Contactor control circuit
A technology for controlling circuits and contactors, applied to circuits, relays, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low power factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
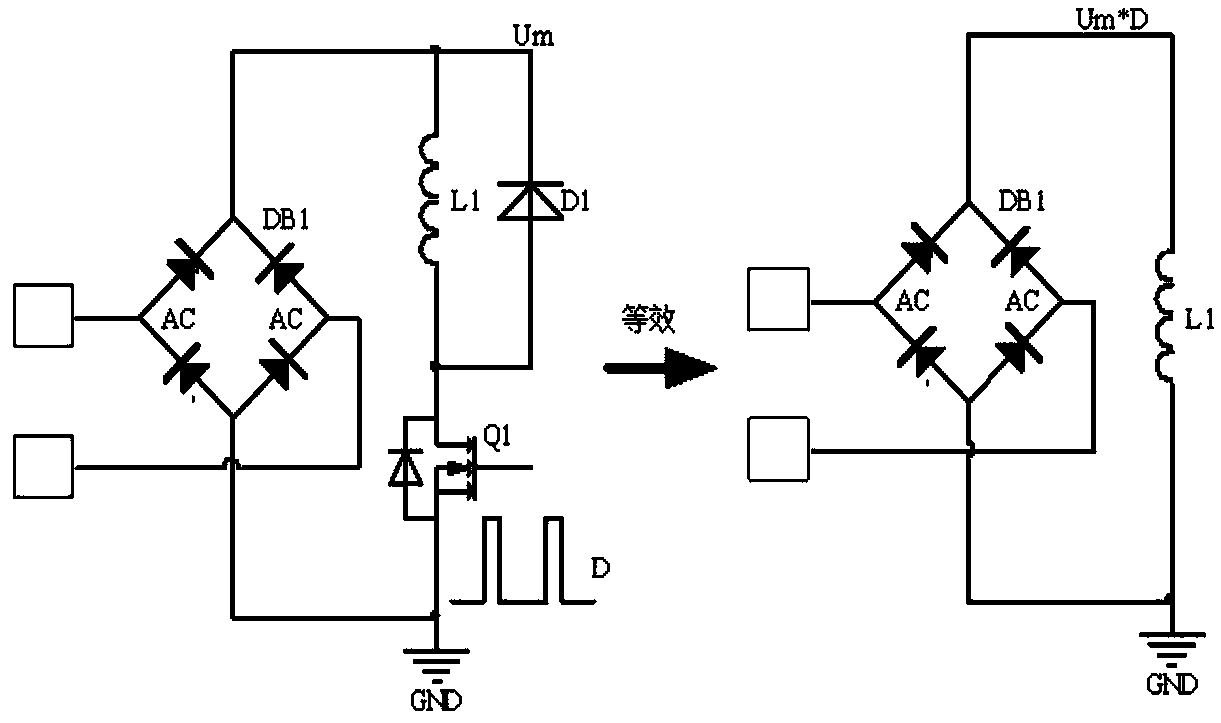
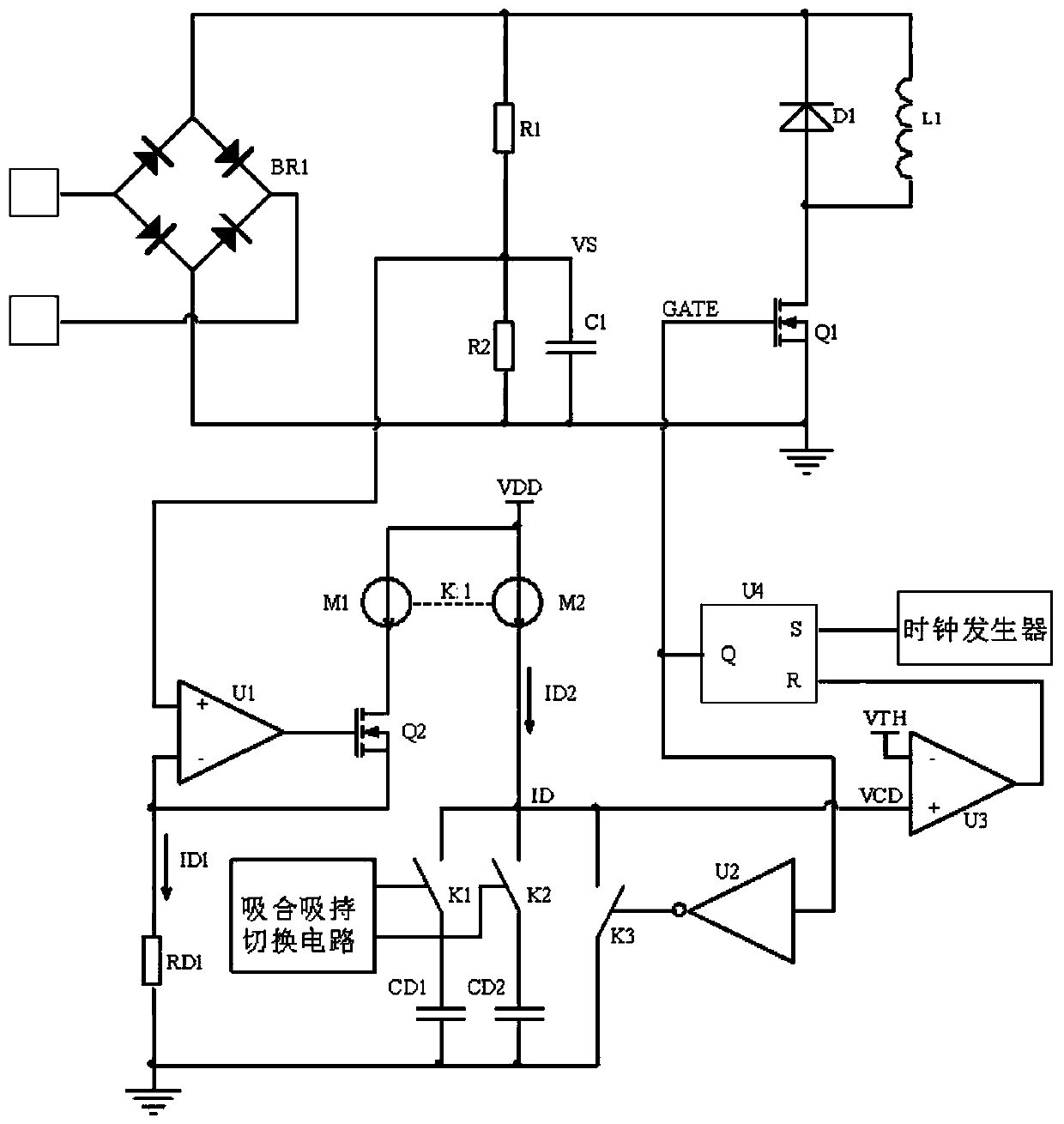
[0055] Such as figure 2 Shown is a schematic diagram of a contactor control circuit according to the first embodiment of the present invention, including a voltage detection circuit and a duty ratio control circuit.
[0056] The voltage detection circuit includes a resistor R1, a resistor R2 and a capacitor C1. The resistor R1 and the resistor R2 are connected in series and connected in parallel at both ends of the rectified bus voltage. One end of the capacitor C1 is connected to the connection point of the resistor R1 and the resistor R2, and serves as the output end of the voltage detection circuit, and the other end of the capacitor C1 is grounded. The function of the voltage detection circuit is to divide the voltage and filter, reduce the bus voltage to an appropriate value and extract its DC component.
[0057] The duty ratio control circuit of the first embodiment includes an operational amplifier U1, a MOS transistor Q2, a resistor RD1, a switch K1, a switch K2, a ...
no. 2 example
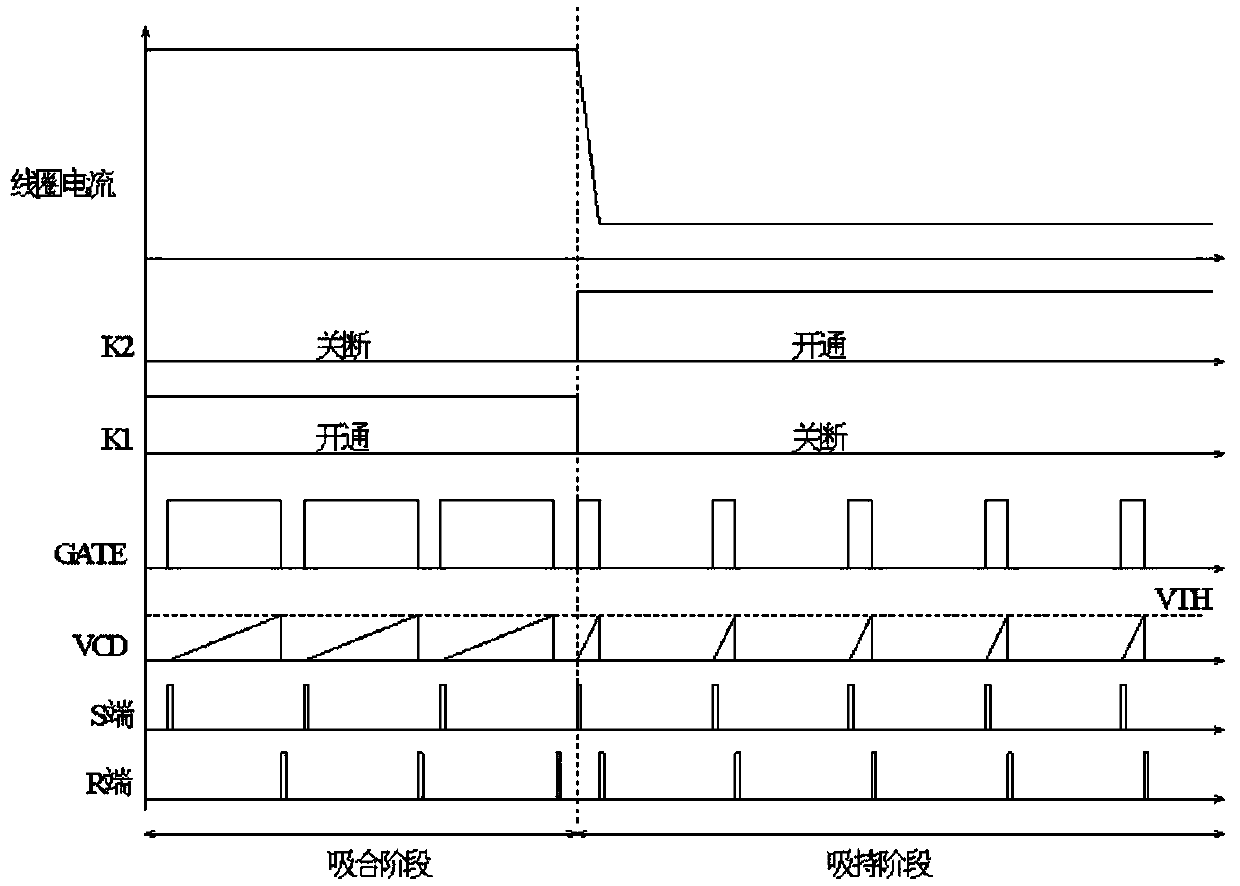
[0071] The circuit schematic diagram of the second embodiment is as follows Figure 4 shown. The basic principle of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment. The difference is that in the second embodiment, the charging current ID2 is controlled through the resistors RD1 and RD2 to set the duty cycle of the pull-in phase and the hold phase. The voltage detection circuit of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment. The connection relationship of the duty ratio control circuit of the second embodiment is as follows.
[0072]The duty ratio control circuit of the second embodiment includes an operational amplifier U1, a MOS transistor Q2, a resistor RD1, a resistor RD2, a switch K1, a switch K2, a switch K3, a capacitor CD1, an inverter U2, a comparator U3, and an RS flip-flop U4 , clock generator, suction and holding switching circuit, constant current source M1, constant current source M2. The positive input terminal of the o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com