Semi-coaxial optical path receiving laser radar system
A laser radar, laser receiving technology, applied in radio wave measurement system, electromagnetic wave re-radiation, utilization of re-radiation and other directions, to achieve the effect of ensuring authenticity, high resolution, and high measurement accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
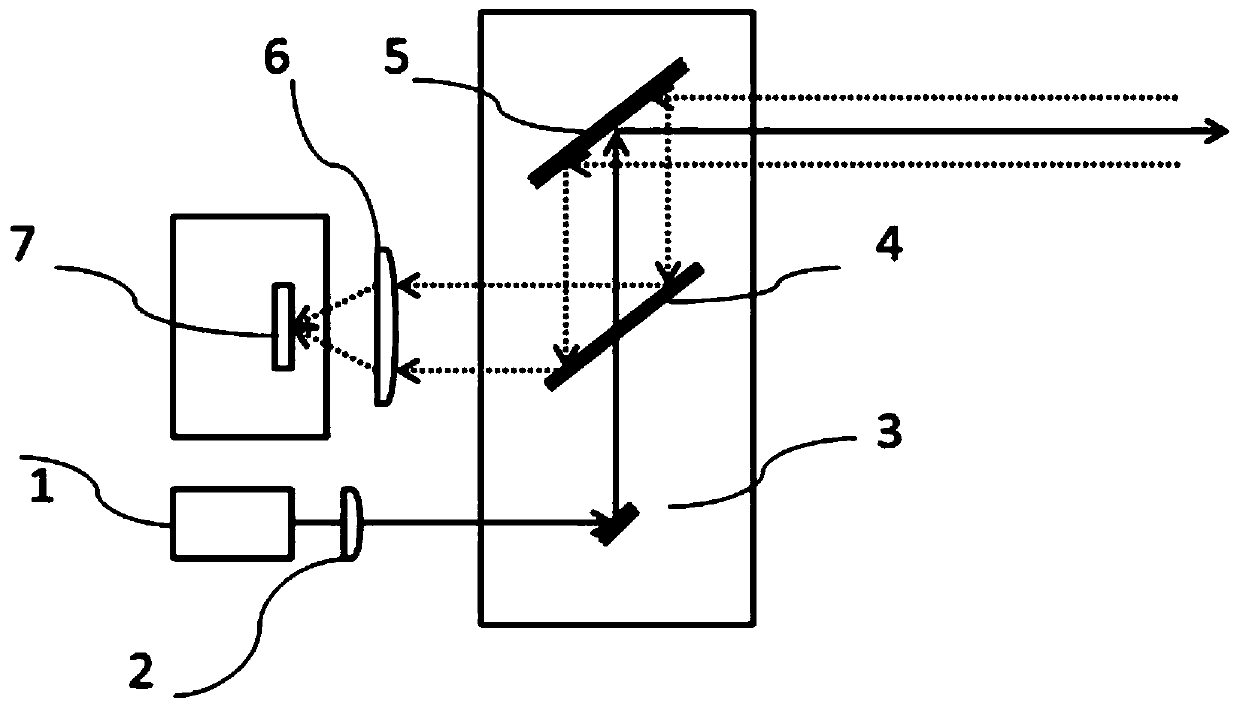
[0039] From figure 1 It can be seen that the semi-coaxial optical path receiving radar galvanometer scanning system in this embodiment includes a pulsed laser 1, a collimator lens 2, a first one-dimensional MEMS galvanometer 3 and a half-mirror 4 arranged sequentially along the optical path, which can Replacing the half-mirror 4 with a polarizing beam splitter, it also includes a second one-dimensional MEMS oscillating mirror 5 arranged in the transmission path of the half-mirror 4 and a receiving lens sequentially arranged in the reflection path of the half-mirror 4 6 and photodetector 7. In this embodiment, the receiving lens 6 is a focusing lens. In other embodiments, in order to realize the scanning requirement of a large field of view, the receiving lens 6 can adopt a wide-angle lens, which is then received by the detector for signal processing. The above-mentioned wide-angle lens is a cylindrical lens, immersed Large field of view receiving lens such as lens or compound...
Embodiment 2
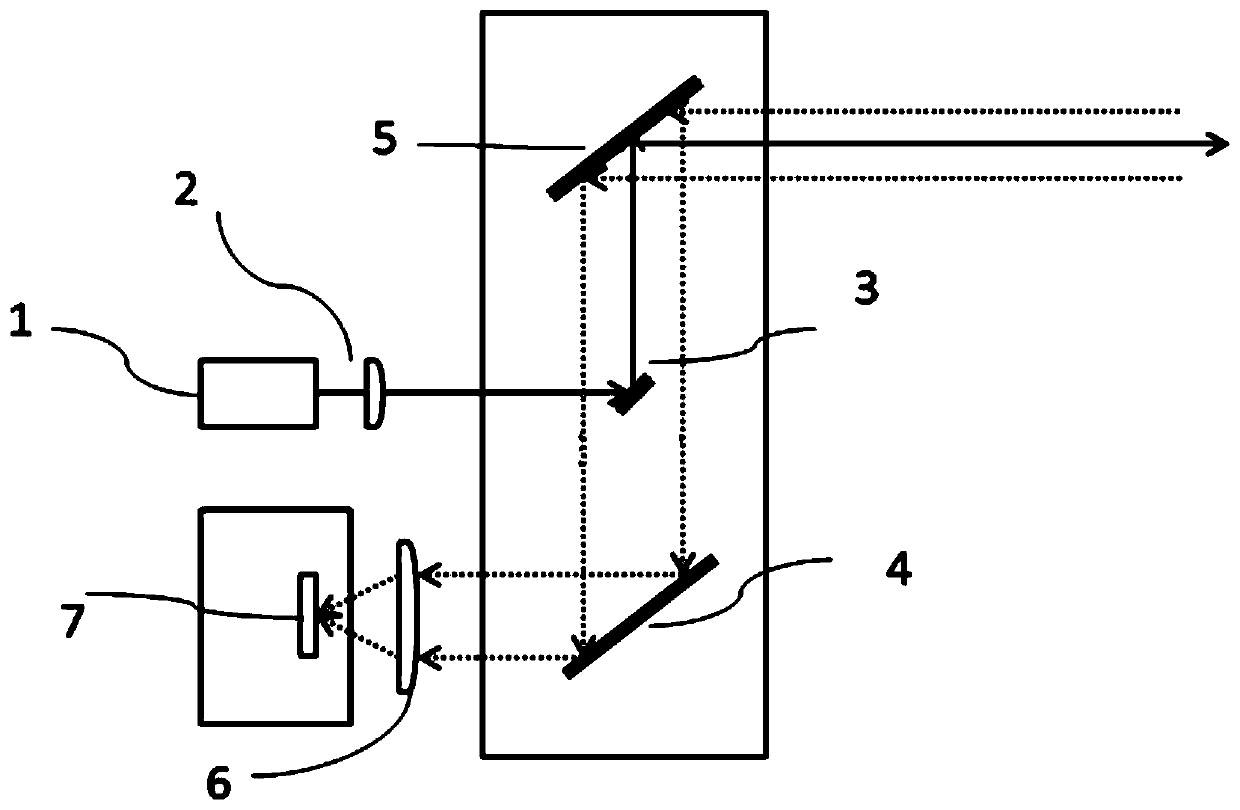
[0044] From figure 2 It can be seen that the semi-coaxial optical path receiving radar galvanometer scanning system in this embodiment includes a pulsed laser 1, a collimating lens 2, a first one-dimensional MEMS galvanometer 3 and a second one-dimensional MEMS galvanometer 5 arranged in sequence along the optical path ; Also includes a total reflection mirror 4 and a receiving lens 6 and a photodetector 7 located in the reflection path of the total reflection mirror 4 in turn. The main function of the collimating mirror 2 is to realize the shaping of the laser spot, to achieve the maximum energy concentration of the pulsed laser, and to improve the emitted light energy and the ability to test farther. The initial position of the first one-dimensional MEMS vibrating mirror 3 is at an angle of 45° to the beam direction, and the initial position of the second one-dimensional MEMS vibrating mirror 5 and the total reflection mirror 4 are parallel to the initial direction of the f...
Embodiment 3
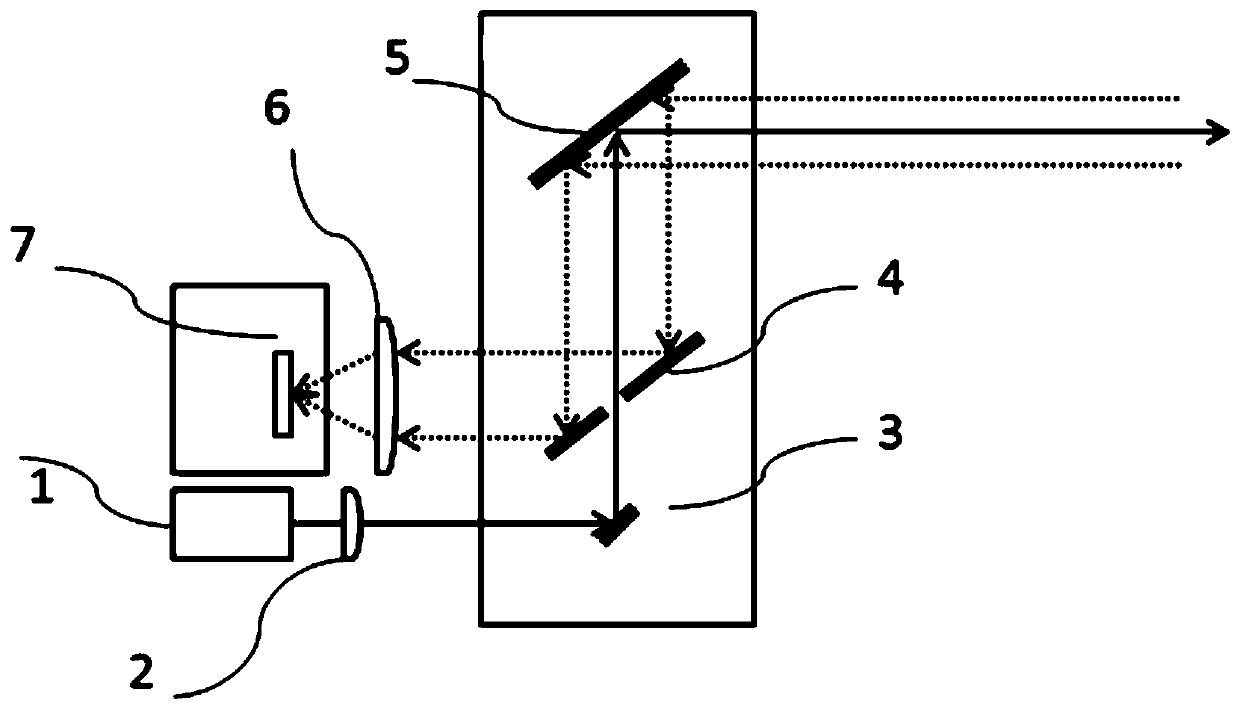
[0048] From image 3 It can be seen that the semi-coaxial optical path receiving radar galvanometer scanning system in this embodiment includes a pulse laser 1, a collimator lens 2, a first one-dimensional MEMS galvanometer 3, and a total reflection mirror with a central opening arranged in sequence along the optical path. 4 and the second one-dimensional MEMS oscillating mirror 5, further comprising a receiving lens 6 and a photodetector 7 sequentially arranged in the reflection optical path of the total reflection mirror 4 with a central opening. The main function of the collimating mirror 2 is to realize the shaping of the laser spot, to achieve the maximum energy concentration of the pulsed laser, and to improve the emitted light energy and the ability to test farther. The first one-dimensional MEMS vibrating mirror 3 is at an angle of 45 degrees to the beam direction at the initial position, the initial position of the second one-dimensional MEMS vibrating mirror 5 and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com