Interlink-type vortex probe and method for detecting deep cracks of opening fatigue and stress corrosion
A technology of stress corrosion and eddy current probes, applied in measuring devices, instruments, and material analysis through electromagnetic means, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, low resolution, and small eddy current penetration depth of Hall elements, etc., to avoid crack leakage The detection situation, the detection depth is large, and the effect of improving sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
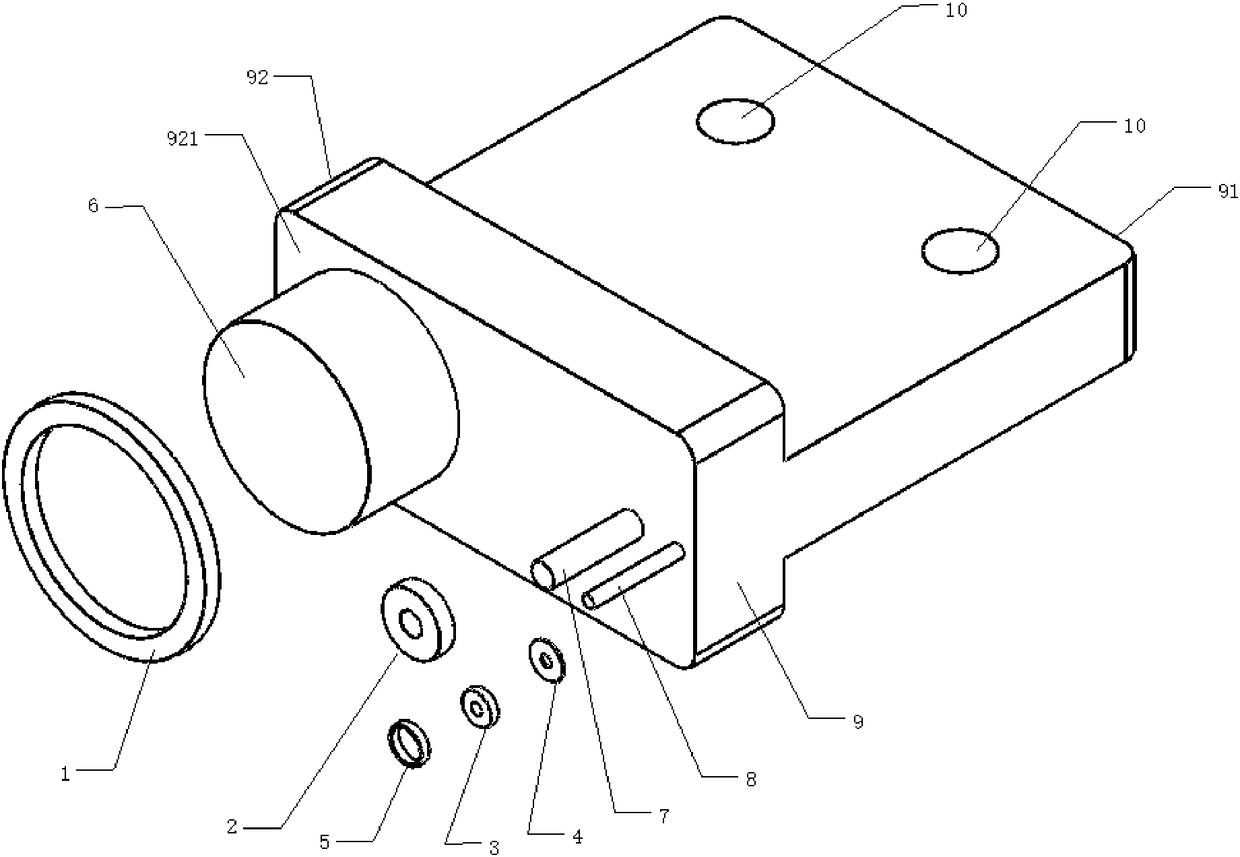
[0058] Such as figure 1 As shown, the serial eddy current probe for detecting opening fatigue and stress corrosion deep cracks includes an excitation element, a detection element and a fixing frame 9; it is characterized in that: the fixing frame 9 includes a scanning frame connecting portion 91 and an element mounting portion 92, The element installation part 92 is provided with an element installation surface 921 ; the excitation element and the detection element are both installed on the element installation surface 921 .
[0059] The excitation element includes a large excitation coil 1, a large excitation coil winding column 6, a small excitation coil 2, and a small excitation coil winding column 7; the large excitation coil winding column 6 and the small excitation coil winding column 7 are vertically fixed Installed on the component mounting surface 921 of the fixing frame 9 ; the large excitation coil 1 is wound on the large excitation coil winding post 6 , and the sma...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Such as figure 2 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1, a method for detecting thick-walled deep crack defects using the above-mentioned serial eddy current probe is characterized in that it includes the following steps:
[0073] S1. Probe assembly: operate as follows:
[0074] First, install the actuator. First fix one end of the large excitation coil winding column 6 and the small excitation coil winding column 7 vertically on the component mounting surface 921 of the component mounting part 92 of the fixing frame 9, and then install the large excitation coil 1 and the small excitation coil 2 respectively Wound on the large excitation coil winding post 6 and the small excitation coil winding post 7, keep the top surfaces of the large excitation coil 1 and the small excitation coil 2 and the tops of the large excitation coil winding post 6 and the small excitation coil winding post 7 face flush.
[0075] Next, install the detection element. First, one end of the ...
Embodiment 3
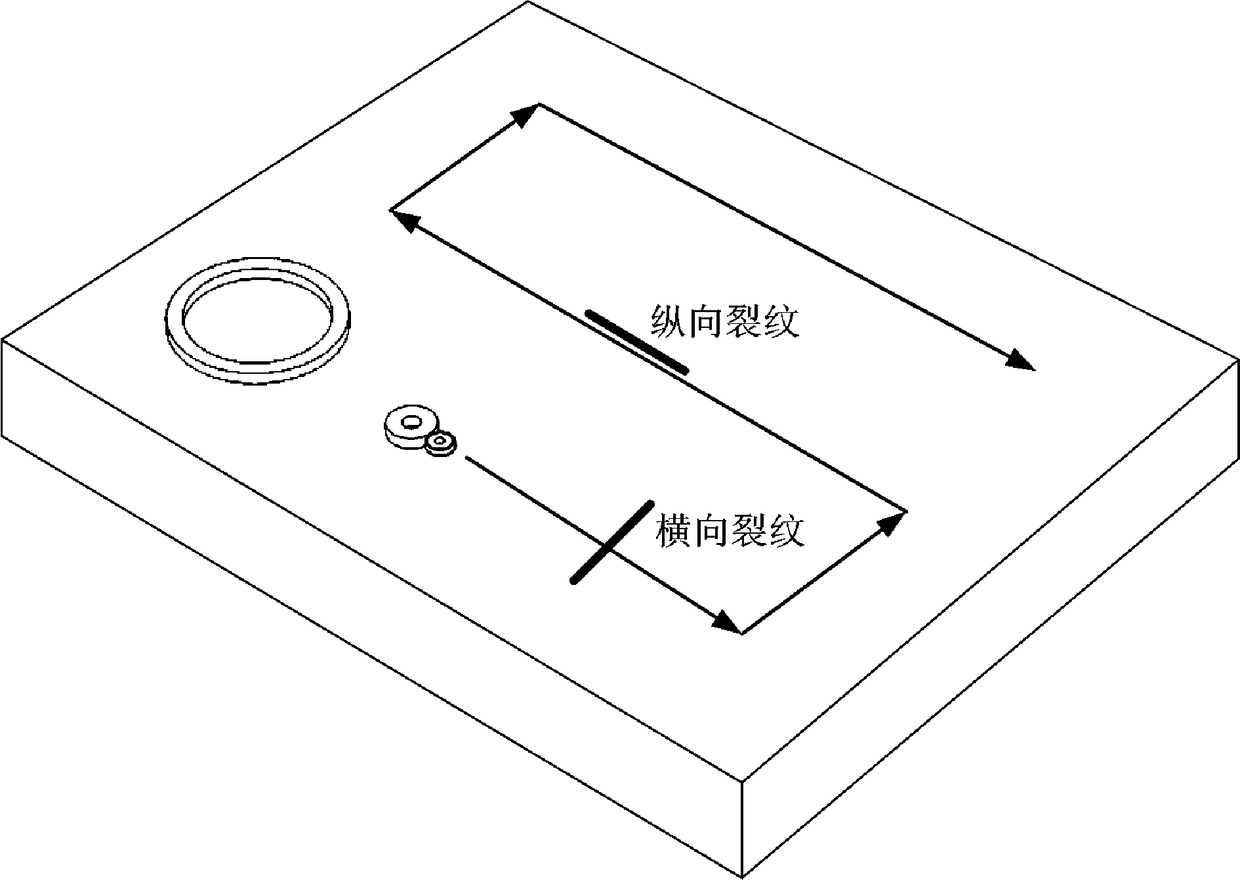
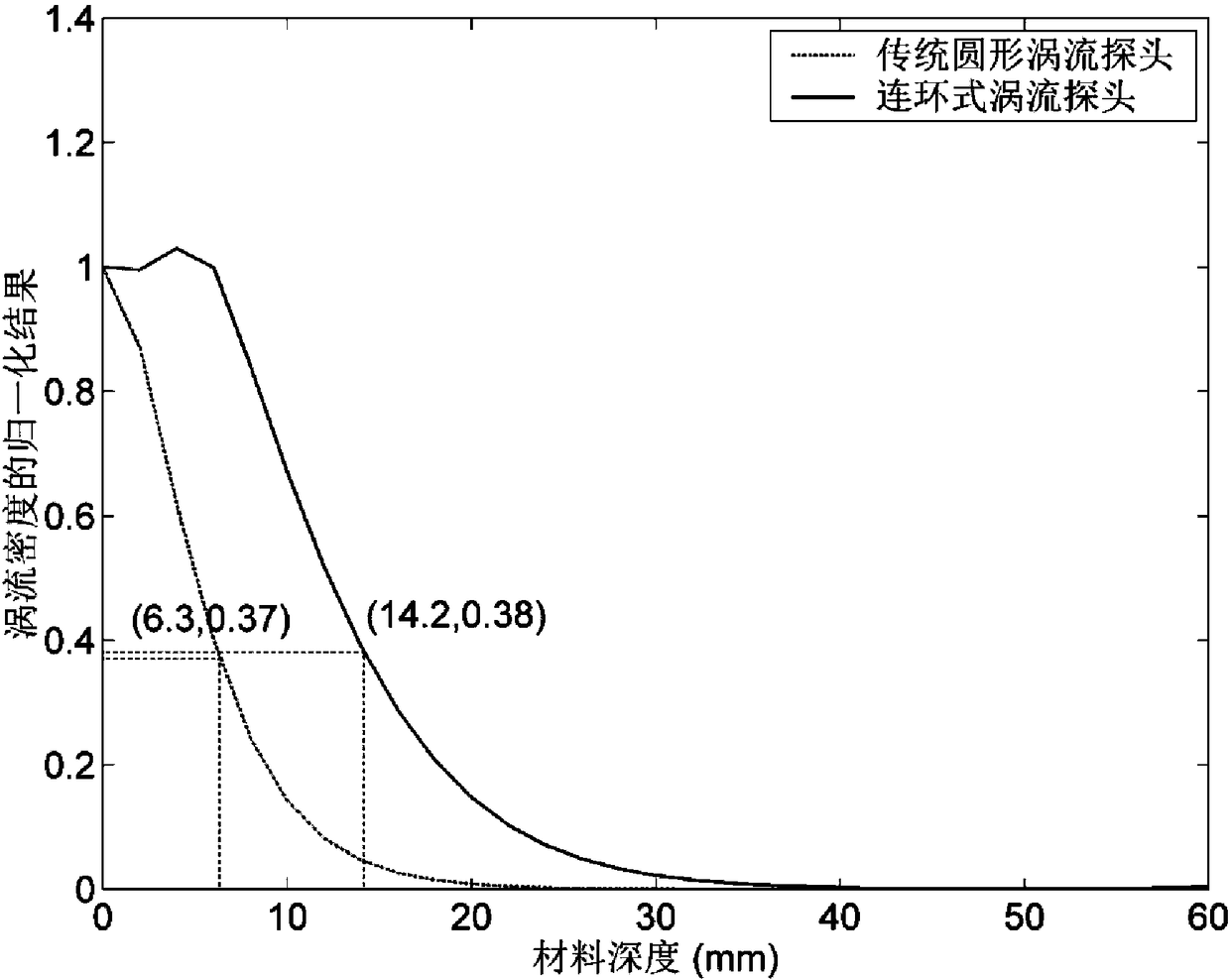
[0083] In order to verify that the penetration depth of the chain-type eddy current probe is better than that of the traditional circular eddy-current probe when detecting thick-walled deep crack defects, on the basis of Examples 1 and 2, a 304 austenitic stainless steel test piece is used to adopt the chain-type eddy current probe of the present invention. The eddy current probe and the traditional self-generating and self-retracting circular eddy current probe obtained when the small excitation coil 2 and the detection coil 3 are not installed, and only the large excitation coil 1 is installed and used for excitation and defect detection, are configured and tested according to the following parameters , with 10kHz excitation frequency, for comparative experiments.
[0084] 1. The detection experiment of the traditional self-generating and self-retracting circular eddy current probe.
[0085] a. On the basis of Examples 1 and 2, only the large excitation coil 1 is used for ex...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com