Biomarker, method for searching disease-related gene, and renal cancer marker
A biomarker and disease technology, applied in the field of kidney cancer markers, which can solve problems such as comparative research on microvesicles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] [Example 1] The separation method of Te-EVs
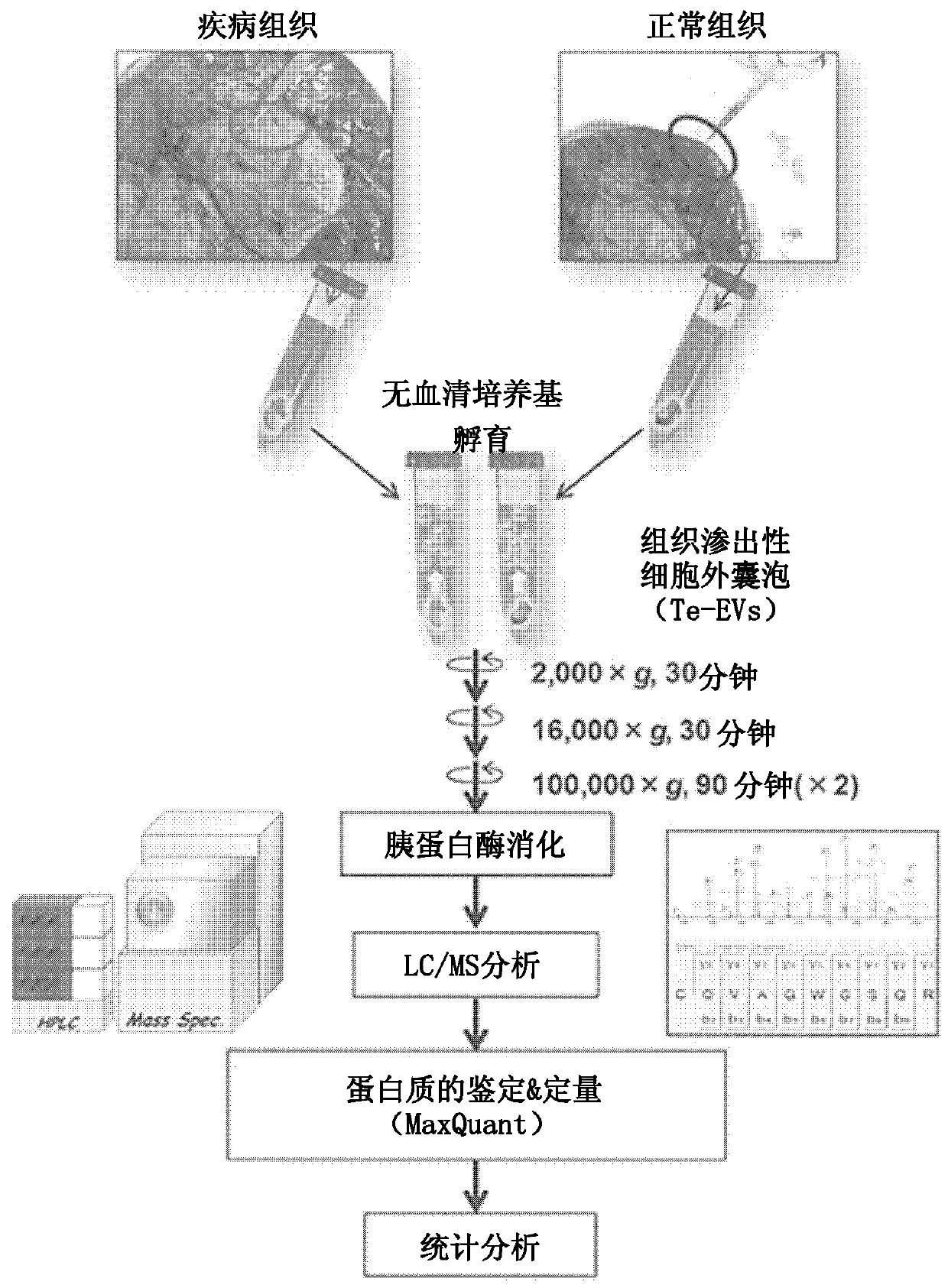
[0065] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing a method for isolating tissue-exudative extracellular vesicles (tissue-exudative EVs, hereinafter sometimes referred to as Te-EVs.) from diseased tissues and analyzing biomarkers. Diseased tissues and normal tissues are excised from surgically removed tissues, and immediately immersed in an immersion solution. In the case of renal cell carcinoma, serum-free DMEM was used as the immersion solution, but the immersion solution can be appropriately selected according to the tissue from which Te-EVs are extracted. Since extracellular vesicles are contained in serum, a serum-free medium is preferably used as the immersion solution, but a serum-containing medium may also be used if extracellular vesicles are removed in advance.
[0066] The tissue slices taken from the disease site and normal site were allowed to stand in the soaking solution at 4°C for about 1 hour to secrete ext...
Embodiment 2
[0068] [Example 2] Purification of kidney tissue-derived extracellular vesicles
[0069] Te-EVs were collected and analyzed from both cancerous tissues and normal tissues (non-cancerous parts) obtained from 20 renal cell carcinoma patients. Histological diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma was performed by hematoxylin-eosin staining. The disease stages of patients classified based on the AJCC TNM 6th edition were T1a to T3c.
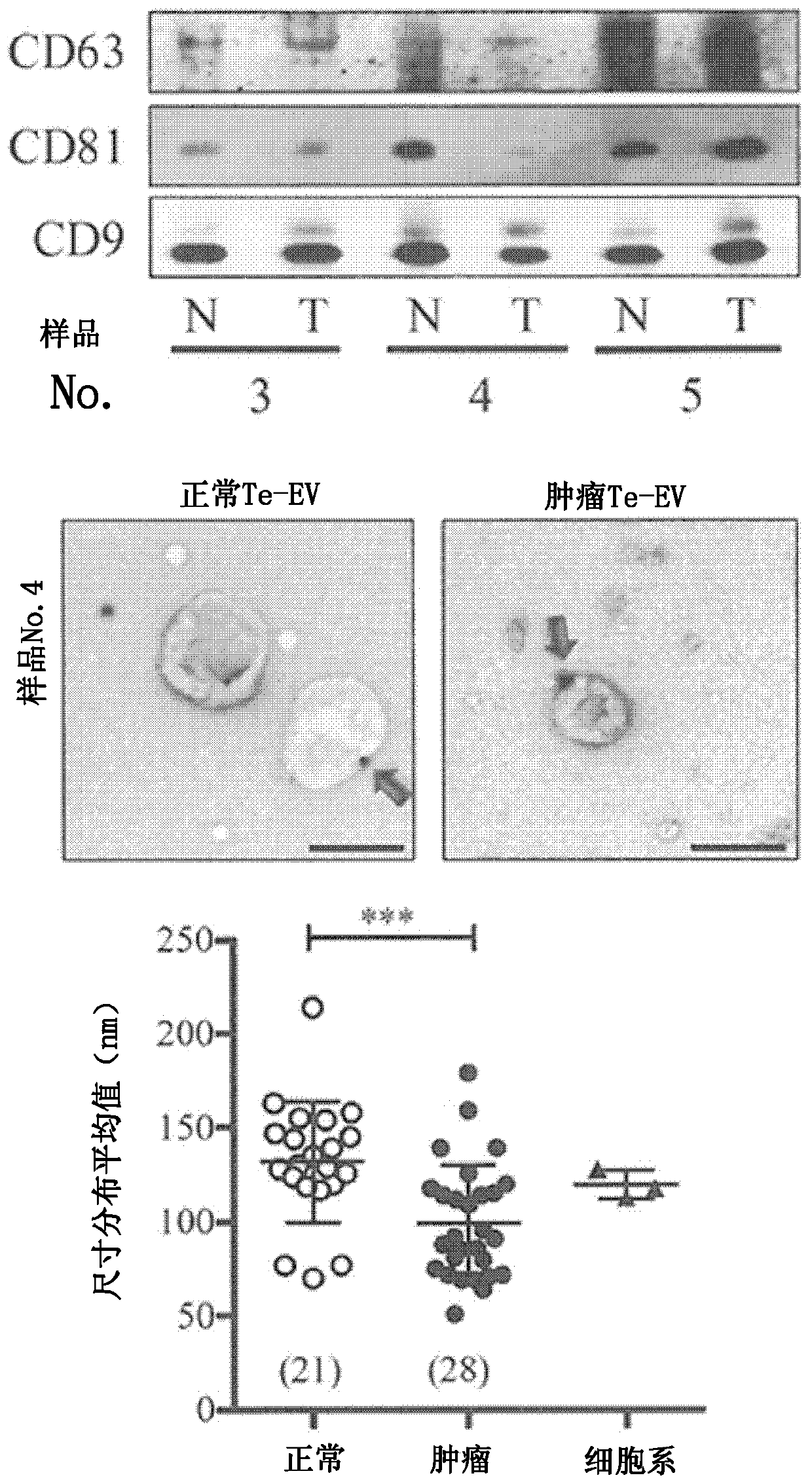
[0070] The degree of refinement of the resulting extracellular vesicles was analyzed by Western blotting, immunoelectron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking ( figure 2 ) and mass spectrometry ( image 3) for analysis. Western blotting was performed by a conventional method using 100 ng each of the obtained Te-EVs proteins. As primary antibodies, anti-CD63 monoclonal antibody (8A12), anti-CD81 monoclonal antibody (12C4), and anti-CD9 monoclonal antibody (12A12) (all manufactured by Cosmo Bio) were used as exosome markers. The antibody was detected by ECL...
Embodiment 3
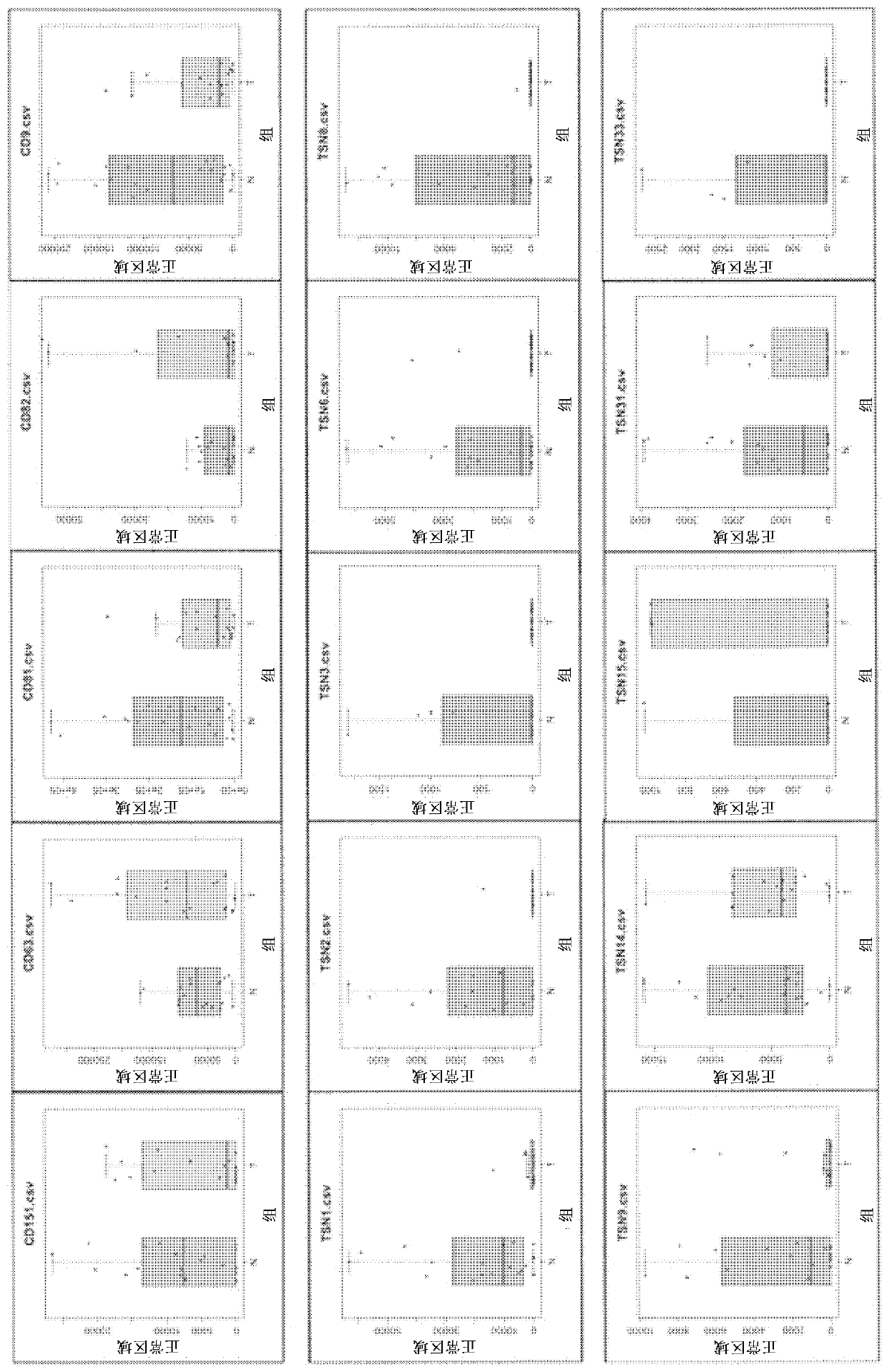
[0078] To investigate the properties of the resulting Te-EVs, the expression levels of tetraspanin molecules were compared. Fifteen tetraspanin molecules were detected, and Te-EVs derived from any tissue were shown to be highly refined substances. Furthermore, it became clear that the expression of most molecules of the tetraspanin superfamily was decreased in Te-EVs derived from cancer tissues compared with Te-EVs derived from normal tissues. [Example 3] Analysis of Te-EVs in cancer tissues and normal tissues in renal cell carcinoma
[0079] Using cancer tissues obtained from 20 patients and Te-EVs derived from normal tissues around the cancer site as a control, LC / MS analysis was performed in the same manner as above ( Figure 4 ). A total of 3871 proteins were identified, of which 160 were specifically expressed in Te-EVs derived from normal tissues, 253 were specifically expressed in Te-EVs derived from cancerous tissues, and 3458 were co-expressed in both ( Figure 4 A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com