Application of PPAR delta inhibitor combined immunotherapy drug in preparation of antitumor drugs
A technology of immunotherapy drugs and anti-tumor drugs, which is applied in the field of biomedicine to achieve strong targeting, avoid toxic and side effects, and enhance anti-tumor effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
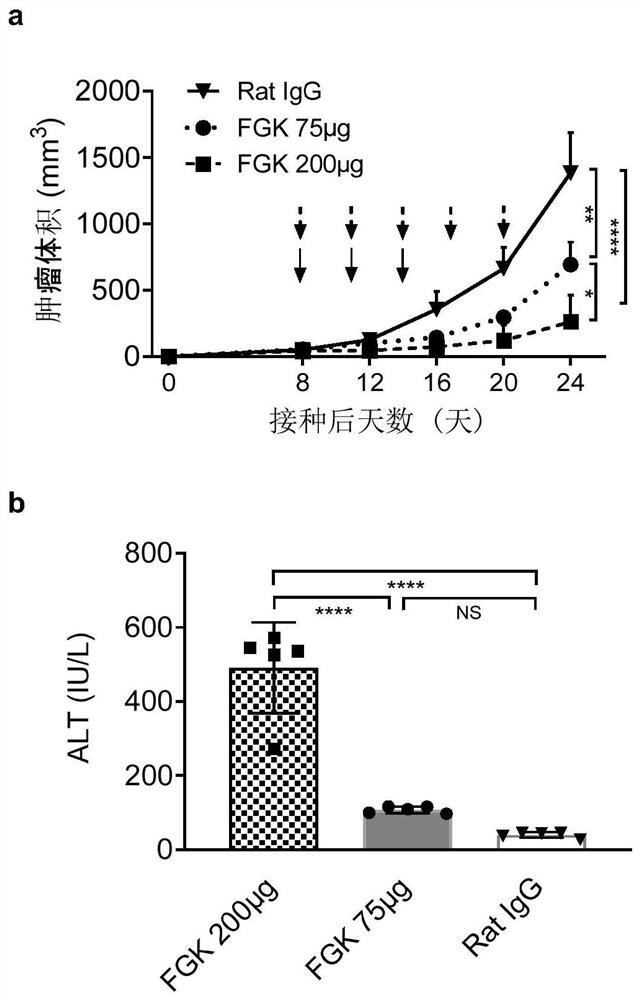
[0073] Example 1 The anti-CD40 agonistic antibody has dose-dependent anti-tumor effect, but high dose can cause obvious liver toxicity.
[0074] Anti-CD40 agonistic antibodies can promote the transformation of cold tumors into hot tumors, and have moderate anti-tumor effects on some tumors, but their effective dose range is narrow and they are toxic to the liver and other tissues. Toxic effects have been reported to be attenuated by intratissue injection and slow release of anti-CD40 agonist antibodies into tumor-draining areas.
[0075] First, we examined whether peritumoral injections of anti-CD40 agonistic antibodies had significant toxicity.
[0076] We used a well-studied and immunogenic mouse B16 melanoma model (C57BL / 6B16 tumor-bearing mouse model): C57BL / 6 mice (8-10 weeks, n=5 / group) were inoculated subcutaneously for 7 ×10 5 For B16 tumor cells (mouse melanoma cells), an anti-CD40 agonist antibody was administered when the tumor was palpable about 8 days after tumo...
Embodiment 2
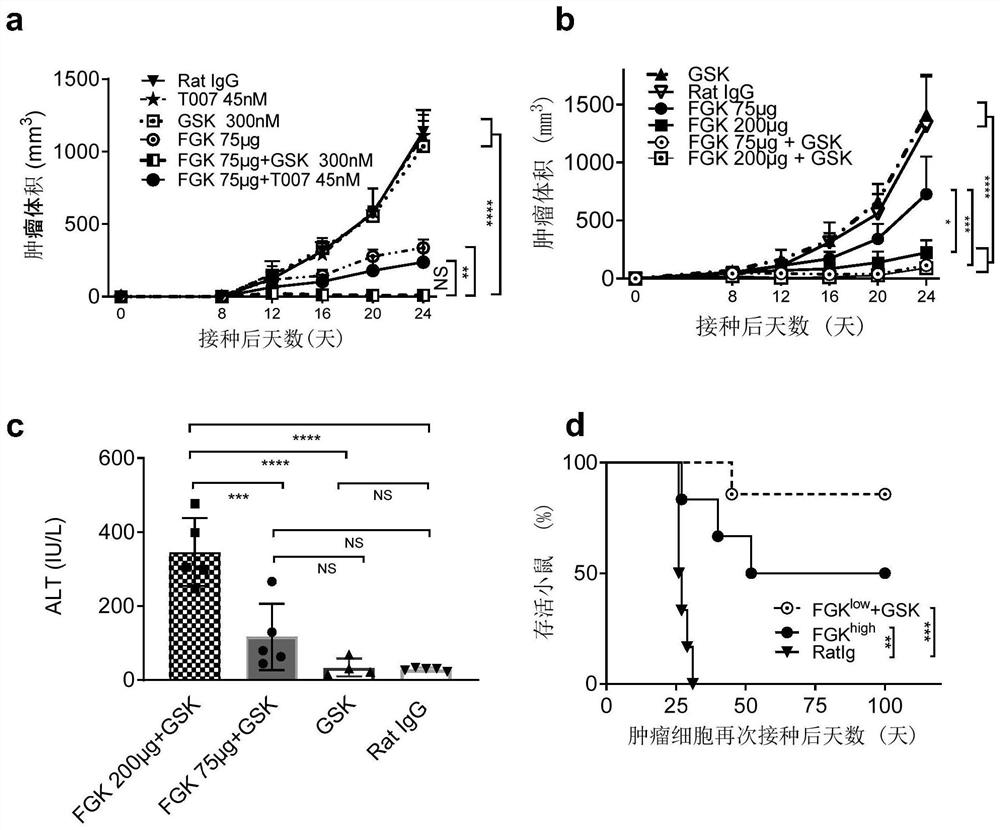
[0083] Example 2 PPARδ inhibitors can enhance the therapeutic effect of small doses of anti-CD40 agonist antibodies without significant liver toxicity, while PPARγ inhibitors have no such effect.
[0084] It has been reported that PPARγ or PPARδ are sensors of fatty acids and are necessary for the maturation of macrophages of the M2 type (a suppressive phenotype), and blocking the PPARγ or PPARδ pathway can promote the polarization of macrophages to the M1 state. In the tumor microenvironment, macrophages are one of the major populations of infiltrating lymphocytes with an M2-like phenotype, which promote tumor progression and resistance to immunotherapy or chemotherapy. Reversing its polarization to the M1 state is considered to be an important anticancer immunotherapeutic strategy. Given its ability to switch tumor-infiltrating macrophages (TAMs) to a predominantly M1 phenotype, we utilized the B16 tumor-bearing mouse model of Example 1 and a treatment regimen of low-dose FG...
Embodiment 3
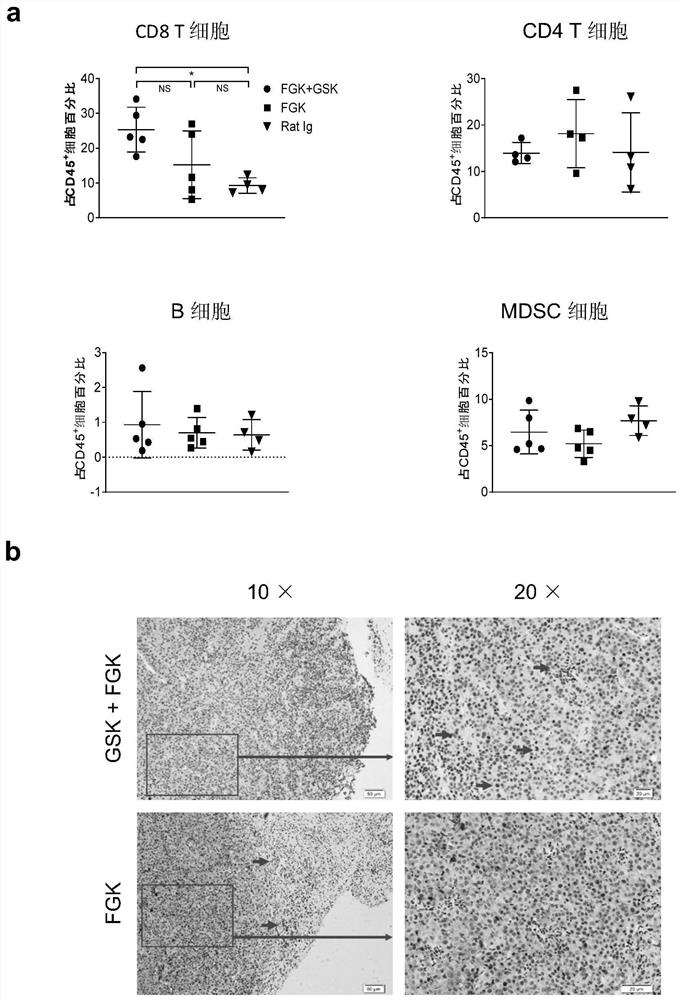
[0094] Example 3 Combination therapy of FGK45.5 and PPARδ inhibitors can effectively increase the depth of CD8 T cells infiltrating tumors.
[0095] Immune effector cells in tumors treated with FGK45.5 alone, low-dose FGK45.5 combined with a PPARδ inhibitor, and controls were quantified by flow cytometry and immunocytostaining of tissue sections.
[0096] The result is as image 3 As shown, though, compared with the FGK45.5 alone treatment group, intratumoral CD8 + T cells account for CD45 + The proportion of cells was only slightly increased, showing no statistically significant difference, but CD8+ cytotoxic T cells accounted for CD45 + The proportion of cells increased significantly. Tumor CD45 in FGK45.5 combined with PPARδ inhibitor treatment group + CD8 + The proportion of T cells increased to about 25%, about 15% in the FGK45.5 treatment group alone, and only 10% in the control group. In contrast, CD4 + T cells, B cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com