Method for counting bacterial colonies in fermented feed
A technology for fermenting feed and feed, which is applied to biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms, can solve the problems of inaccurate counting, affecting the counting of lactic acid bacteria and yeast, and achieve the effect of improving counting accuracy and easy operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1: the enumeration of three kinds of strains in fermented feed 1
[0044] Weigh 10g of fermented feed 1 and add it to 90mL sterile saline and mix well to obtain 10 -1 The sample suspension, draw 1mL of the sample suspension and dilute it 10 times with sterile normal saline, and obtain dilutions of 10 times in turn. 2 、10 3 、10 4 、10 5 、10 6 times the sample dilution.
[0045] Draw 1mL respectively and the dilution factor is 10 4 、10 5 、10 6 and added to the center of 3 sterile plates with a diameter of 90mm (three repetitions were set up for each concentration of sample dilution, a total of 9 plates), and 20mL of 50°C containing 500ppm Natal was added to each plate. MRS medium of mycin, mix well, cool until it solidifies completely, then place it upside down in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for about 48 hours, and take out the plate when clearly separated colonies can be seen with the naked eye.
[0046] Draw 1mL respectively and the dil...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Enumeration of three bacterial strains in fermented feed 2
[0054] Except that fermented feed 1 in embodiment 1 was replaced by fermented feed 2, the same method as in embodiment 1 was used to count lactic acid bacteria, bacillus and yeast.
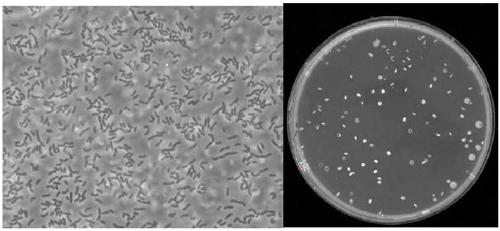
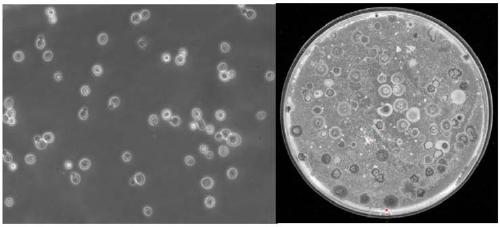
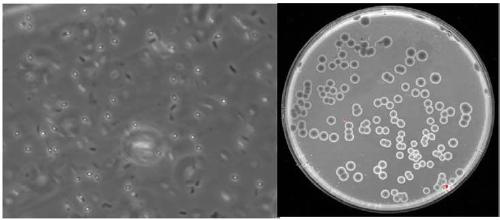
[0055] The result is as Figures 5A-5C As shown, most of the colonies on the MRS medium plate are lactic acid bacteria colonies, and the number of viable bacteria is 1.0×10 8 cfu / mL( Figure 5A left). Most of the colonies on the LB medium plate are Bacillus colonies, and the number of viable bacteria is 3.0×10 8 cfu / mL( Figure 5B left). The colonies on the YPD solid medium plate are all yeast colonies, and the number of viable bacteria is 1.6×10 8 cfu / mL( Figure 5C left).
[0056] The national standard method [1] GBT13093-2006 was used to count the lactic acid bacteria, bacillus and yeast in the same sample dilution. As a result, yeast and bacillus grew on the MRS medium plate and seriously affected the coun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com