Nucleic acid group suitable for detection of SNP sites of tumor drug-related genes and application
A drug and gene technology, applied in the nucleic acid group field of tumor drug-related gene SNP site detection, can solve the problems of high failure rate, detection failure, complicated result interpretation, etc., and achieve the effect of simple result interpretation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] The kit for detecting SNP sites of tumor drug-related genes provided in this embodiment includes a nucleic acid set for detecting SNP sites of tumor drug-related genes. The nucleic acid set includes the following primer combination 1-primer combination 15.
[0087] Wherein, primer combination 1 includes: amplification primers shown in SEQ ID NO.1-2 and detection primers shown in SEQ ID NO.31;
[0088] Primer combination 2 includes: amplification primers shown in SEQ ID NO.3-4 and detection primers shown in SEQ ID NO.32;
[0089] Primer combination 3 includes: amplification primers shown in SEQ ID NO.5-6 and detection primers shown in SEQ ID NO.33;
[0090] Primer combination 4 includes: amplification primers shown in SEQ ID NO.7-8 and detection primers shown in SEQ ID NO.34;
[0091] Primer combination 5 includes: amplification primers shown in SEQ ID NO.9-10 and detection primers shown in SEQ ID NO.35;
[0092] Primer combination 6 includes: amplification primers sho...
Embodiment 2
[0125] Using the kit and method of Example 1, 6 samples (all from clinics, the sample type being whole blood or buccal swab) with known SNP locus genotypes were tested, and the results are shown in Table 5-7 below.
[0126] table 5
[0127]
[0128] Table 6
[0129]
[0130] Table 7
[0131]
[0132]
[0133] Among them, the known results in Table 5-7 are statistics of sample results detected by traditional methods (fragment analysis, single base extension and sanger sequencing), and the detection results on the right are the results of detection using the nucleic acid group in Example 1. The results show that the results using the nucleic acid group and detection method of Example 1 are consistent with those of the traditional method.
experiment example 1
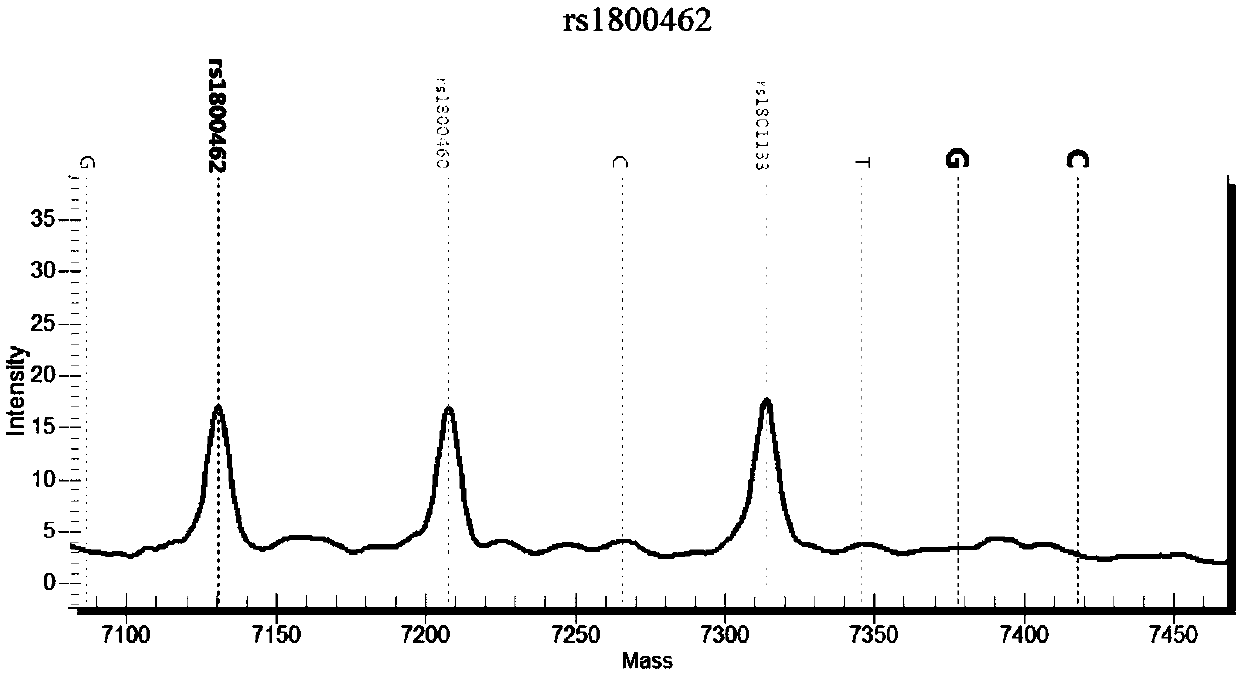
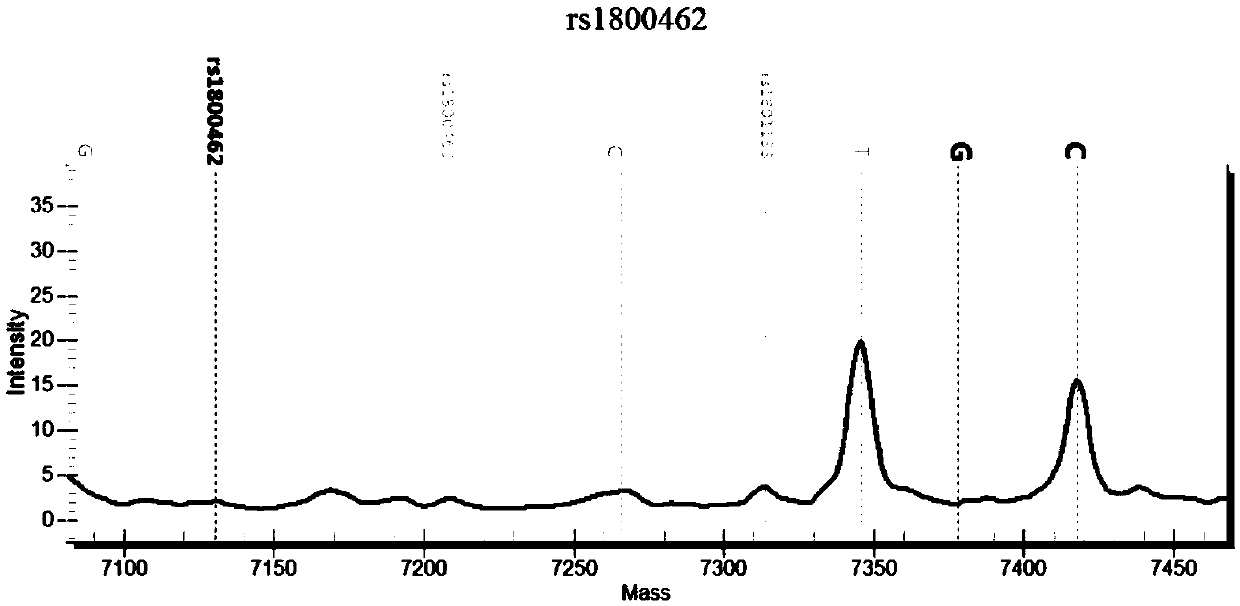
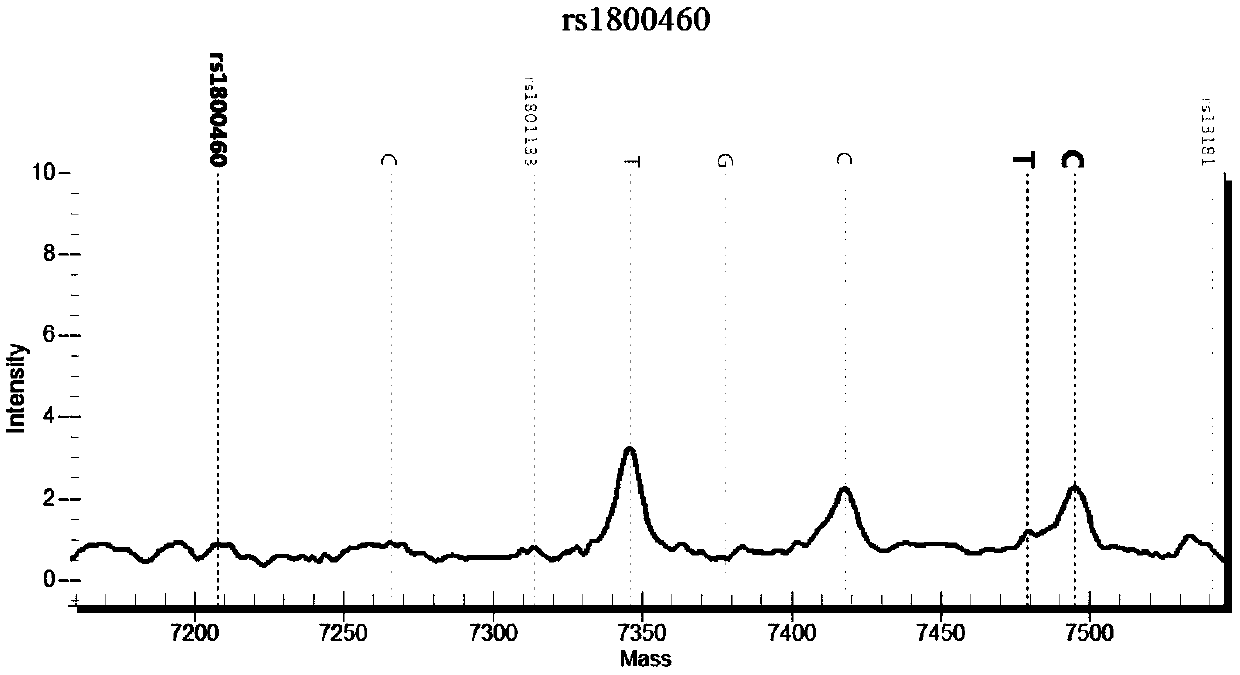
[0135] There are many SNP sites before and after the rs1800462 site. Within 3 bases, there are 2 SNP sites, rs771921981 and rs190484211. There are 10 SNP sites within 10 bases, and within 20 bases. There are 16 SNP sites in the base range. In addition, there is a fragment deletion mutation (ra750040431) at 27 bp upstream of the rs1800462 site, which can easily lead to sample amplification failure and may also cause detection failure. In addition, there are pseudogenes in the genome, and it is very easy to amplify non-target fragments, so the general strategy in primer design is to amplify as long as possible fragments, and then detect, which will easily result in fewer single detection sites and low throughput (such as Sequencing analysis, fragment analysis); if the amplification length is reduced, the detection will easily fail. These reasons indicate that the design of various primers for the nucleic acid set of the present invention requires creative efforts.
[0136] Bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com