Loading and climbing robot with target tracking and automatic obstacle avoidance functions
An automatic obstacle avoidance and target tracking technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of insufficient maneuverability of robots, inability to climb stairs, and inability to climb over ladder ridges, etc., to achieve strong practicability and operability, stable center of gravity, and optimized climbing movements Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
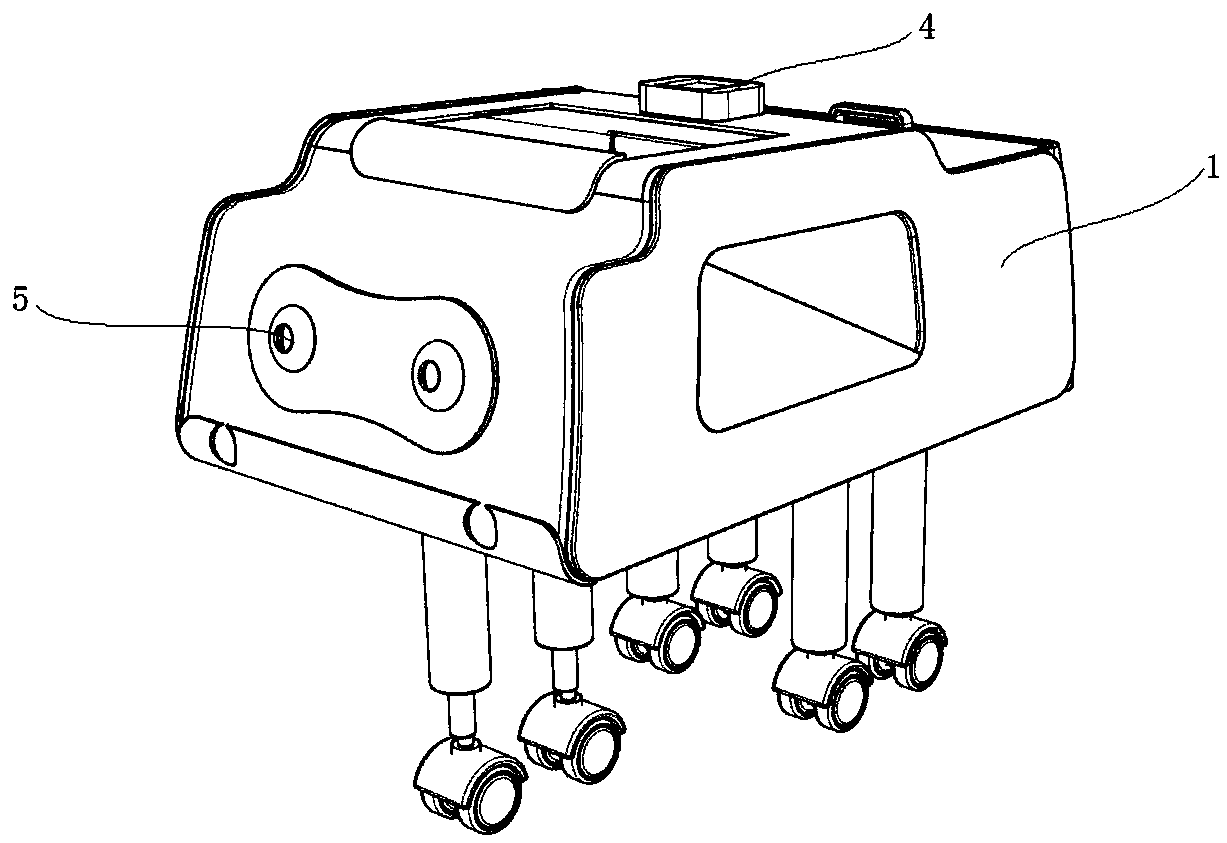
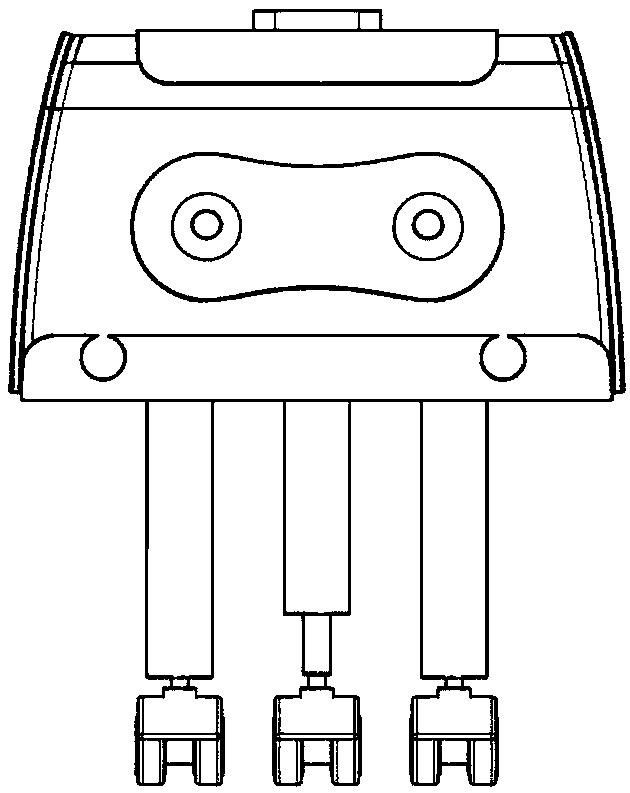
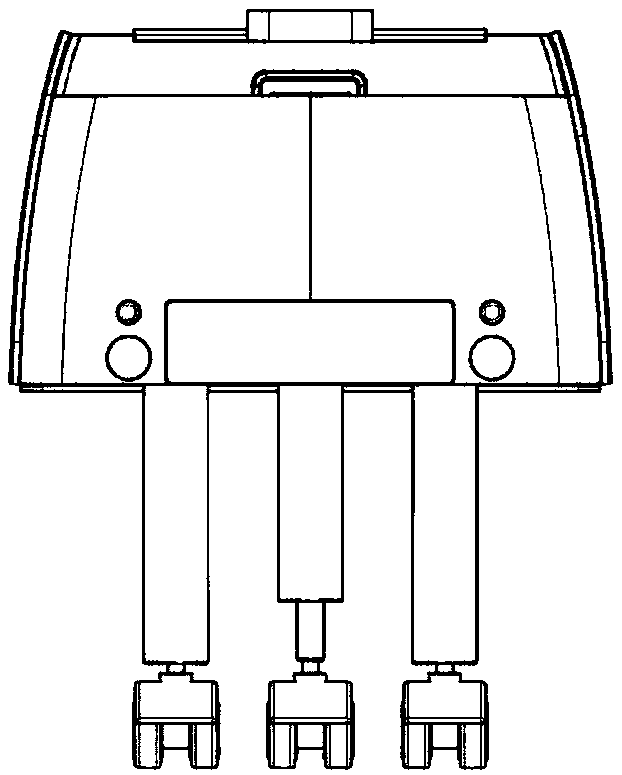
[0071] Such as Figures 1 to 14 and Figure 16 As shown, a load-carrying stair-climbing robot with target tracking and automatic obstacle avoidance is characterized in that it includes a housing 1, a frame mechanism 2, a wheel-leg mechanism 3 and a control system.
[0072] The housing 1 has a hollow inner cavity and is provided with a loading platform. A frame mechanism 2 is installed in the cavity of the housing 1 .
[0073] The frame mechanism 2 includes a first frame 21 and a second frame 22 .
[0074] The second frame 22 is a rectangular frame. The length direction of the rectangular frame is marked as X direction, and the width direction is marked as Y direction. The X direction is the forward or backward direction of the stair climbing robot.
[0075] The first frame 21 includes a beam 211 and a longitudinal beam 212 supported above the second frame 22 , that is, the ends of the three branches of the first frame 21 are supported above the rectangular frame by uprigh...
Embodiment 2
[0090] The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1. With reference to pictures 15 to 16, a further description of the climbing process of a load-carrying stair-climbing robot with target tracking and automatic obstacle avoidance is made, including the following:
[0091] 1) The STM32 MCU sends a signal to the hardware circuit, and controls the drive motor to drive the robot forward through the hardware circuit. When the ultrasonic module in the horizontal direction of the ultrasonic distance sensor detects a step, it feeds back the detected information to the STM32 MCU, and the STM32 MCU sends The signal is sent to the hardware circuit, and the telescopic leg I 311 of a wheel leg I 31 closer to the forward direction of the robot is controlled by the hardware circuit to shrink, so that the wheel leg I 31 is lifted, and the robot continues to move forward.
[0092] 2) When the ultrasonic module in the vertical direction of the ultrasonic distance sen...
Embodiment 3
[0102] The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1. With reference to picture 16, the image recognition and tracking process of a load-carrying stair-climbing robot with target tracking and automatic obstacle avoidance is further described, including the following:
[0103] 1) The robot obtains the image of the person to be tracked through the camera 5, and transmits the obtained image to the PC.
[0104] 2) The PC analyzes the image returned by the camera 5 in real time, judges the position of the tracking object in the picture, and judges the position of the tracking object relative to the robot itself.
[0105] 3) The PC sends control commands to the STM32 microcontroller through the USB serial port according to the position information, and the STM32 microcontroller processes the commands and controls the hardware circuit, and realizes differential steering by controlling two drive motors.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com