Rapid degradation method for corrodible organic solid wastes
A technology for rapid degradation of organic solid waste, applied in the direction of organic fertilizers, preparation of organic fertilizers, and treatment of biological organic parts, etc., can solve problems such as slow degradation speed, pollution of the surrounding environment, and the inability to quickly eliminate the odor of organic solid waste. Accelerated heating rate, reduced environmental hazards, and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
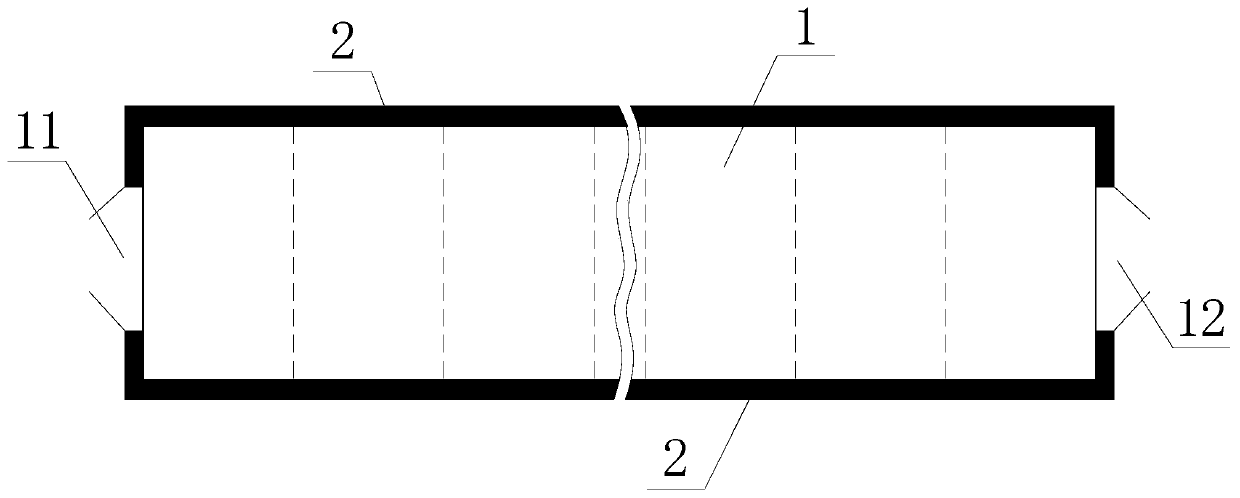
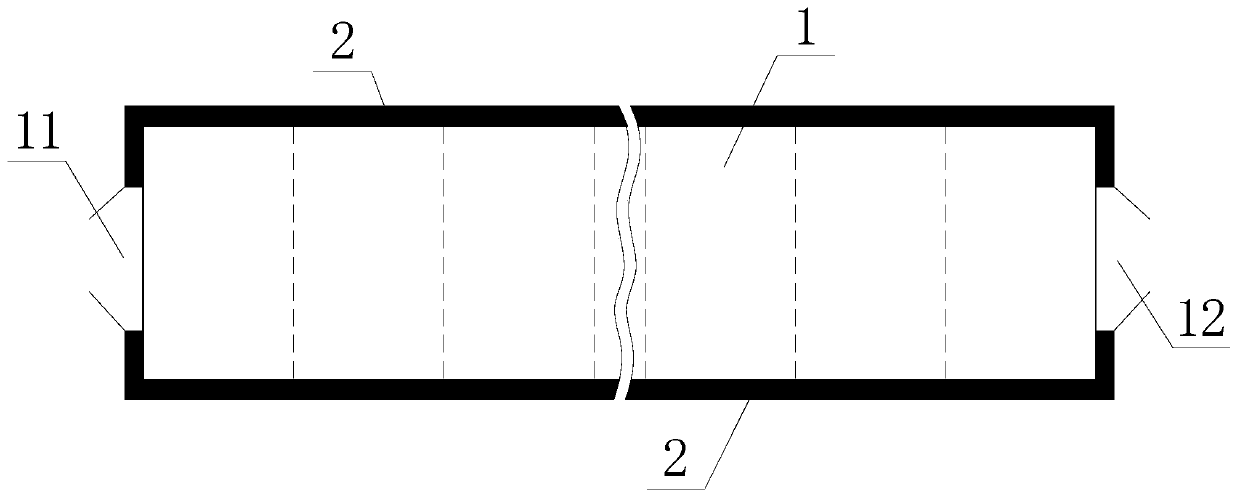
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the rapid degradation method of rotten organic solid waste of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0036] 1) Add water or organic solid waste leachate to the organic solid waste to make the moisture content of the organic solid waste reach 30%-70%;
[0037] 2) Control the number of viable bacteria in organic solid waste, so that the number of viable microorganisms in organic solid waste reaches 0.01-1 billion / m3;
[0038] 3) Use conveying machinery or mobile equipment to send the organic solid waste obtained in step 2) from the feed end 11 of the biochemical bin 1, and stack it at the end of the biochemical bin 1 near the discharge end 12, and adjust the oxygen supply in the biochemical bin 1 , Ventilate, and measure the temperature on a daily basis. It is required that the time of 50°C-70°C in the high temperature period reaches 80-120 hours;
[0039] 4) Repeat steps 1) and 2) for the next batch of organic solid waste. When ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the rapid degradation method of rotten organic solid waste of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0044] 1) Select a certain amount of organic solid waste with an initial temperature of 10°C (consistent with the ambient temperature), and add organic solid waste leachate to the organic solid waste so that the moisture content of the organic solid waste reaches 60%;
[0045] 2) Control the number of viable bacteria in organic solid waste. If the amount of microorganisms contained in organic solid waste is insufficient, add microbial agent to make the number of viable microorganisms in organic solid waste reach 0.02 billion / m 3 ;
[0046] 3) Use a conveying machine to send the organic solid waste obtained in step 2) from the feed end 11 of the biochemical bin 1, and stack it at the end of the biochemical bin 1 near the discharge end 12, with a stack height of 2m, and adjust the supply in the biochemical bin 1. Oxygen, ventila...
Embodiment 3
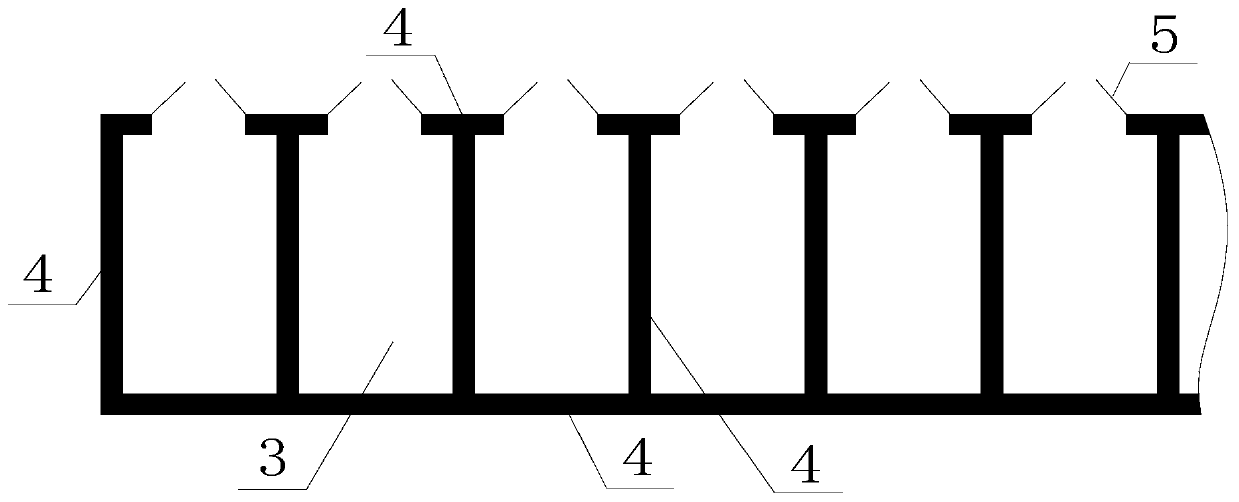
[0052] Such as figure 2 As shown, the rapid degradation method of rotten organic solid waste comprises the following steps:
[0053] 1) Select a certain volume of organic solid waste with an initial temperature of 10°C (consistent with the ambient temperature), and add organic solid waste leachate to the organic solid waste so that the moisture content of the organic solid waste reaches 60%;
[0054] 2) Control the number of viable bacteria in organic solid waste. If the amount of microorganisms contained in organic solid waste is insufficient, add microbial agent to make the number of viable microorganisms in organic solid waste reach 0.02 billion / m 3 , the type and amount of the microbial inoculant used are the same as in Example 2;
[0055] 3) transporting the organic solid waste obtained in step 2) to an independently separated fermentation bin 3 with a stacking height of 2 m by means of a conveying machine; A warehouse door 5, the rest of the oxygen supply device, air ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com