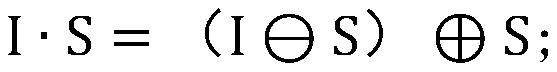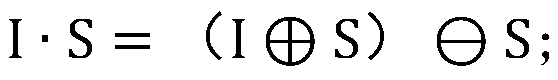Small target detection method based on Markov random field and visual contrast mechanism
A small target detection and visual comparison technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve the problem of poor detection performance of weak and small targets, and achieve the effect of reducing running time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
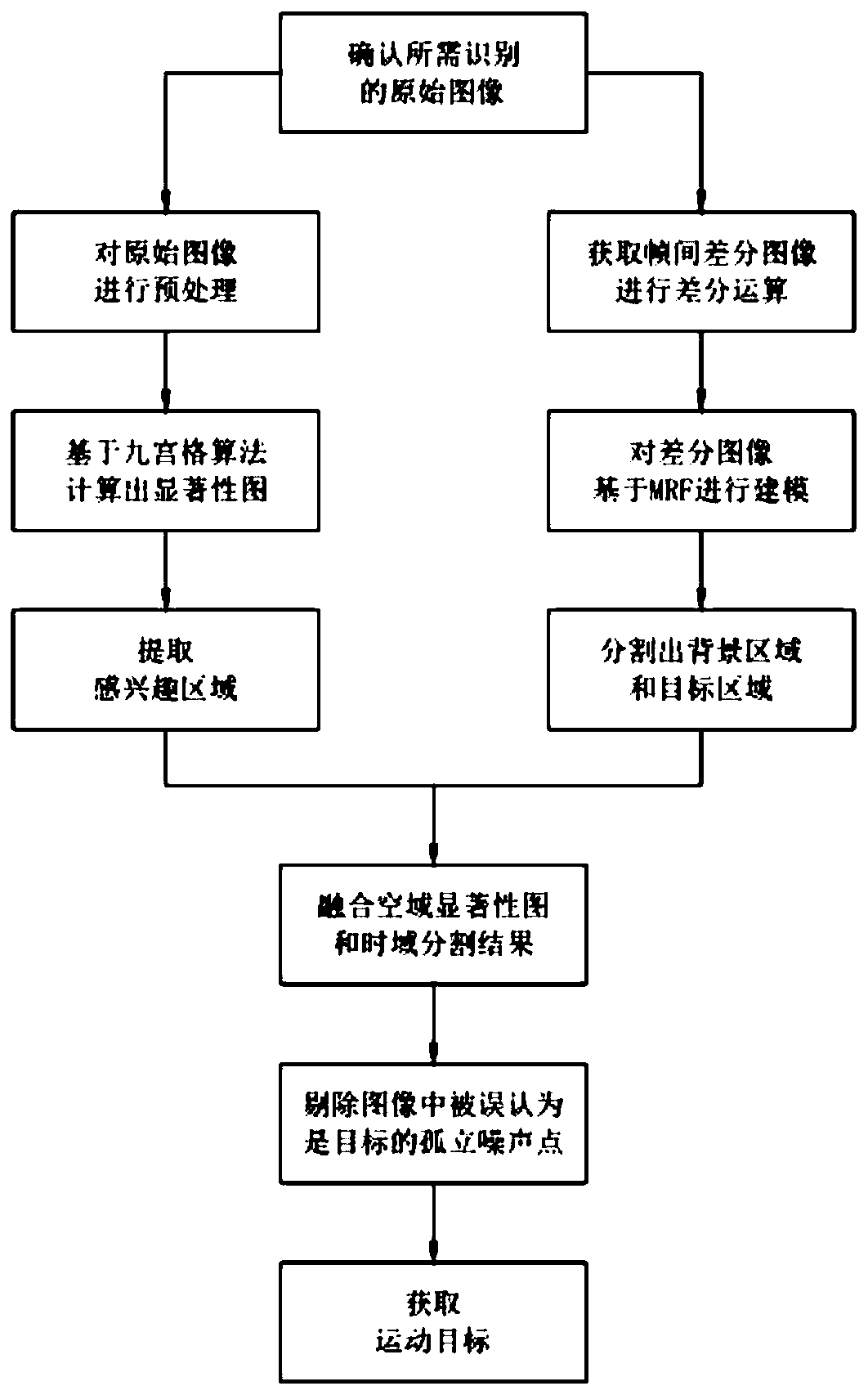
[0084] Such as figure 1 As shown, a small target detection method based on Markov random field and visual contrast mechanism includes the following steps:
[0085] a. Preprocessing the original infrared image of the small target to be identified;
[0086] b. Calculate the saliency map of the preprocessed infrared image based on the Jiugongge algorithm;
[0087] c. Model the inter-frame difference image based on the Markov random field, and segment the motion area and background area;
[0088] d. Fusion the saliency map in the space domain and the segmented area in the time domain, and remove the isolated noise points in the image that are mistaken for the target.
[0089] In this embodiment, the original image is modeled and a saliency map is generated respectively, that is, on the one hand, the original image is firstly subjected to single-frame image preprocessing, and then a saliency map is generated, and finally a region of interest (ROI) is extracted; On the one hand, ...
Embodiment 2
[0091] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, said step a includes the following steps:
[0092] The original infrared image is processed based on the Top-hat morphological filter, including erosion and expansion operations, and the opening and closing operations are composed of erosion and expansion operations;
[0093] If the opening operation is performed, the erosion operation is performed first and then the expansion is performed, and the formula is as follows:
[0094]
[0095] If the closed operation is performed, the expansion operation is performed first and then the corrosion is performed, and the formula is as follows:
[0096]
[0097] Among them, I is the original infrared image, S is the structured element, represents the expansion operation, Indicates a corrosion operation.
[0098]In this embodiment, the target signal in the infrared image is usually dim and mixed background clutter, which makes it difficult to detect small targets. In ord...
Embodiment 3
[0100] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 2, said step a also includes the following steps:
[0101] If the background of the original infrared image is too large and the small targets on it are regularly distributed, the background extraction can be performed based on the top-hat operation; including opening the top-hat operation and closing the top-hat operation, where:
[0102] The formula for opening the top hat operation is: OTH(x,y)=(I-S·I)(x,y);
[0103] The formula for closing the top hat operation is: CTH(x,y)=(I·S-I)(x,y).
[0104] In this embodiment, the top-hat transformation can be used to enhance the target. Opening the top-hat operation is often used to separate the patches that are brighter than the adjacent ones. When an image has a large background, and the tiny objects are more regular In some cases, the top-hat operation can be used for background extraction; closing the top-hat operation is the difference between the result image of the closed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com