Polypeptide cross-linked protein molecularly imprinted polymer and its preparation method and application
A molecular imprinting and polymer technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, peptides, specific peptides, etc., can solve problems such as poor imprinting effect and difficult template elution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
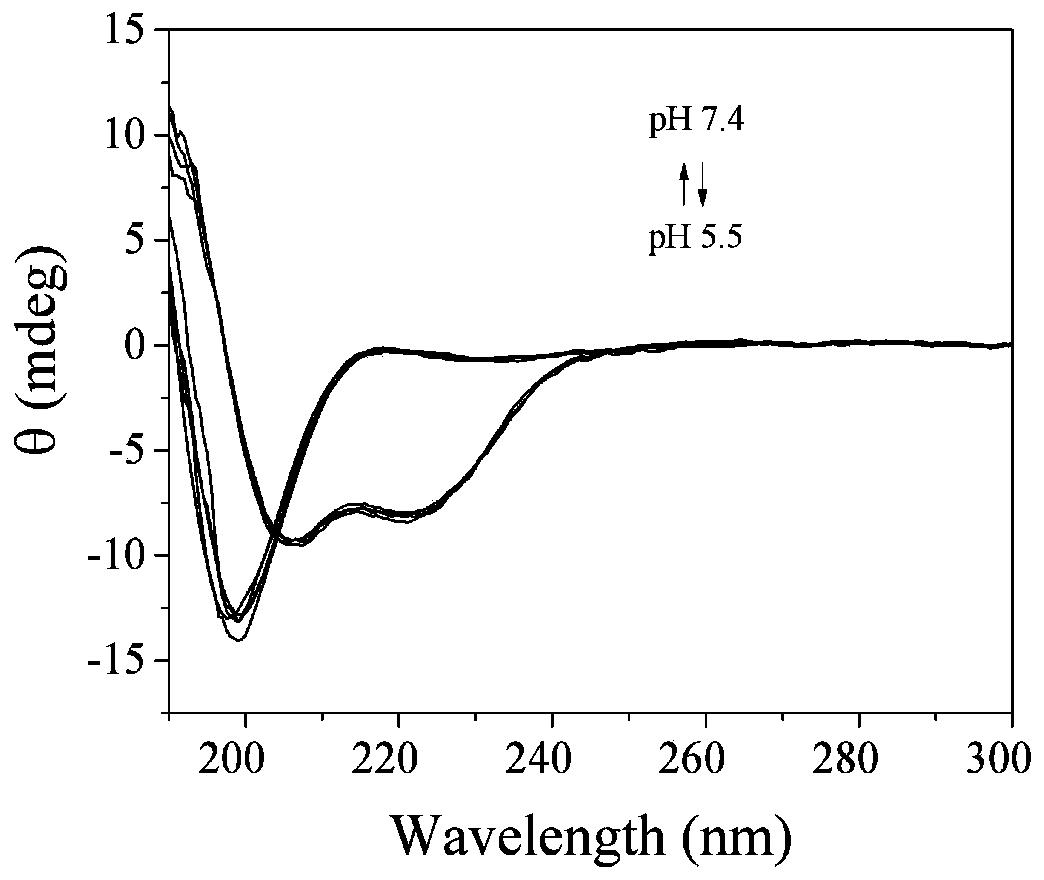
[0029] The invention provides a method for preparing a polypeptide crosslinked protein molecularly imprinted polymer, comprising the following steps: 1) mixing and dissolving a main monomer, a functional monomer, a polypeptide crosslinking agent and a template protein in a water-soluble solvent to obtain a mixed solution; 2) adding an initiator to the mixed solution described in step 1), and polymerizing under the condition that the polypeptide cross-linking agent exists in a helix conformation to obtain a polymer; 3) under the condition that the polypeptide cross-linking agent exists in a coil conformation, Perform template elution on the polymer described in step 2) to obtain a protein molecularly imprinted polymer cross-linked by the polypeptide; the polypeptide cross-linking agent has double bonds capable of polymerizing at both ends of the amino acid sequence, and can generate helix-coil Conformational switched peptides.
[0030]In the present invention, the polypeptide c...
Embodiment 1
[0042] Synthesis of imprinted polymers:
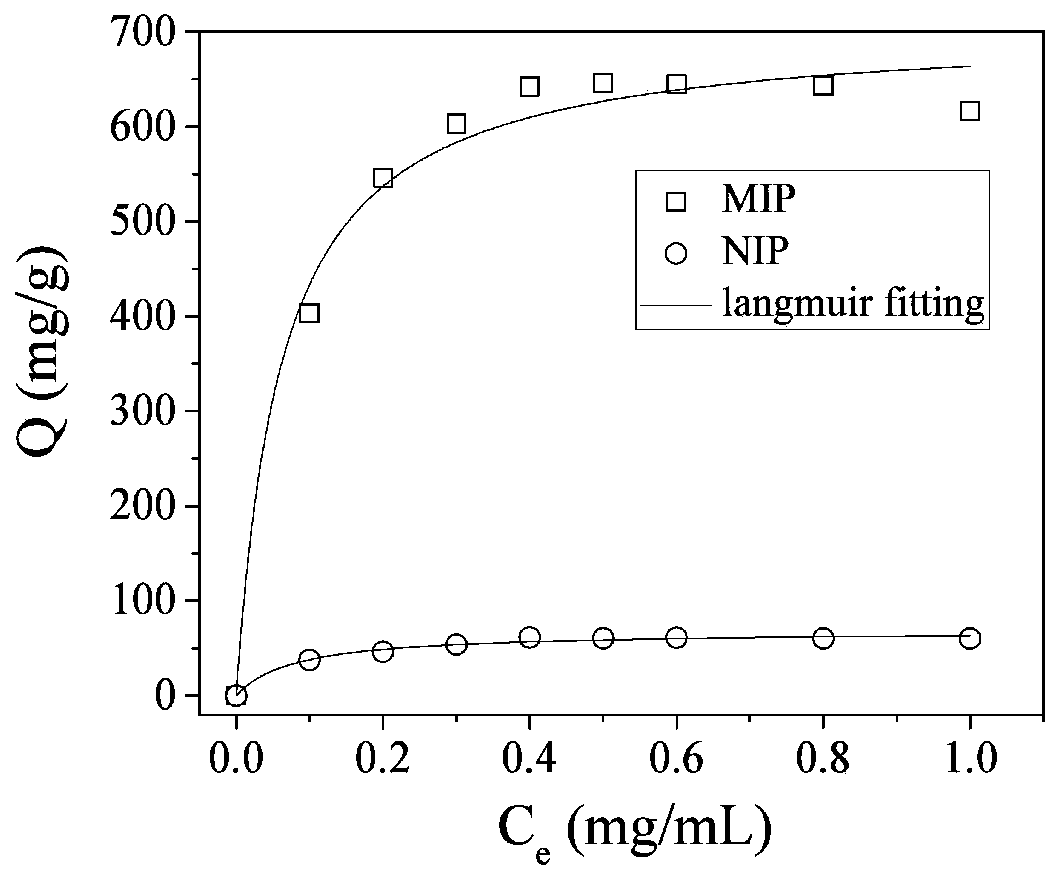
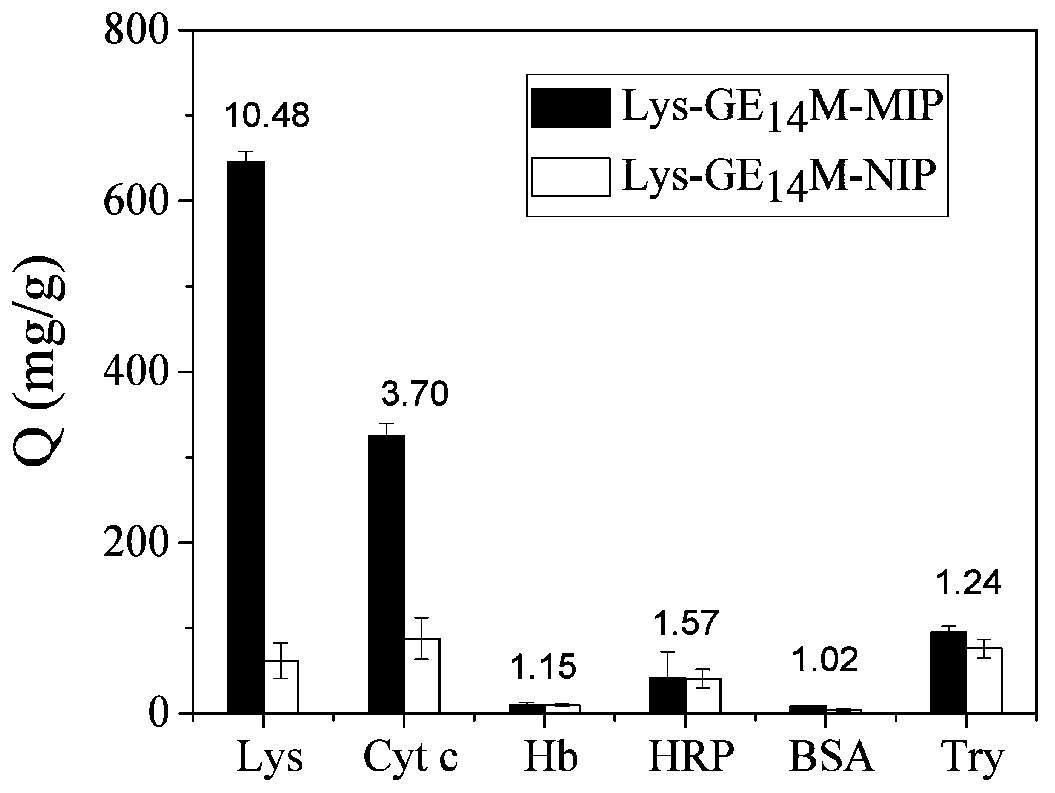
[0043] 200 mg of N-isopropylacrylamide, 5 mg of acrylamide, 4 μL of methacrylic acid, 115 mg of polypeptide cross-linker and 100 mg of template protein lysozyme were dissolved in 2 mL of 20 mM pH5.5 phosphate buffer solution. After thorough mixing, 50 μL of 10% APS and 5 μL TEMED were added to initiate polymerization, and reacted at 37° C. for 24 hours to obtain the imprinted polymer MIP. The non-imprinted polymer NIP was prepared in the same way as the imprinted polymer, except that the template protein lysozyme was not added. The structure of the polypeptide cross-linking agent is shown in formula I:
[0044]
[0045] Elution of template protein:
[0046] Protein elution was carried out at 37° C. with 20 mM pH7.4 phosphate buffer solution (containing 0.154 M NaCl to simulate physiological ionic strength). Measure the absorbance value of the eluate, use a UV spectrophotometer to draw a standard curve of absorbance-concentration ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Synthesis of imprinted polymers:
[0061] Dissolve 200 mg N-isopropylacrylamide, 2.5 mg acrylamide, 8 μL dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, 115 mg polypeptide cross-linker and 100 mg template protein bovine serum albumin (BSA) in 2 mL 20 mM pH5.5 phosphate buffer solution. After mixing well, add initiator 50 μL 10% APS and 5 μL TEMED, react at 37° C. for 24 h. Obtain the imprinted polymer MIP. The non-imprinted polymer NIP was prepared in the same way as the imprinted polymer, except that the template protein BSA was not added. The structure of the polypeptide cross-linking agent is the same as in Example 1.
[0062] Elution of template protein:
[0063] Protein was eluted with 20mM pH7.4 phosphate buffer solution (containing 0.154M NaCl to simulate physiological ionic strength) at 37°C, and the four elution rates were 95.24%, 2.05%, 0.24%, and 0%, respectively. The total elution rate was 97.51%. Finally, the imprinted polymer was washed with deionized water to remo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com