Near infrared fluorescent polymer probe for recognizing hydrazine as well as preparation method and application thereof
A fluorescent polymer and near-infrared technology, applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, etc., can solve problems such as damage and limited applications, and achieve the effects of eliminating interference, uniform distribution, and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] The preparation method of a near-infrared fluorescent polymer probe for identifying hydrazine provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0036] Taking chitosan as the main chain of the polymer, and the near-infrared fluorescent molecule as an activatable fluorescent functional molecule, the amino group of chitosan and the carboxyl group of the near-infrared fluorescent molecule undergo an amidation reaction to introduce chitosan into chitosan, which has the ability to specifically recognize hydrazine. "Turn on" near-infrared fluorescent molecules to obtain near-infrared fluorescent polymer probes that can recognize hydrazine.
[0037] The near-infrared fluorescent molecule used in the present invention has the structure of formula II:
[0038]
[0039] Formula II
[0040] Chitosan is a natural biopolymer with a wide range of sources, safe and non-toxic, and low price. Compared with synthetic polymers, it has good biocompatibility and biodegra...
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 Preparation of near-infrared fluorescent polymer probes for hydrazine recognition
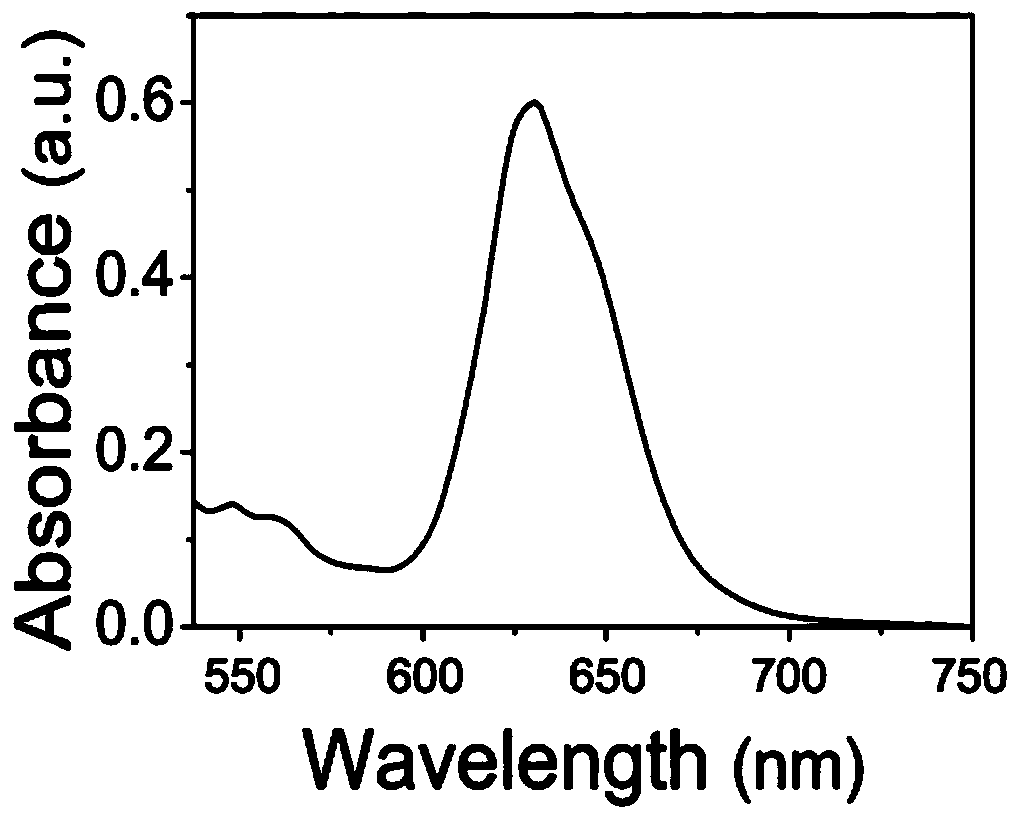
[0042] Dissolve 3.0g chitosan (Mw=10kDa, DA=0.85) in 25mL N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF), add 5.0g near-infrared fluorescent molecule II and 5mL containing 0.01molN under nitrogen protection -Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), then 0.04mol of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) was added, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 24h. Dialyzed in deionized water for two days and vacuum freeze-dried to obtain the target probe, which was tested in an ultraviolet absorption spectrometer. figure 1 As shown in the UV-Vis absorption spectrum, the maximum absorption peak of the visible target near-infrared fluorescent probe in aqueous solution is located at 633 nm.
Embodiment 2
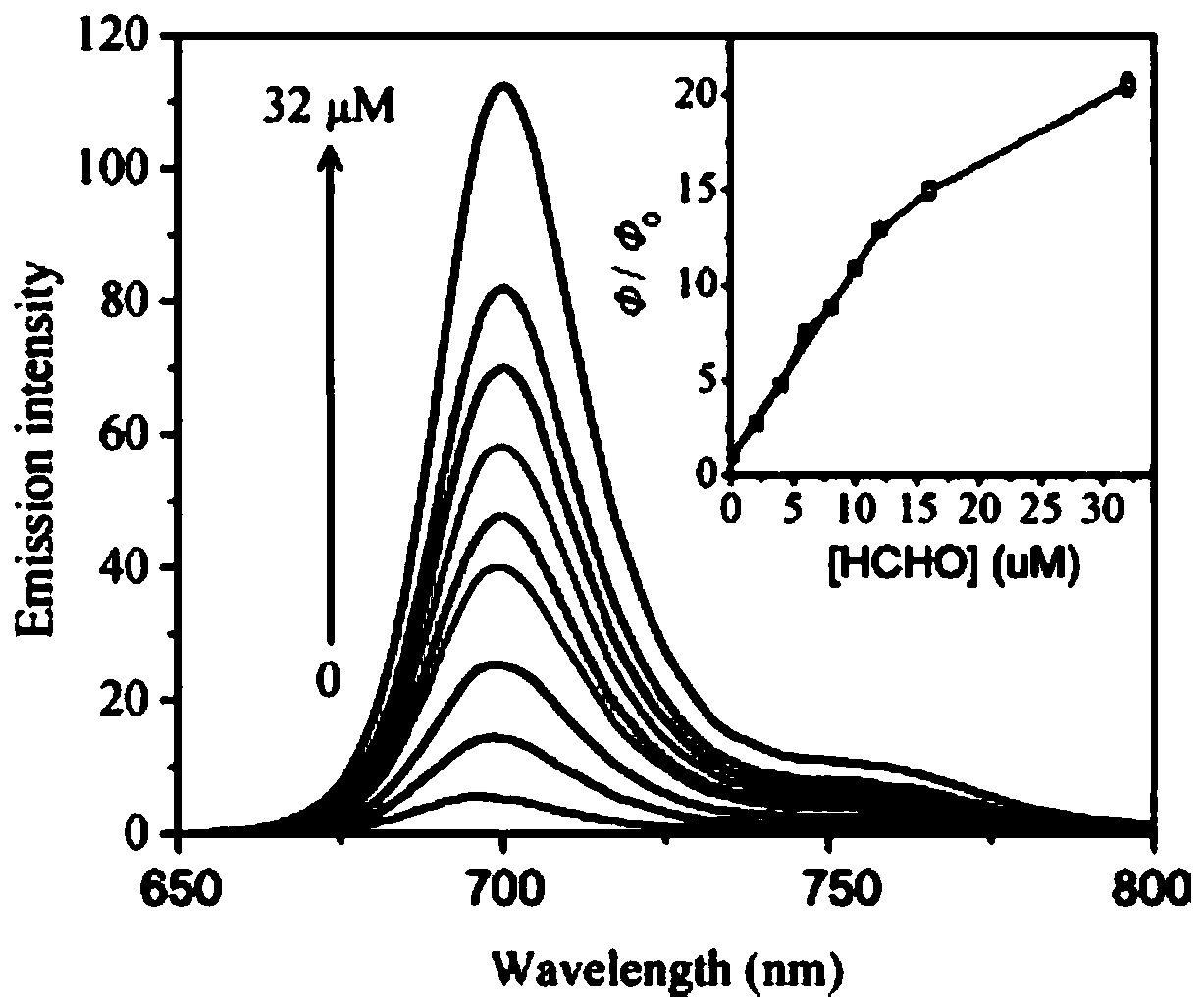
[0043] Example 2 Near-infrared fluorescent polymer probes with different equivalents of N 2 H 4 Fluorescence spectral changes of the reaction
[0044] To the probe solution (5 μmol / L) prepared in Example 1, hydrazine solutions of different equivalents (0-3 equiv) were added, mixed evenly, and then shaken for 30 min to perform a fluorescence titration test. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that with the gradual addition of hydrazine, the fluorescence peak of the probe at 698 nm is gradually enhanced. When the fluorescence intensity reaches the maximum value, it is about 20 times stronger than that of the probe blank solution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com