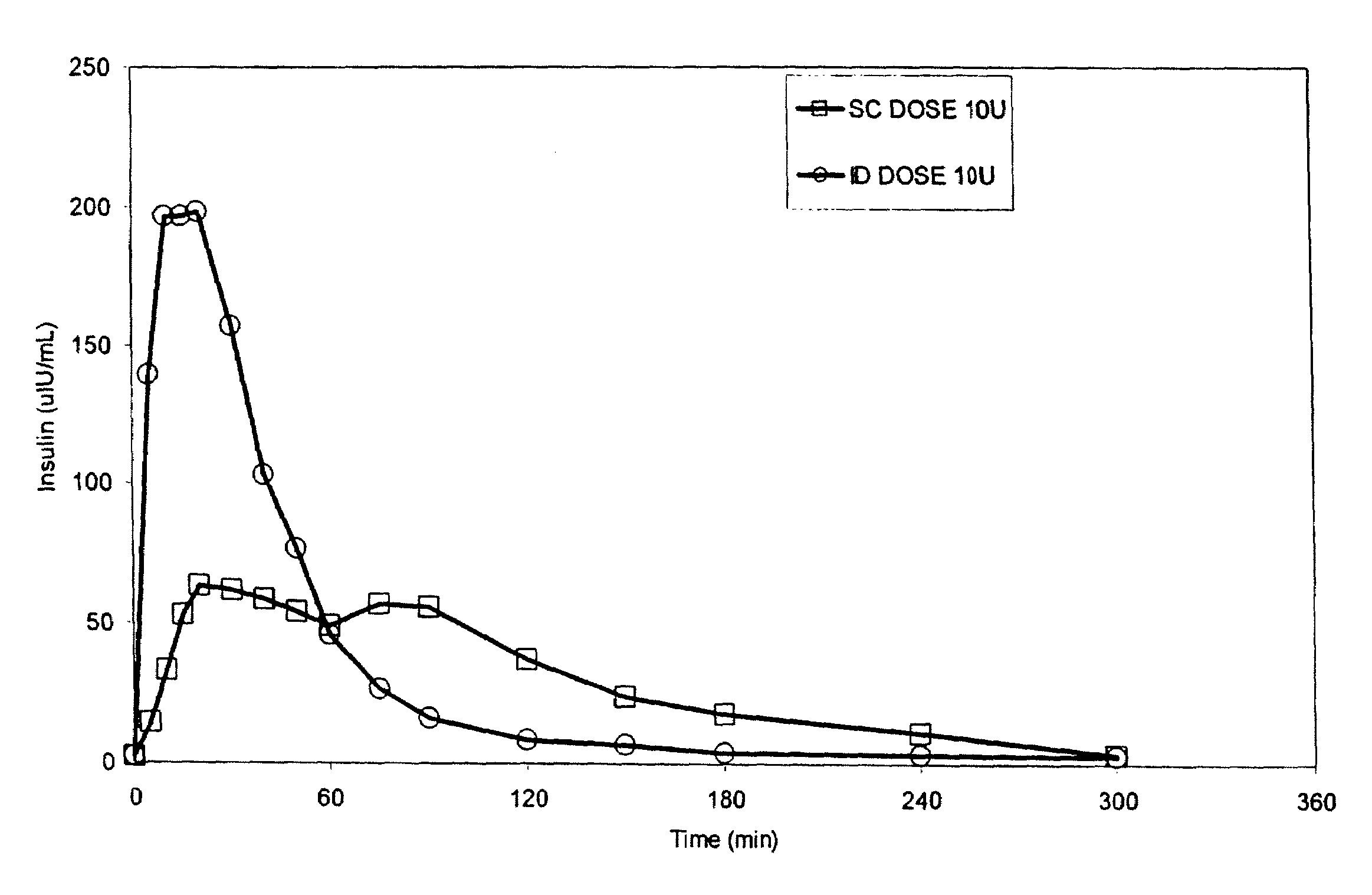
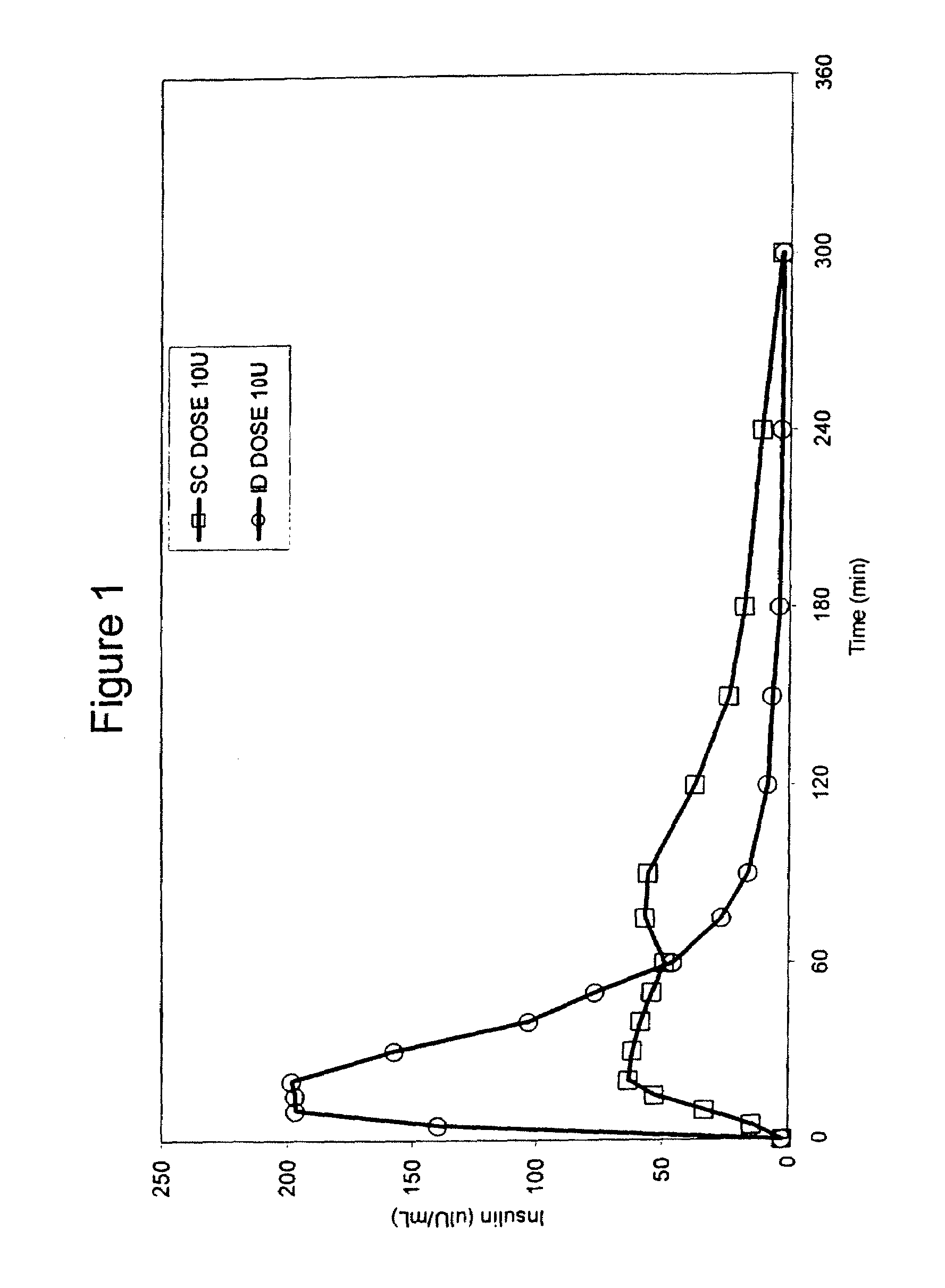
Enhanced pharmacokinetic profile of intradermally delivered substances
InactiveUS20030073609A1Increase uptakeEnhanced iontophoresisPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWhole bodyGrowth hormone
A method for administration of a substance into the dermis of a mammal is disclosed. The method involves administration into the dermis by injection which results in improved systemic absorption relative to that obtained upon subcutaneous administration of the substance. The substance administered may be a growth hormone, a low molecular weight heparin or a dopamine receptor agonist.
Owner:PHARMACIA CORP
Corticosteroid Topical Dispersion with Low Content of Surfactant
ActiveUS20070299044A1Improved pharmacological profileReduce systemic absorptionOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticSide effectAdditive ingredient
The invention provides novel compositions of water-insoluble corticosteroid drug in combination with antimicrobial agents and very low concentrations of polymers and surfactants for topical, otic and ophthalmic treatment. The invention provides stable aqueous suspension where the ingredients remain in such a state so as to allow for immediate re-suspension, when desired, even after extended periods of settling. The invention provides also a method for treating inflammation with low systemic absorption and side-effects of the corticosteroid.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE ANIMAL HEALTH
Chemically modified small molecules
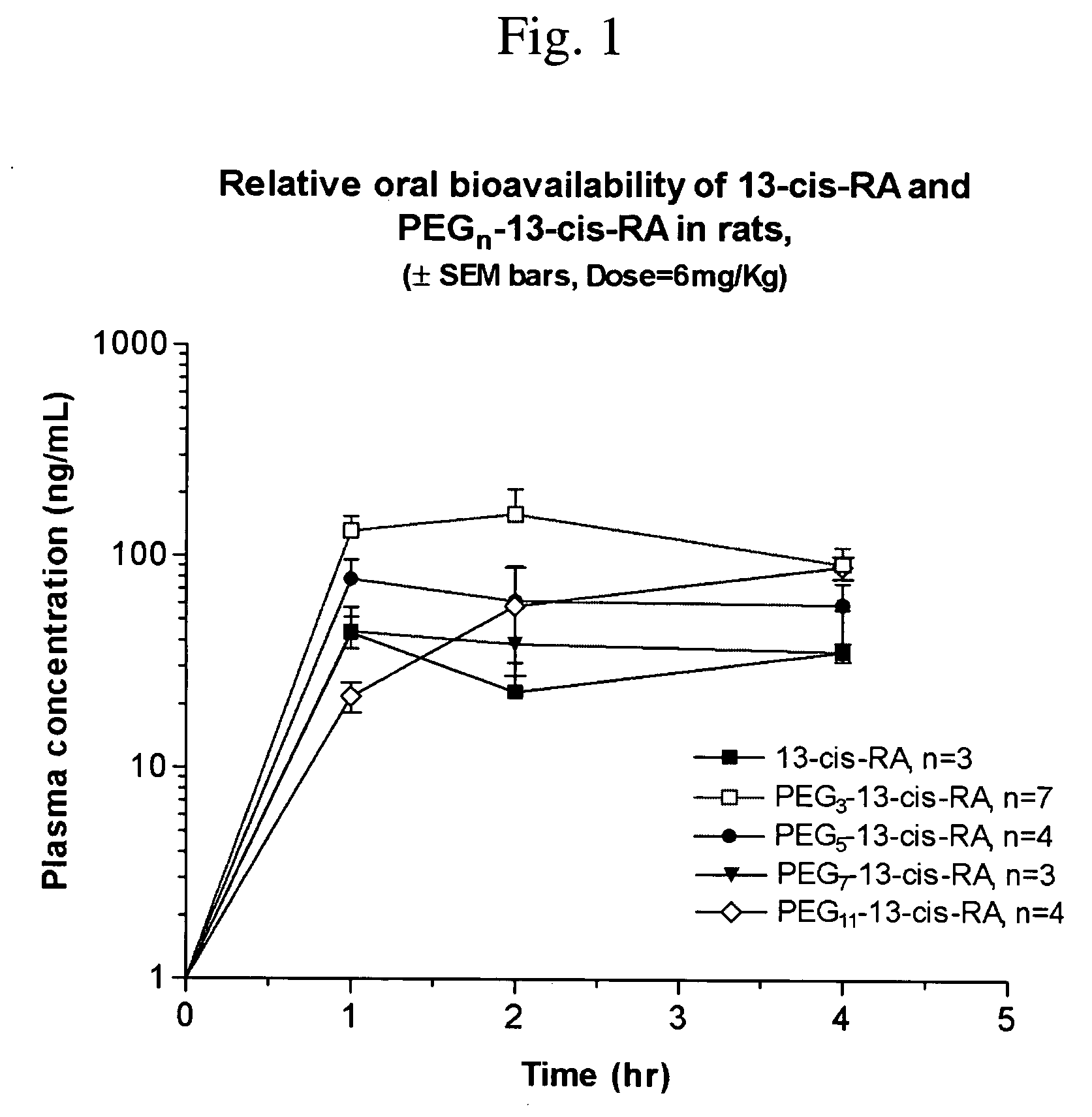
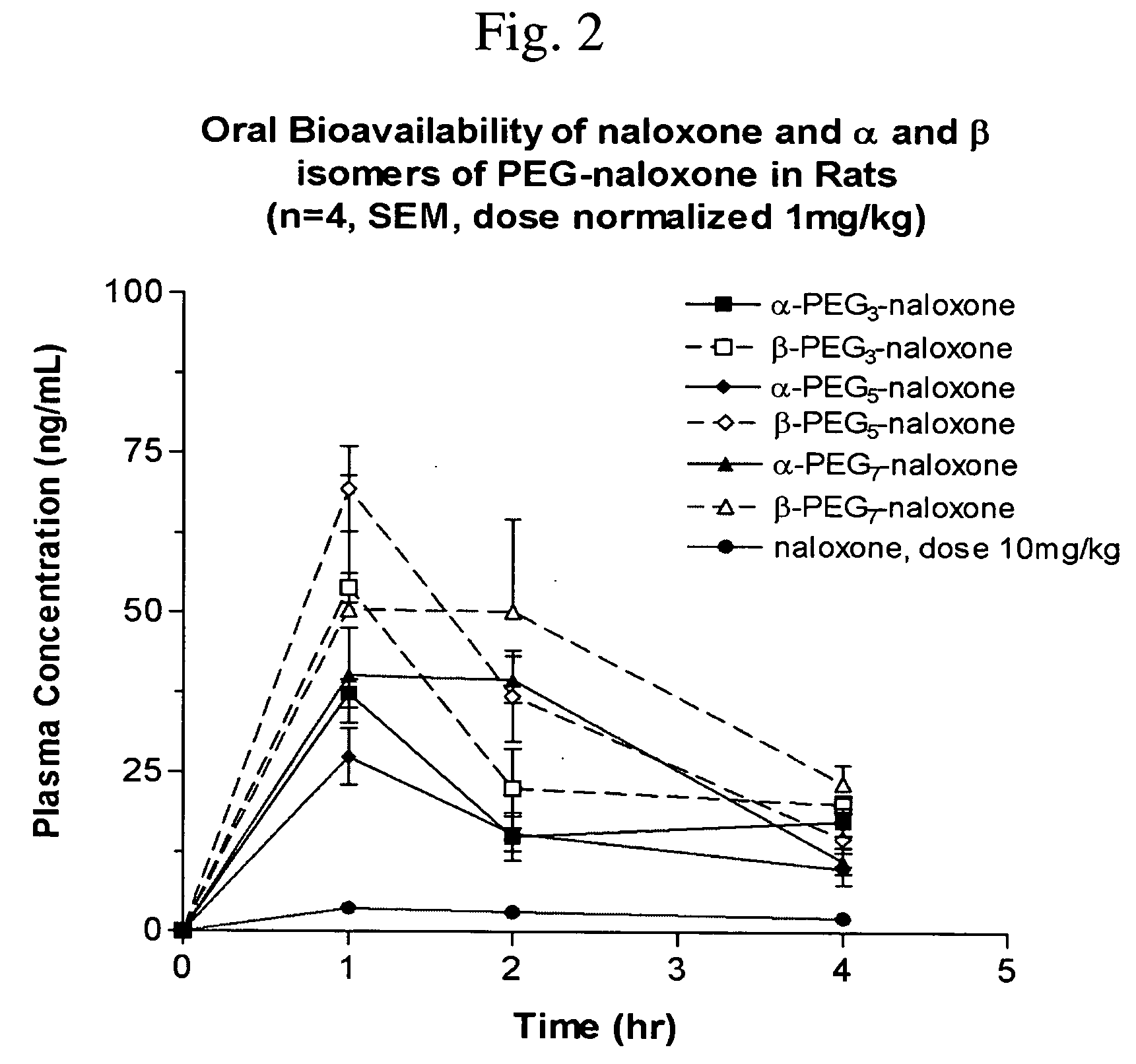
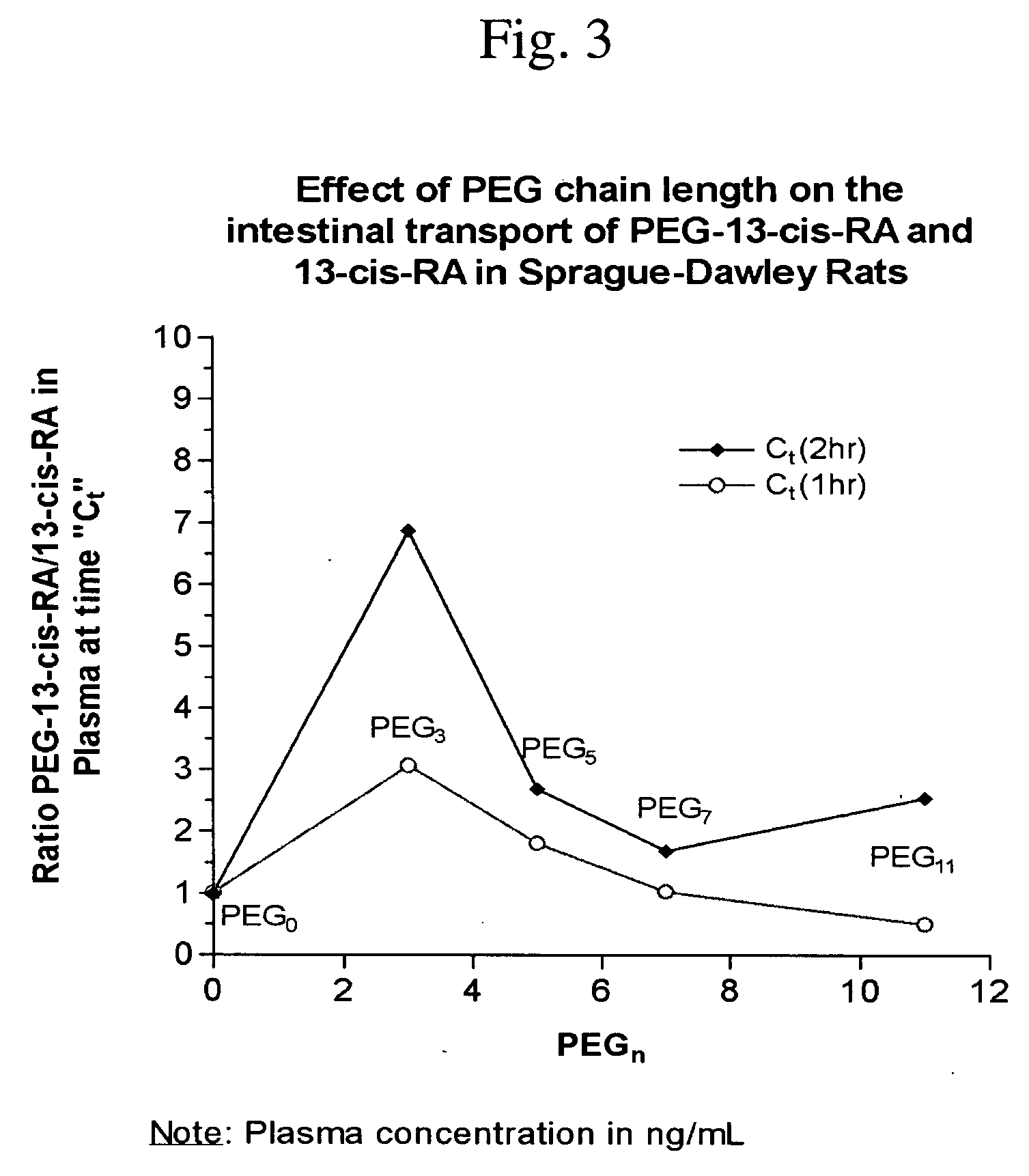
Methods of modifying the rate of systemic absorption of a drug administered to a subject by a pulmonary route, the method comprising covalently conjugating a hydrophilic polymer to a drug, wherein the drug has a half-life of elimination from the lung of less than about 180 minutes, to form a drug-polymer conjugate, wherein the drug-polymer conjugate has a net hydrophilic character and a weight average molecular weight of from about 50 to about 20,000 Daltons, and wherein the half-life of elimination from the lung of the drug-polymer conjugate is at least about 1.5-fold greater than the half-life of elimination from the lung of the drug, wherein the half-life of elimination from the lung is measured by bronchoalveolar lavage followed by assaying residual lung material.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Metered dose delivery device for liquid and powder agents
InactiveUS20060260608A1Reduces and overcomes deficiencyReduce deliveryMedical devicesMedical atomisersInhalationDose delivery
A delivery device for the delivery of an agent to the mouth, nose or other bodily site of a user. The delivery device includes an aerosol canister that is actuated to expel propellant, which captures and disperses the agent. In a preferred embodiment, the propellant captures and disperses the agent into the mouth or nose of a user, and inhalation by the user directs the agent to the lungs of the user. The delivery device is particularly suitable for the treatment of bronchial asthma, respiratory conditions and for the delivery of systemically absorbed agents.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND PHARMA
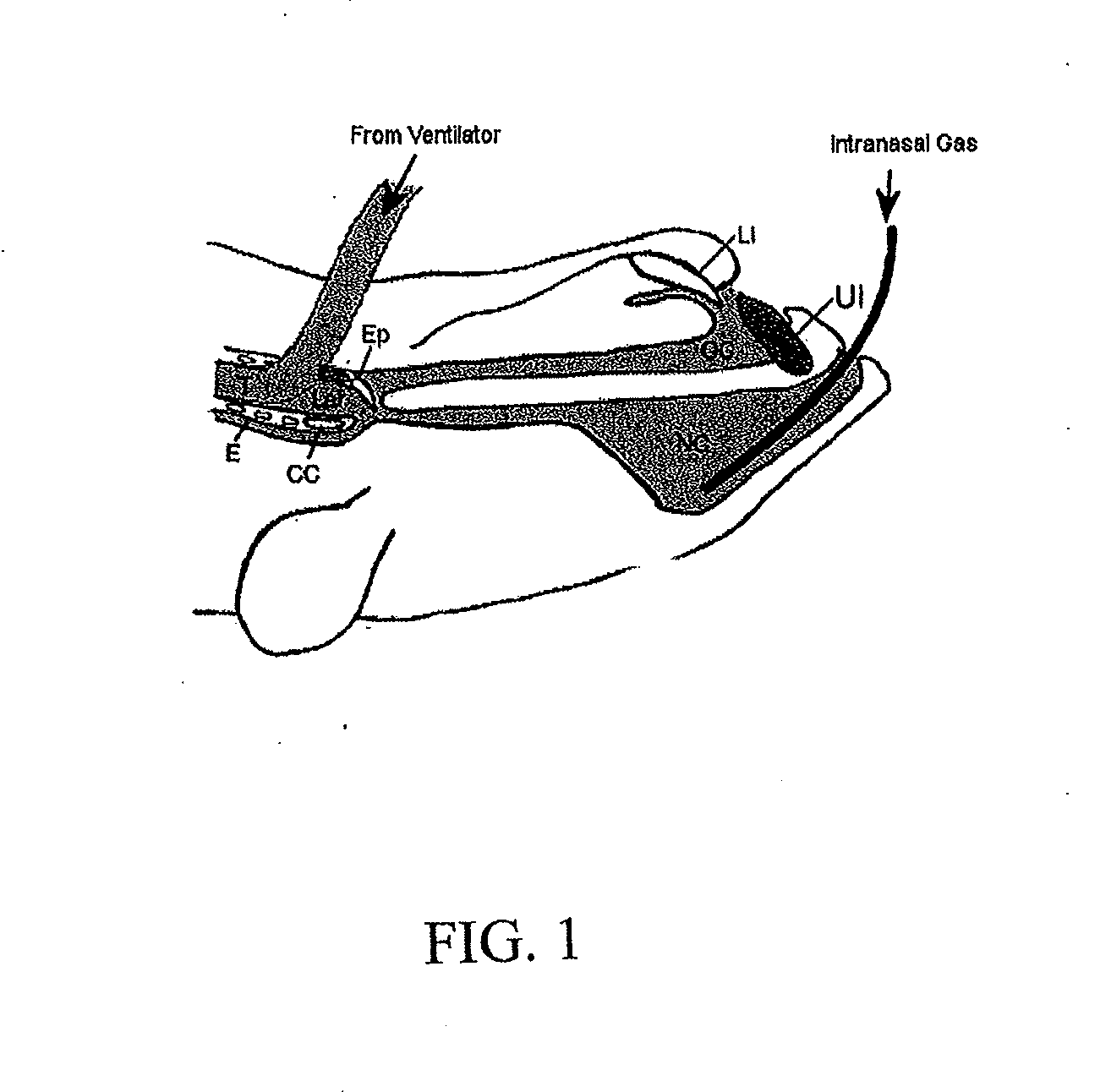
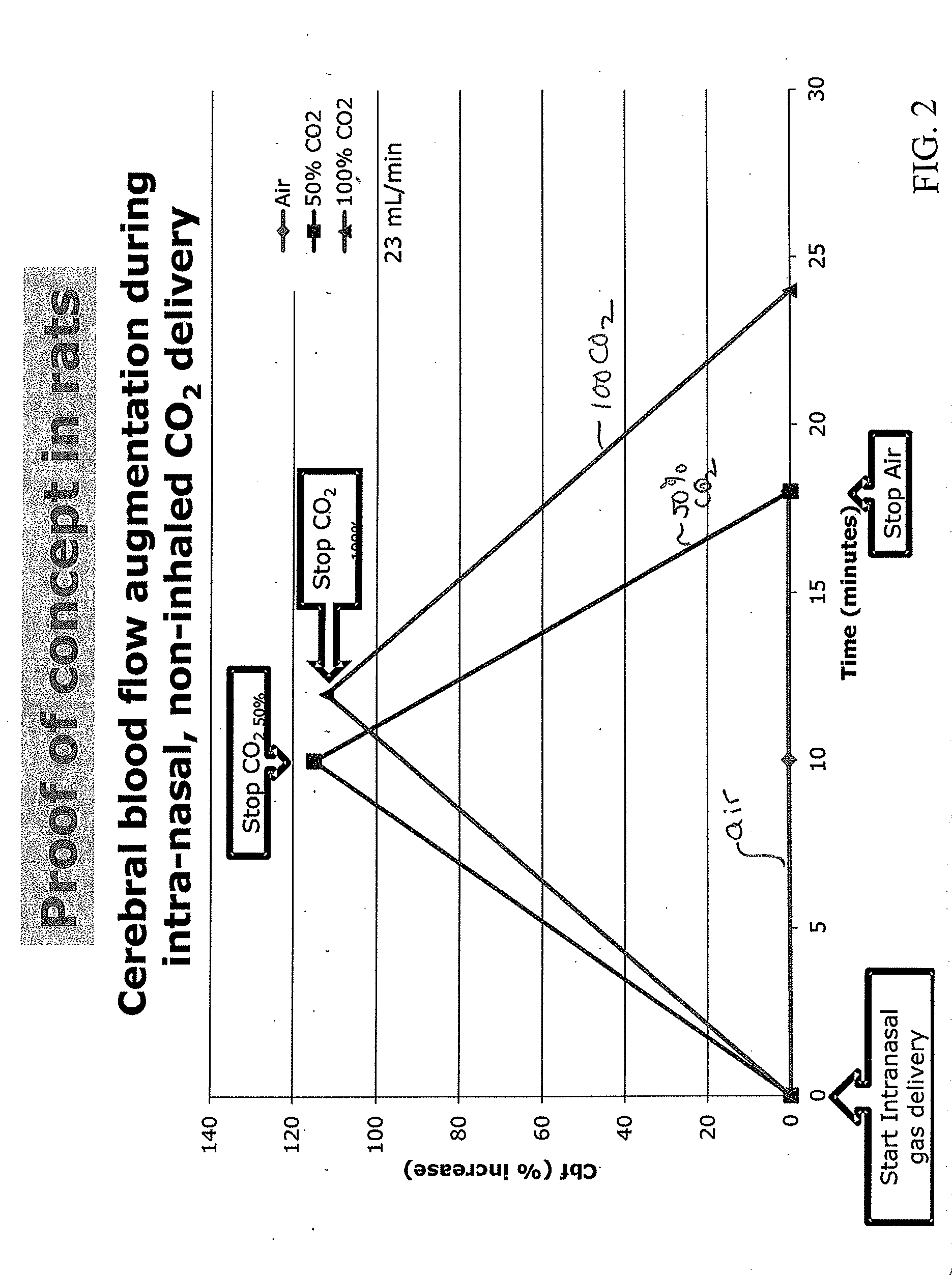
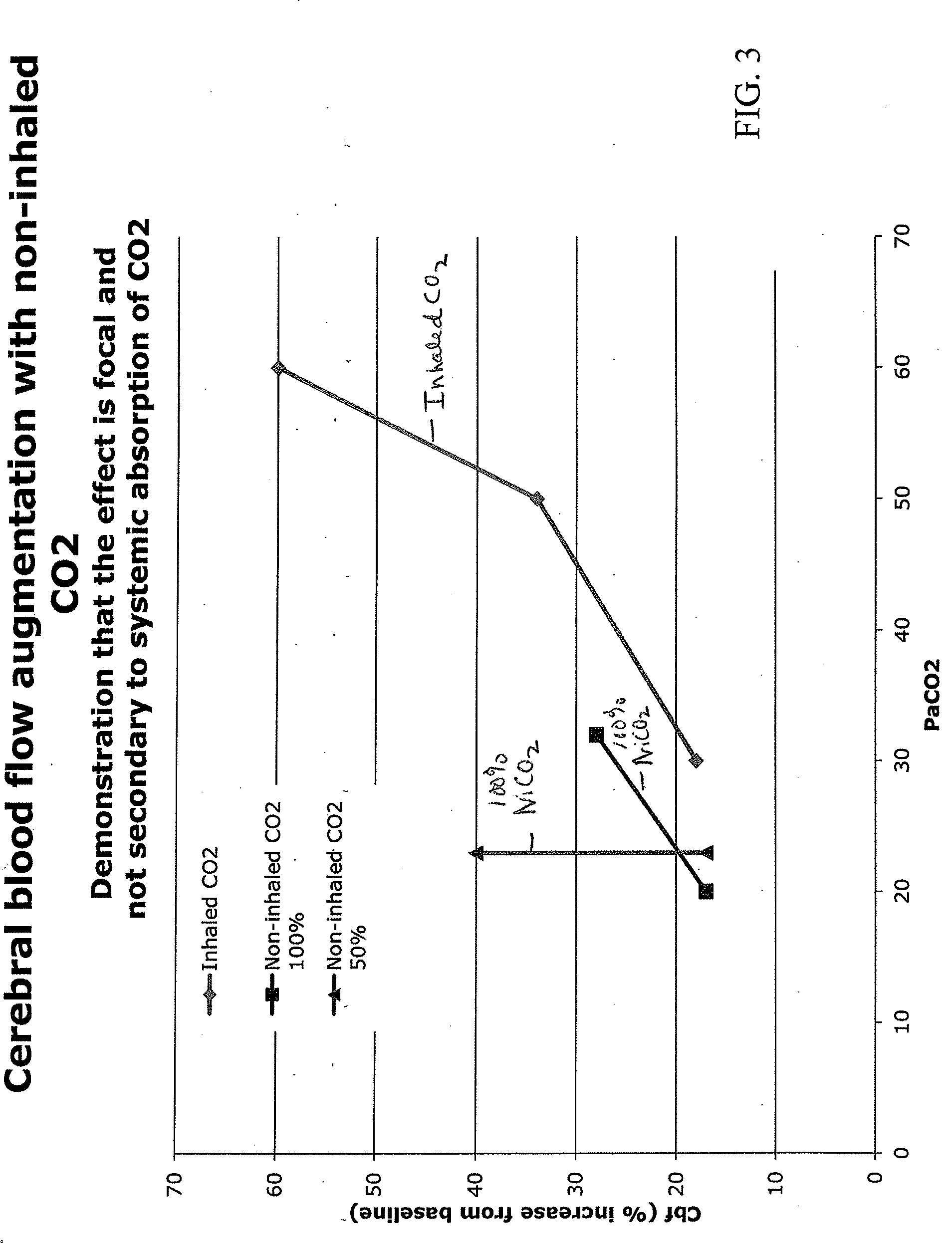
Apparatus and method for treating cerebral ischemia using non-inhaled carbon dioxide
InactiveUS20130302445A1Increase perfusionPromote resultsRespiratorsBiocideTreatment choicesVascular dilatation
A non-invasive method of treating cerebral ischemia, involving the use of non-inhaled, intra-nasally delivered carbon dioxide (CO2), alone or in combination with other gases to augment cerebral perfusion and improve outcome following a stroke is provided. A vasodilator gas is delivered intranasally, alone or in combination with a second gas, for prolonged periods of time without systemic absorption. The second gas may be selected from NO, hydrogen, xenon, anesthetic gases, oxygen, nitrogen, nitrous oxide, carbon monoxide, or air. The treatment selectively increases cerebral perfusion and provides neuroprotection in the treatment of cerebral ischemia.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE +2
Novel application of eye medicine wrapped with erythrocyte membrane
ActiveCN103550223AExtended stayImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseErythrocyte membrane
The invention provides application of an eye medicine wrapped with an erythrocyte membrane in preparation of an eye preparation, and also provides the eye preparation. The preparation is in a form of biodegradable nano particles wrapped with the erythrocyte membrane. The preparation has the advantages that the shortcomings of the traditional eye drops that partial removal is quickly realized, the bioavailability is low, the eye drops are absorbed by the whole body, and the side effect is difficult to avoid, are overcome; the time of the medicine standing in eyes is obviously prolonged; the controlled-released administration of the medicine is realized. Therefore, the bioavailability of the medicine is improved, the side effect on the whole body is reduced, and a new hope is brought to clinical ophthalmology on treatment of intraocular diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGRUI BIOLOGICAL PHARMA TECH CO LTD
Insulin Derivatives Conjugated with Structurally Well Defined Branched Polymers
Insulin conjugated with structurally well defined, bifurcated and trifurcated polymers can be use by pulmonary delivery for systemic absorption through the lungs to reduce or eliminate the need for administering other insulins by injection.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Vaginal inserted estradiol pharmaceutical compositions and methods
InactiveUS20190022107A1Reduce in quantityIncrease the number ofOrganic active ingredientsSuppositories deliveryDiseaseWhole body
The invention described herein relates to pharmaceutical compositions that are capable of delivering active pharmaceutical ingredients, such as estrogens, to the vagina and vagina-associated tissues and related methods of making and using such compositions (e.g., in the treatment of disease). Compositions of the invention are capable of being absorbed by the vagina or vagina-associated tissues such that subjects receiving treatment with the compositions may resume ambulatory activity immediately after receiving the treatment, the frequency or amount of discharge associated with the composition is low or negligible, there is little or no systemic absorption associated with the administration of the active pharmaceutical composition, or results in a combination of any or all thereof.
Owner:THERAPEUTICSMD
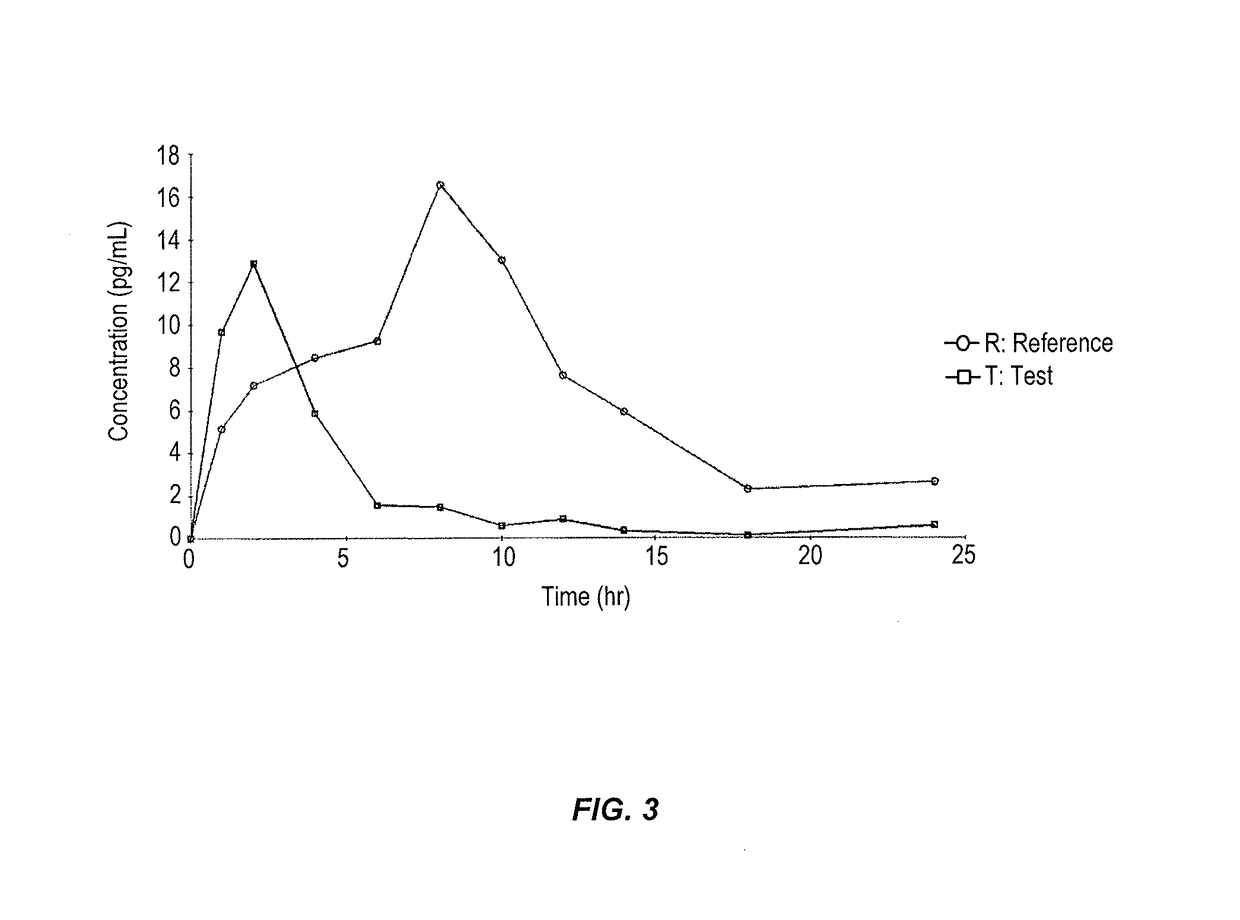
Compositions methods and systems for pulmonary delivery of recombinant human interferon alpha-2b
Stable aqueous formulations which are free of products derived from human or animal origin and which maintain high biological activity and high chemical and physical stability of alpha-type interferon, and proteins in general, for an extended period of time. Methods of producing stable aerosol formulations of the same for delivery to the lungs are also provided, as well as systems and methods of delivering the formulations to the lungs for systemic absorption.
Owner:ARADIGM
Fat composition
InactiveUS20070122452A1Promote absorptionSufficient exhibition of pharmacological effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFatty acids.polyunsaturatedPhospholipid
Provided is a composition permitting high systemic absorption of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and high transfer of them to tissues and capable of fully exhibiting pharmacological effects which the fatty acids have. A fat composition containing one or more phospholipids having, as a constituent fatty acid, an n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid selected from docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid; and α-linolenic acid and / or a fat containing α-linolenic acid.
Owner:WAKUNAGA PHARMA CO LTD
Vitamin-mineral compositions
InactiveUS20060127499A1Avoid interactionImprove stabilityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsWhole bodyMedicine
This invention provides compositions of vitamins and minerals used in the prevention and treatment of vitamin and mineral deficiency. These compositions provide a minimization of the intake dosage of vitamins and minerals while still meeting the nutritional daily requirements for these vitamins and minerals. At the same time, these compositions are easier to manufacture, have an improved prolonged shelf-life, and are easy and convenient to use. These compositions comprise 3 to 5 dose formulations that are ingested separately. Each dose formulation contains vitamins and minerals that are compatible with each other regarding systemic absorption and storage shelf-life.
Owner:LAZAREV MIKHAIL I +1
Phenylephrine pharmaceutical formulations and compositions for transmucosal absorption
InactiveUS20090280160A1Sustained deliveryBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWhole bodySystemic absorption
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising phenylephrine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and methods for administering the pharmaceutical compositions wherein the composition is formulated for systemic absorption of phenylephrine that avoids first pass metabolism. The compositions of the invention are formulated to be applied to oral mucosa of an animal to allow for enhanced systemic delivery of therapeutically active form of phenylephrine.
Owner:MSD CONSUMER CARE INC
Low dose corticosteroid powders for inhalation
InactiveUS20060134009A1Treat conditionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSteroid responsiveThroat
The invention relates to a method of treating a corticosteroid-responsive condition of the air passage ways and lungs by delivering a corticosteroid to the pulmonary system of a patient, comprising administering a particle mass comprising a corticosteroid from an inhaler characterized in that the corticosteroid is not substantially deposited in the mouth and throat and is not substantially systemically absorbed. The invention also relates to receptacles containing the particle mass and the inhaler for use therein.
Owner:ADVANCED INHALATION RES
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption
InactiveUS20080118465A1Increase uptakeShorter TmaxAmpoule syringesJet injection syringesWhole bodySystemic absorption
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption.
Owner:PETTIS RONALD J +2
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption
InactiveUS20080119392A1Increase uptakeShorter TmaxAmpoule syringesElectrotherapyWhole bodySystemic absorption
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption.
Owner:PETTIS RONALD J +2
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption
InactiveUS20080140050A1Increase uptakeFaster rateAmpoule syringesPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodySystemic absorption
Owner:PETTIS RONALD J +2
Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease with 6-mercaptopurine
InactiveUS20090263482A1Reduce morbidityImprovement of immunological statusBiocideDigestive systemSide effectWhole body
Methods of administering a delayed release 6-mercaptopurine pharmaceutical composition to patients suffering from inflammatory bowel disease which provide for release of the 6-mercaptopurine after passage of the pharmaceutical composition through the stomach are disclosed. The methods result in significant clinical improvement despite leading to very little systemic absorption of 6-mercaptopurine and also result in very few undesirable side effects.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption
InactiveUS20080138286A1Increase uptakeFaster rateAmpoule syringesPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodySystemic absorption
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption.
Owner:PETTIS RONALD J +2
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption
InactiveUS20080118507A1Increase uptakeShorter TmaxAmpoule syringesPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodySystemic absorption
Methods and devices for administration of substances into the intradermal layer of skin for systemic absorption.
Owner:PETTIS RONALD J +2
Alficetin in situ forming eye gel
InactiveCN101352408AExtended stayAvoid discomfortOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderWater useSide effect
The invention discloses a chloramphenicol eye ophthalmic gel and a preparation method thereof; every 1000ml of the chloramphenicol eye ophthalmic gel contains 5-50g of chloramphenicol, 0.05-1g of preservative, 1.0-7.5g of osmoregulation agent, 30-150g of gel stroma, and rest amount of acid-base buffering agent and water used for injection. Due to the optimization and technique improvement of the auxiliary materials, the medicine dosage forms of the chloramphenicol are enriched, detention time of the medicine in the eyes are greatly prolonged, and the medicine can exert the drug effect, thus not only improving healing efficacy, but also reducing the times and days for taking medicine, decreasing the part side effect of the medicine and the untoward effect caused by the whole body absorption, as well as having no pessimal stimulation response.
Owner:肖正连
Azithromycin ultrafine powder in-situ gel eye drops and preparation method thereof
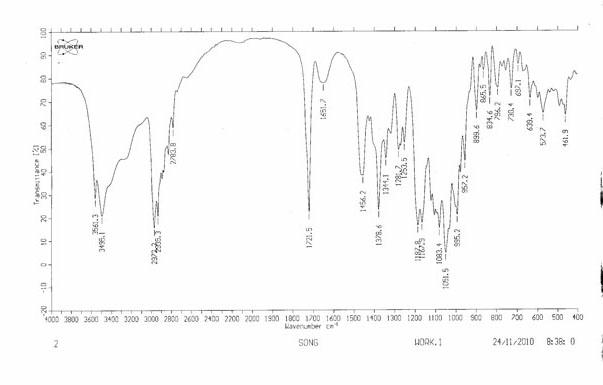
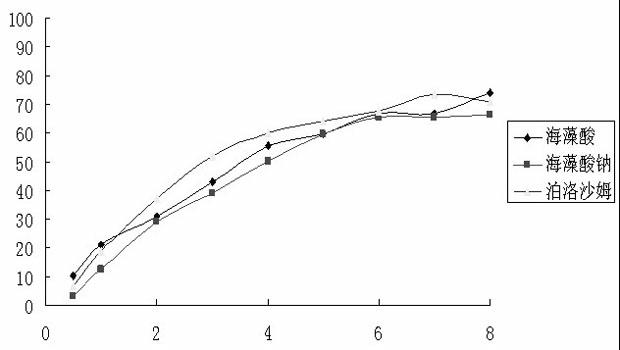
InactiveCN102106812AHelps maintain effective concentrationImprove topical bioavailabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacterial keratitisEye drop
The invention provides azithromycin ultrafine powder in-situ gel eye drops and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, micronizing a medicament by using a proper method to remarkably improve the dissolution rate and solubility of the medicament; and secondly, preparing an ophthalmic preparation which is in a liquid state in vitro and is in a gel state when dripped into eyes by adopting sodium alginate as an ion-sensitive gel matrix or adopting poloxamer 407 and poloxamer 188 as thermosensitive gel matrixes. The eye drops are steady in storage at 4 DEG C and uniform in content, and are not required for secondary preparation so as to reduce contamination. In the method, azithromycin ultrafine powder and in-situ gel are combined for the treatment of bacterial keratitis and trachoma; and by the dual effects of the ultrafine powder and the gel, the sustained release effect is achieved when the retention time of the preparation in the eyes is prolonged, so that the local bioavailability of the medicament and the compliance of patients are improved, and the medicament absorption of the cornea is increased to reduce the toxic or side effect caused by the systemic absorption of ophthalmic medicaments.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease with 6-mercaptopurine
InactiveUS20130280328A1Reduce morbidityImprovement of immunological statusBiocideDigestive systemSide effectInflammatory Bowel Diseases
Methods of administering a delayed release 6-mercaptopurine pharmaceutical composition to patients suffering from inflammatory bowel disease which provide for release of the 6-mercaptopurine after passage of the pharmaceutical composition through the stomach are disclosed. The methods result in significant clinical improvement despite leading to very little systemic absorption of 6-mercaptopurine and also result in very few undesirable side effects.
Owner:ROSENBERGER VERED +3
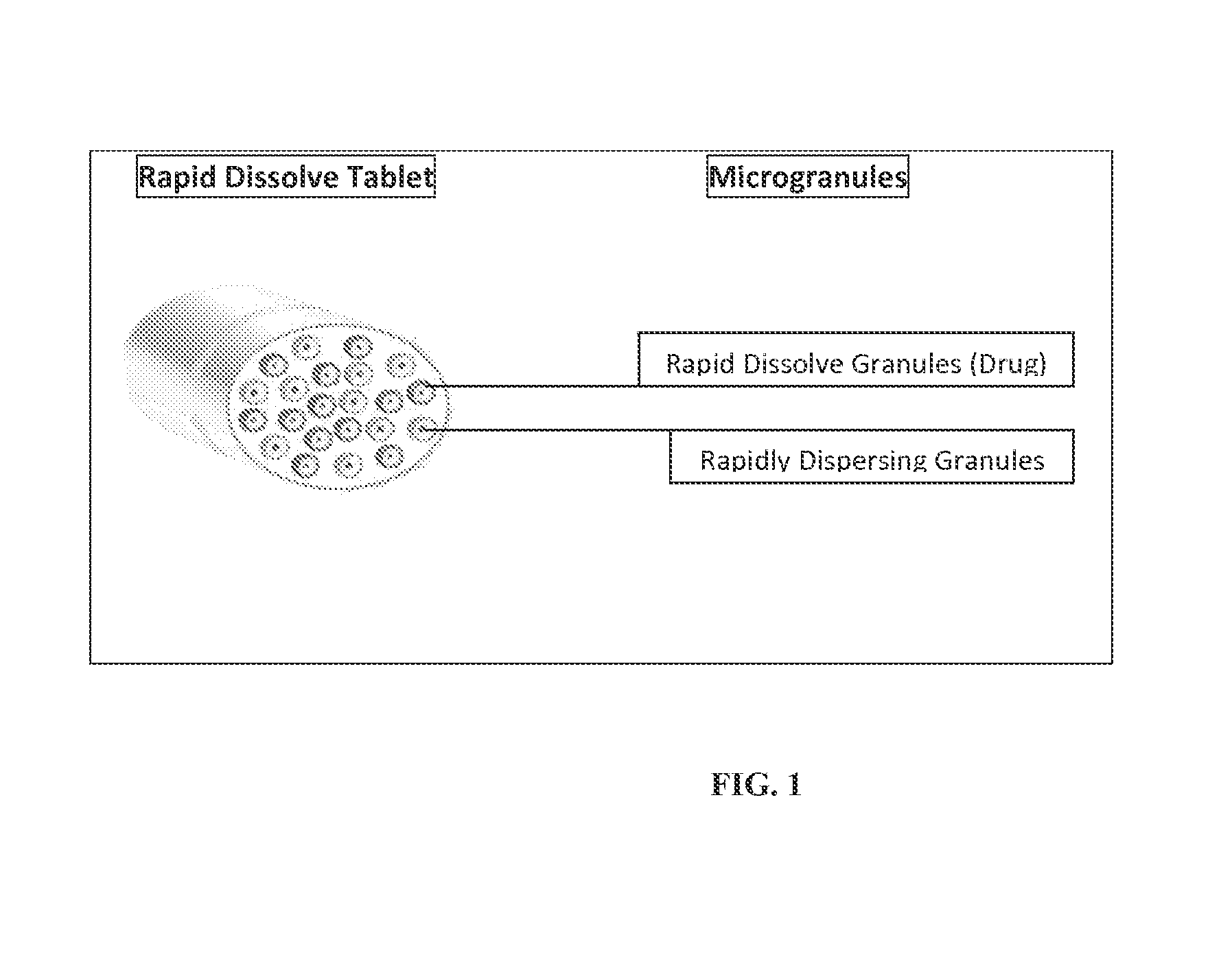
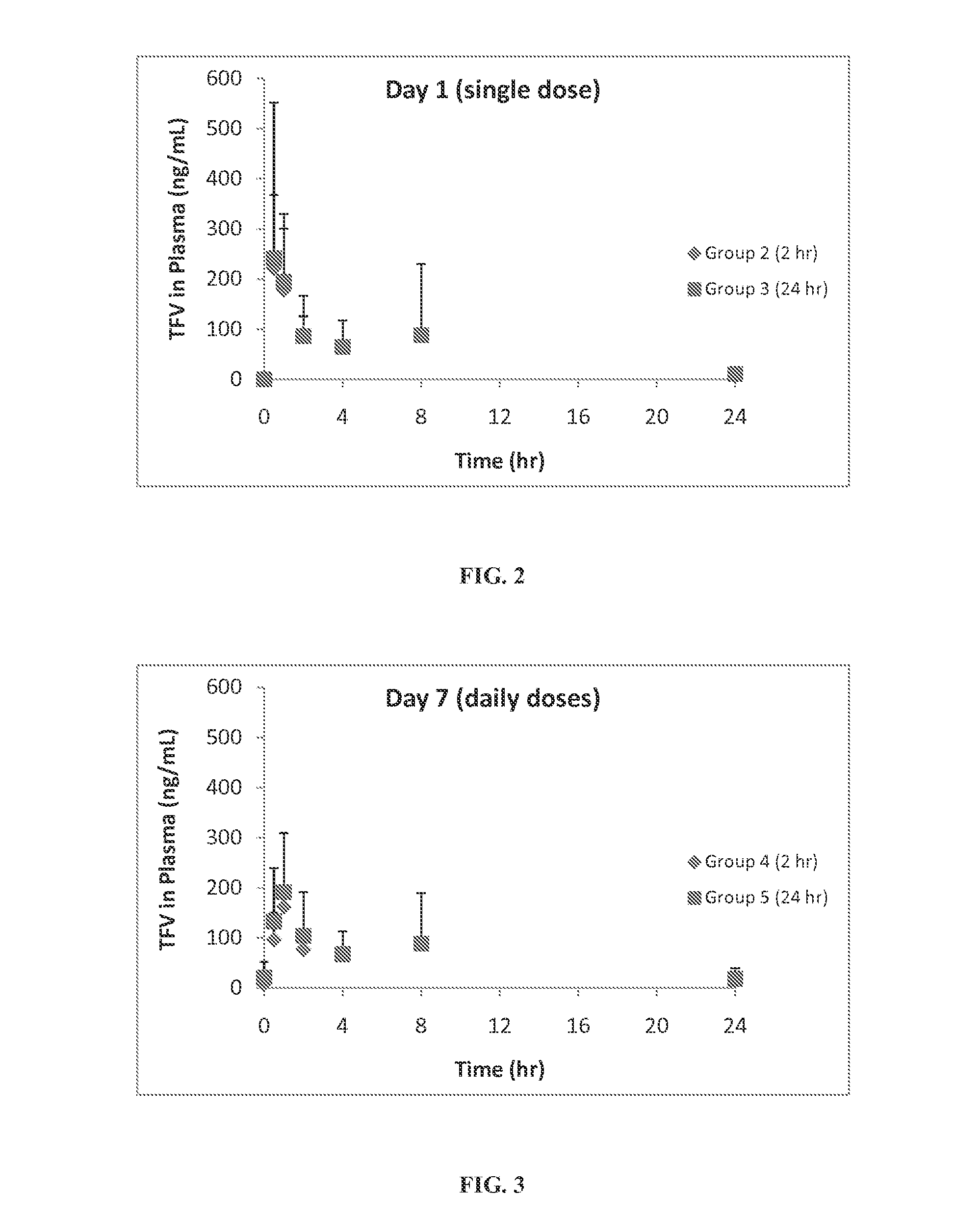
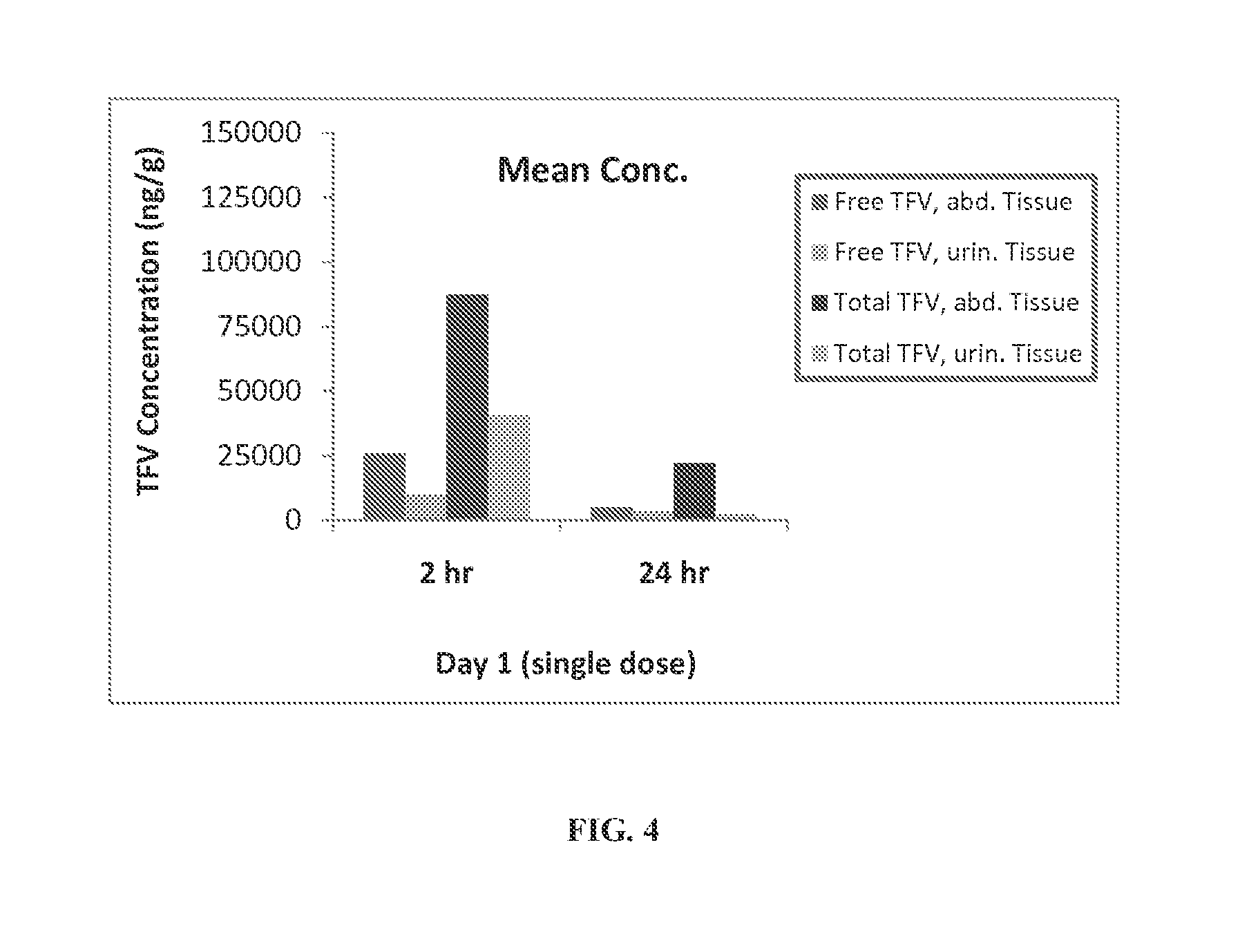
Rapid dissolve tablet compositions for vaginal administration
InactiveUS20140134246A1Enhance bioadherence of the active ingredientEnhance/sustain systemic absorptionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSystemic absorptionPharmaceutical medicine
Disclosed herein are pharmaceutically acceptable rapid dissolve vaginal tablet compositions comprising one or more active pharmaceutical ingredients suitable for therapy via topical action or systemic absorption, and methods of making and using such compositions.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
Phenylephrine pharmaceutical formulations and compositions for transmucosal absorption
InactiveCN101938991AOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticSystemic absorptionPharmaceutical formulation
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising phenylephrine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and methods for administering the pharmaceutical compositions wherein the composition is formulated for systemic absorption of phenylephrine that avoids first pass metabolism. The compositions of the invention are formulated to be applied to oral mucosa of an animal to allow for enhanced systemic delivery of therapeutically active form of phenylephrine.
Owner:SCHERING PLOUGH HEALTHCARE PRODUCTS INC
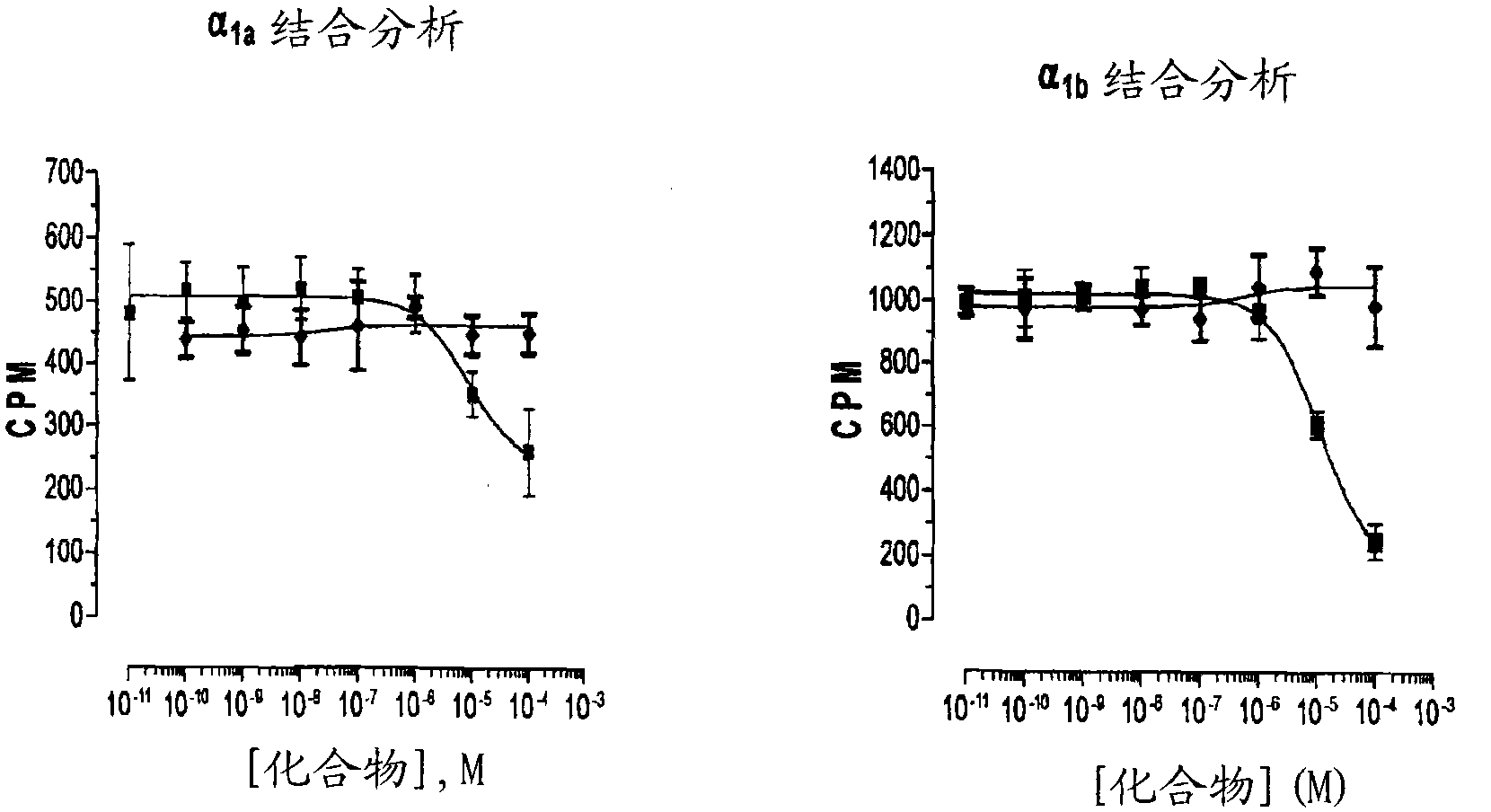
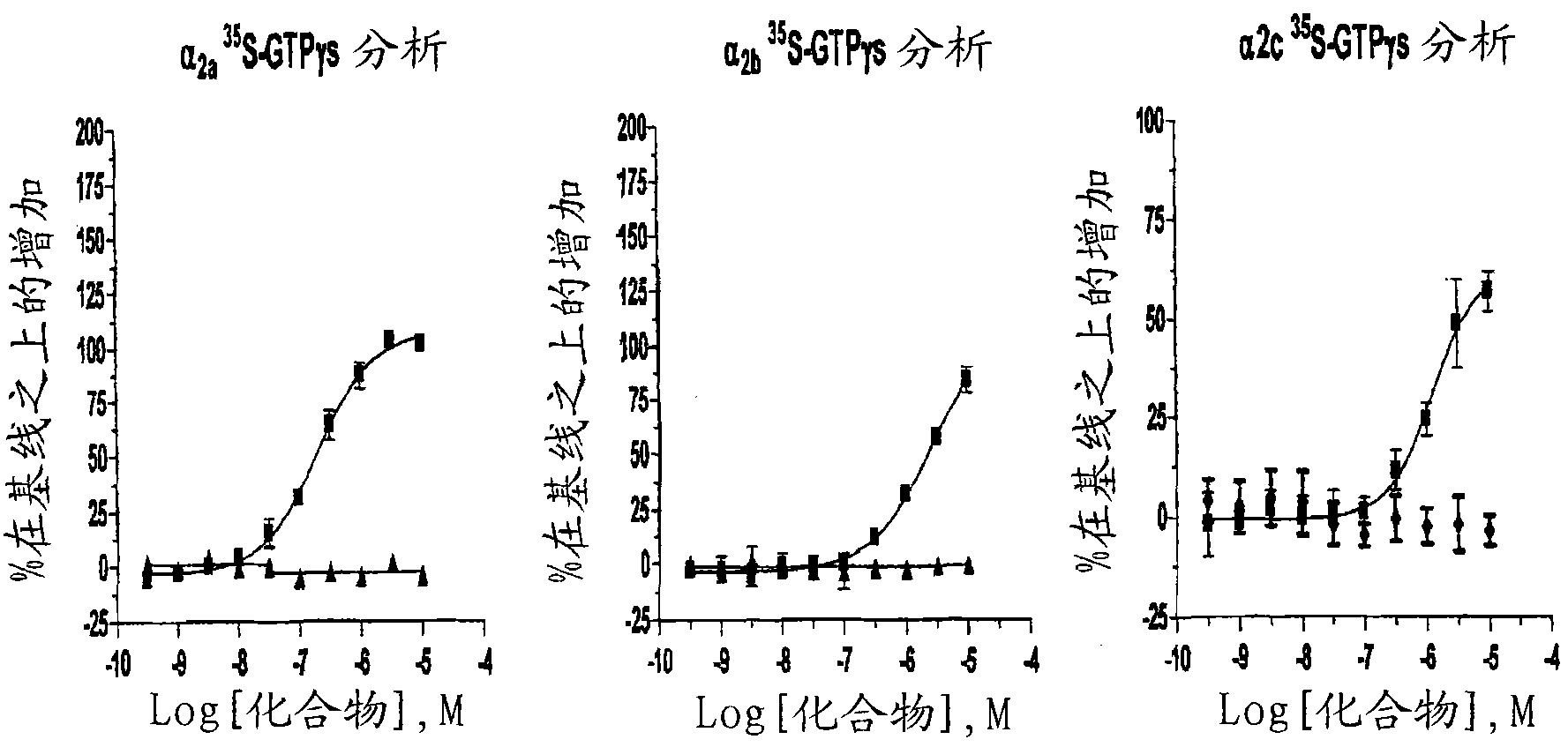
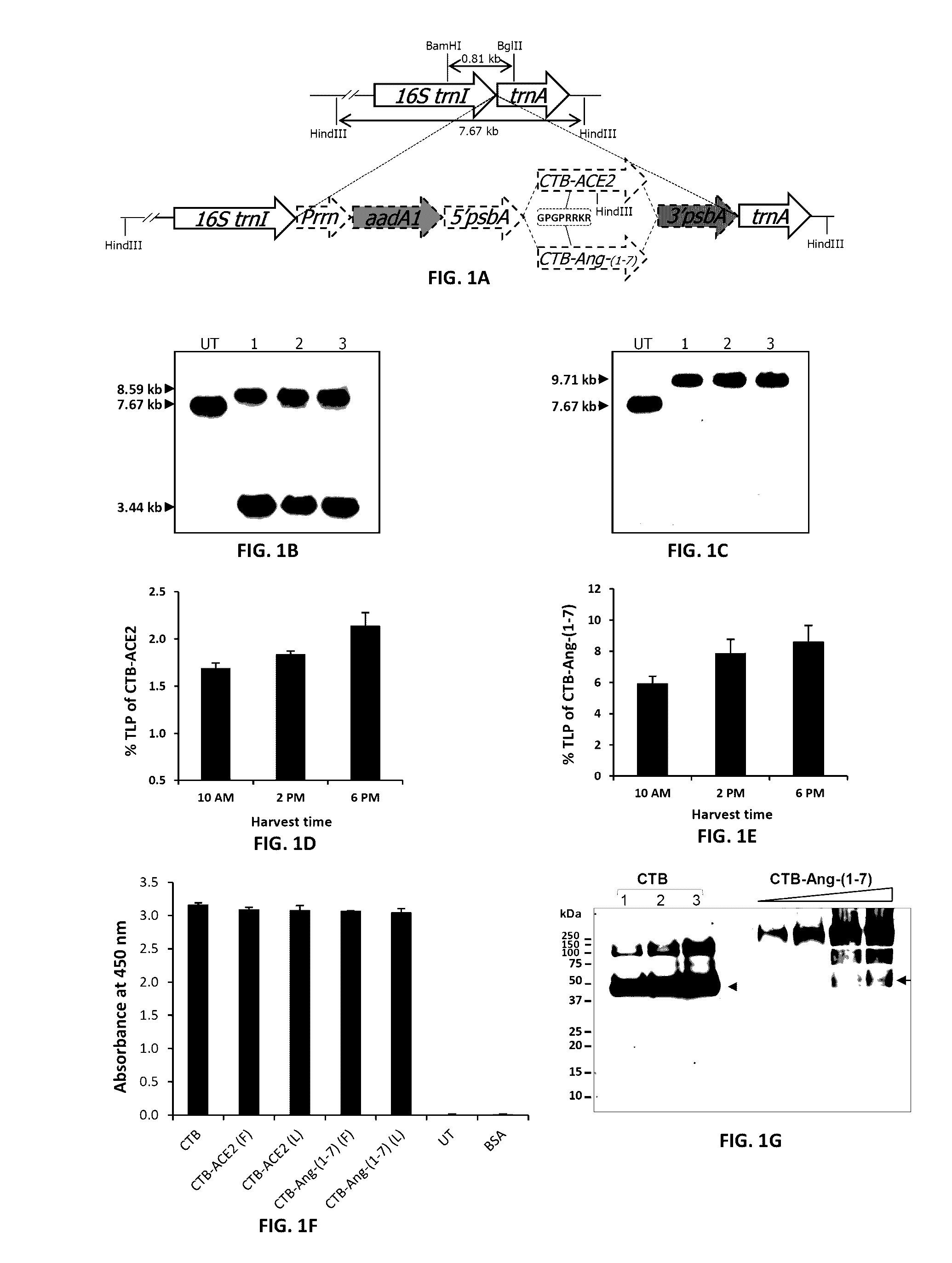
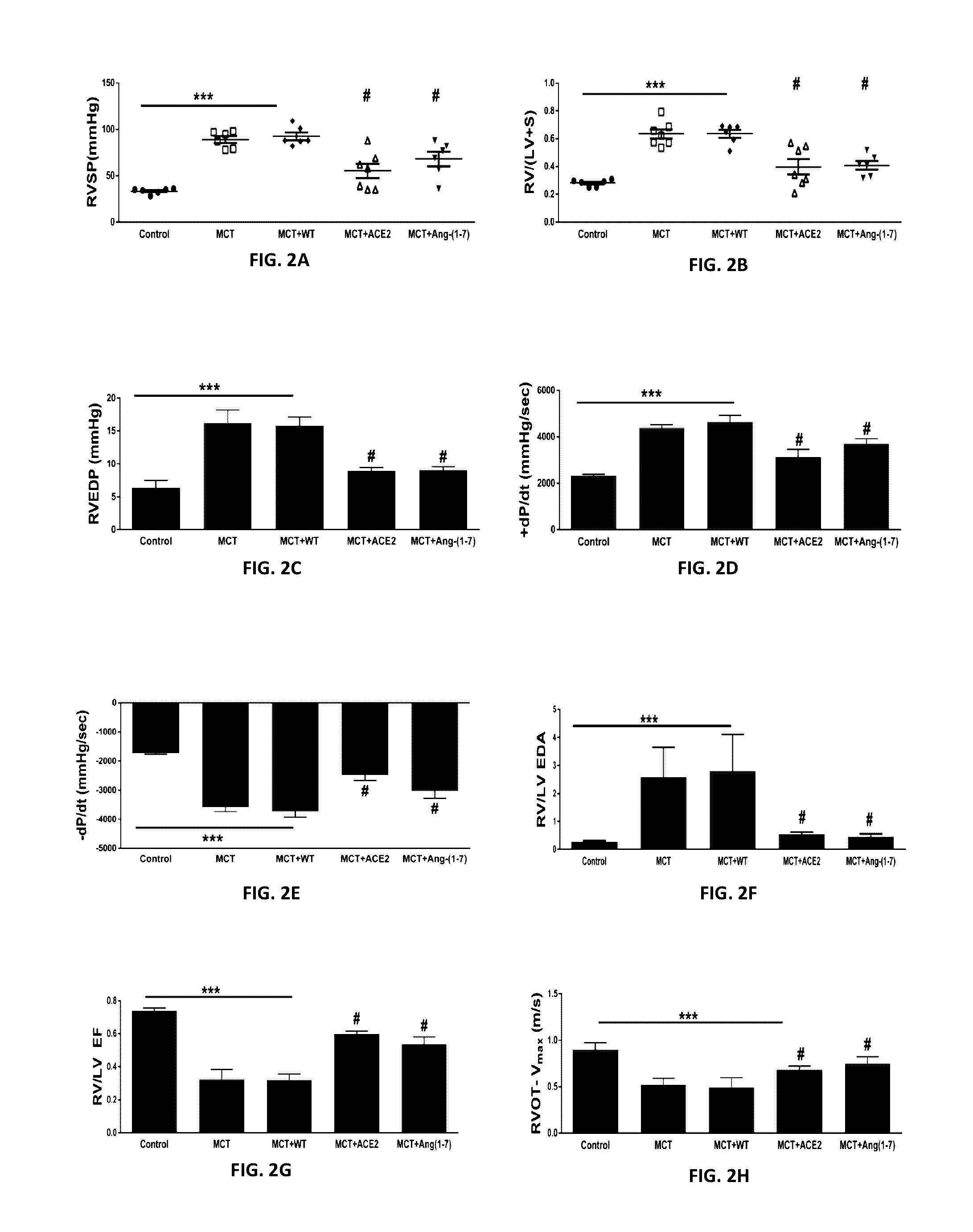
Oral delivery of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) or angiotensin-(1-7) bioencapsulated in plant cells attenuates pulmonary hypertension, cardiac dysfunction and development of autoimmune and experimentally induced ocular disorders
ActiveUS20160331816A1Improved right heart functionDecreased pulmonary vessel wall thicknessPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseUveitis
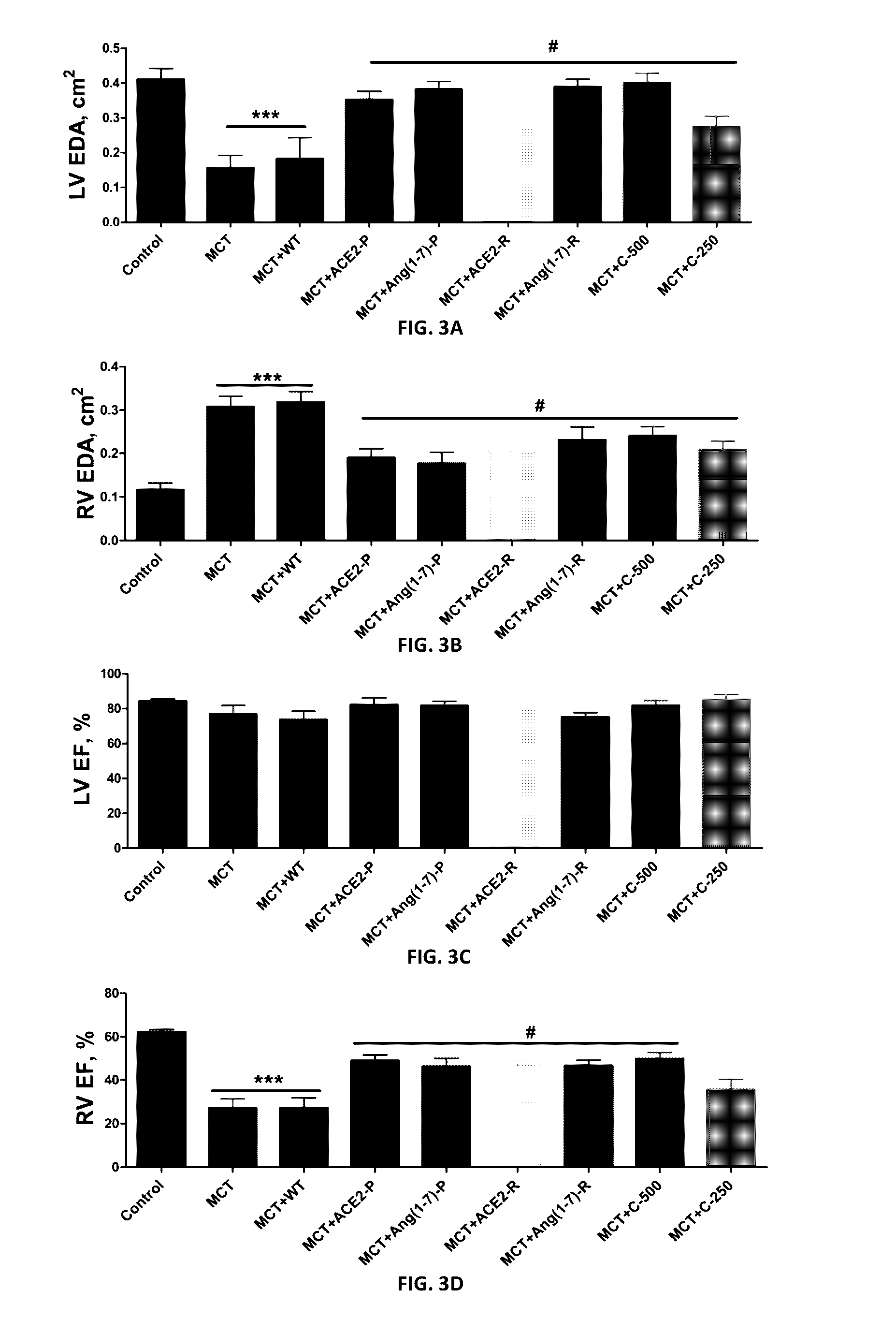
Emerging evidence indicates that diminished activity of the vasoprotective axis of the renin-angiotensin system, constituting angiotensin converting enzyme2 (ACE2) and its enzymatic product, angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] contribute to pulmonary hypertension (PH). However, clinical success for long-term delivery of ACE2 or Ang-(1-7) would require stability and ease of administration to increase patient compliance. Chloroplast expression of therapeutic proteins enables their bioencapsulation within plant cells to protect from acids and gastric enzymes; fusion to a transmucosal carrier facilitates effective systemic absorption. Oral feeding of rats with bioencapsulated ACE2 or Ang-(1-7) attenuated monocrotaline (MCT)-induced increase in right ventricular systolic pressure, decreased pulmonary vessel wall thickness and improved right heart function in both prevention and reversal protocols. Furthermore, combination of ACE2 and Ang-(1-7) augmented the beneficial effects against cardio-pulmonary pathophysiology induced by MCT administration.Experiments have also been performed which indicate that this approach is also suitable for the treatment or inhibition of experimental uveitis and autoimmune uveoretinitis These studies provide proof-of-concept for a novel low-cost oral ACE2 or Ang-(1-7) delivery system using transplastomic technology for pulmonary and ocular disease therapeutics.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Metered dose delivery device for liquid and powder agents
InactiveUS7025058B2Reduces and overcomes deficiencyReduce deliveryRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsDose deliveryWhole body
A delivery device for the delivery of an agent to the mouth, nose or other bodily site of a user. The delivery device includes an aerosol canister that is actuated to expel propellant, which captures and disperses the agent. In a preferred embodiment, the propellant captures and disperses the agent into the mouth or nose of a user, and inhalation by the user directs the agent to the lungs of the user. The delivery device is particularly suitable for the treatment of bronchial asthma, respiratory conditions and for the delivery of systemically absorbed agents.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND PHARMA
Methods for using ultrasound for enhancing efficiency and targeting of intranasal administration of therapeutic compounds to the central nervous system
ActiveUS20130096488A1Reduce systemic absorptionImprove efficiencySonopheresisSurgeryNasal cavityEnteral administration
The present invention is directed to methods for reducing systemic absorption of therapeutic compounds or agents while enhancing efficiency of delivery and targeting of intranasal administration of such compounds or agents to the central nervous system. More specifically, use of ultrasound technology in conjunction with intranasal delivery of a therapeutic compound, or pharmaceutical composition, wherein the intranasal delivery is preferably to the upper one third of a patient's nasal cavity, thereby reducing therapeutic compound or agent absorption into the blood. At the same time, the present invention results in reducing the delivery of therapeutic compounds and / or agents to the peripheral tissues, increases therapeutic delivery of the compounds and / or agents to the central nervous system generally, and increases targeting of the therapeutics and / or agents to specific target regions within the central nervous system.
Owner:HEALTHPARTNERS RESEACH FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com