A kind of synthetic method of i-type n-glycan antenna
A synthesis method and glycan technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of difficult derivatization, low yield, high efficiency and flexibility of I-type N-glycan antenna, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the synthesis route.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
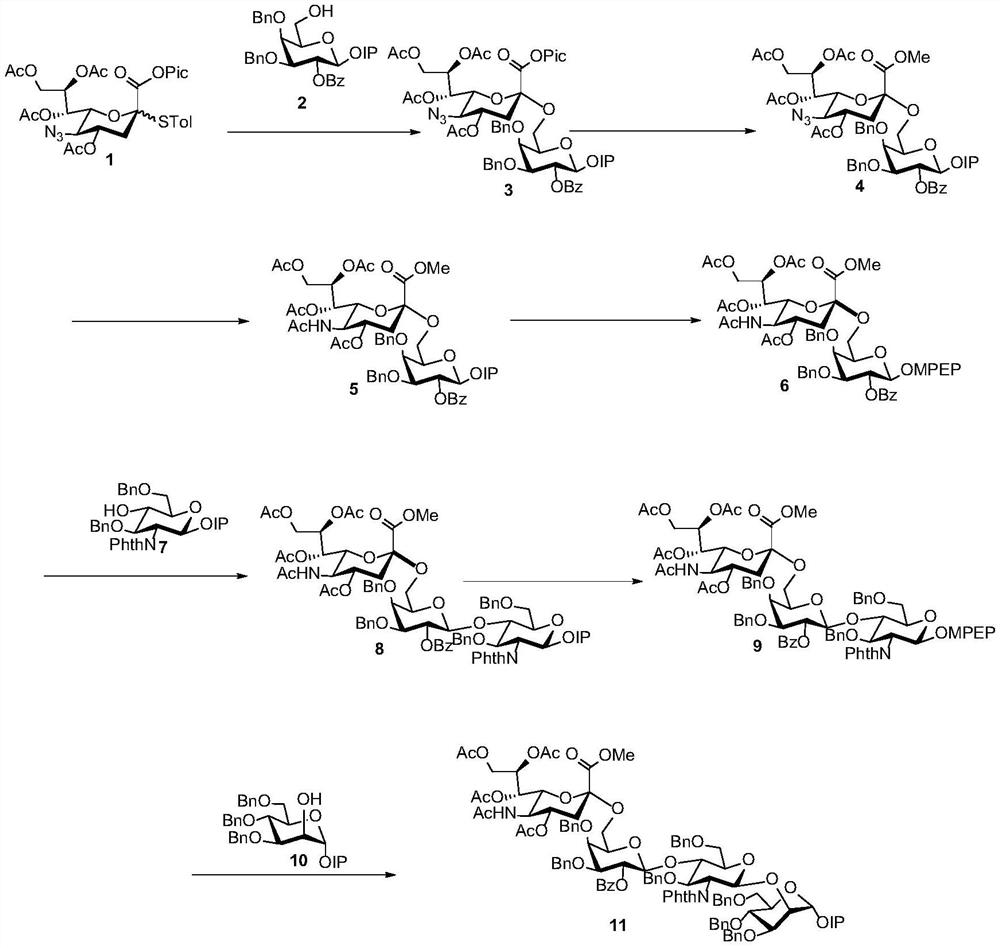
[0079] (1) Synthesis of compound 3
[0080]
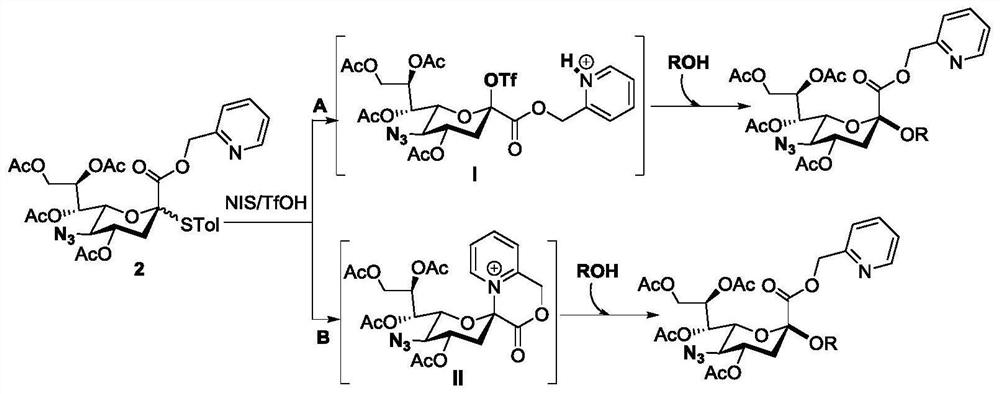
[0081] Compounds 1 (60 mg, 0.092 mmol) and 2 (30.6 mg, 0.046 mmol) were dissolved in dry CH 2 Cl 2 (1 mL), add activated 4A MS in N 2 under the protection of After the reaction system was stirred at room temperature for 15 minutes, it was placed at -40°C and continued to stir for 5 minutes. NIS (49.4mg, 0.221mmol) and TfOH (8.0μL, 0.092mmol) were added, and the reaction was continued at low temperature for 2 hours. TLC Point the plate to monitor the reaction is complete, add Et 3 Quench the reaction with N. Filter, wash with saturated sodium bicarbonate and saturated NaCl, and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Filtration and concentration under reduced pressure gave the crude product, and finally column chromatography (PE:EA:DCM=3:1:1) gave white solid compound 3 (49.7mg, 90%).[α] D 25 =-3.0 (c 0.9, CHCl 3 ); 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ8.58(d, J=4.8Hz, 1H), 8.05(dd, J=1.2, 8.4Hz, 2H), 7.74(td, J=1.2, 7.6Hz, 1H), 7.64(dd...
Embodiment 2
[0101] (1) The steps and parameters of step (1) in the reaction reference example 1, the difference is that the molar ratio of glycosyl donor compound 1, glycosyl acceptor compound 2, NIS and TfOH is 2:1:5:5 , the concentration of the compound 1 in the first solvent is 0.003mol / L; the glycosylation reaction temperature is -20°C; the yield of the full α configuration is 87%
[0102] (2) Steps and parameters of step (2) in the reaction reference example 1, the difference is that the molar ratio of compound 3 and copper acetate is 1:4, and the concentration of said compound 3 in the second solvent is preferably 0.004mol / L , the solvent is methanol and dichloromethane, the temperature is 50°C, and the yield is 60%
[0103] (3) Steps and parameters of step (3) in the reaction reference example 1, the difference is that the mol ratio of the compound 4 and thioacetic acid is preferably 1:10, and the dichloromethane with a volume ratio of 1:1 and pyridine as solvent. The concentrati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com