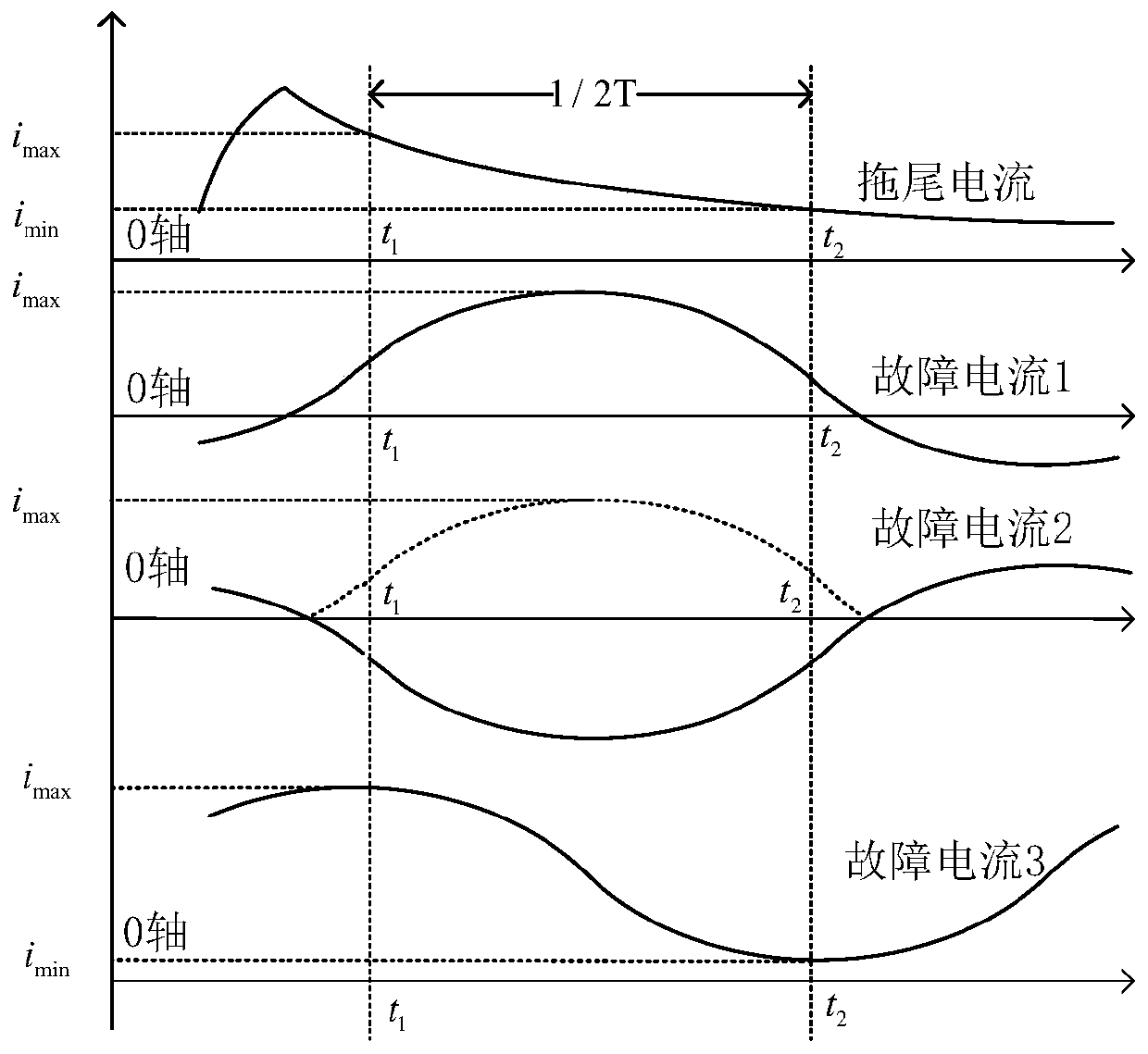
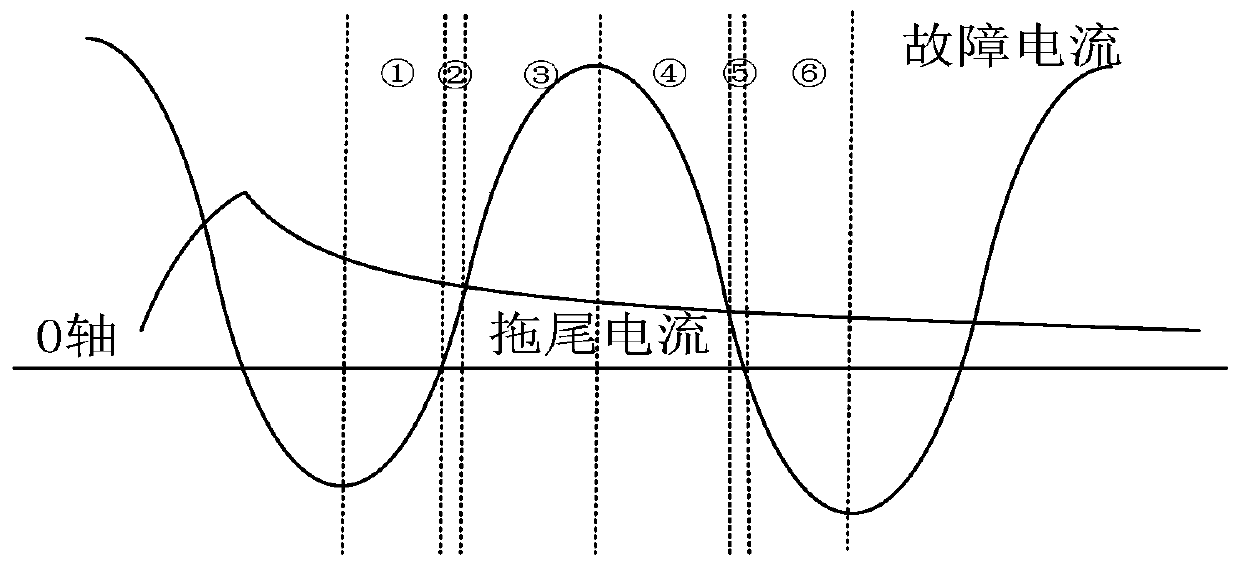
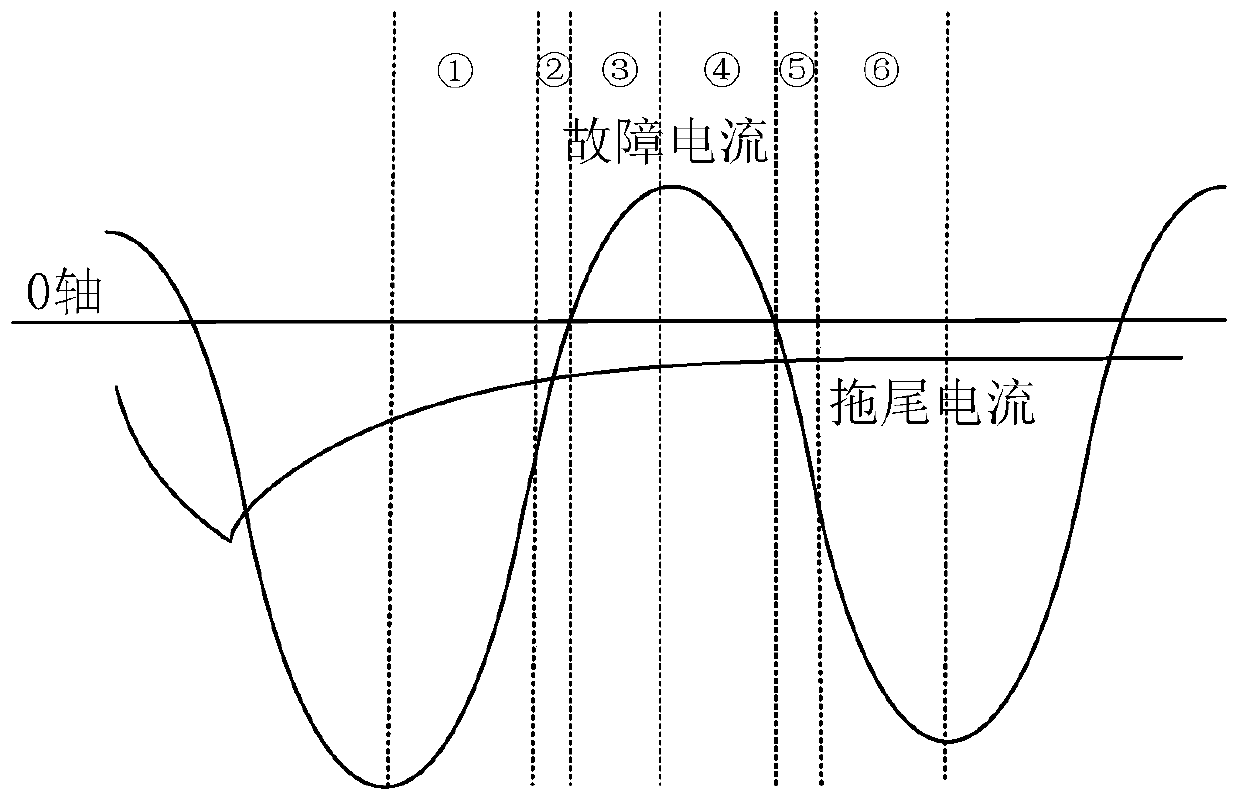
Current transformer trailing current identification algorithm based on waveform characteristic difference
A current transformer and tailing current technology, which is applied in the field of current transformer tailing current identification algorithm, can solve the problems of power system influence, long identification time, misjudgment of time constant protection, etc., and achieve strong engineering practicability and electrical quantity Less information, good anti-interference effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example
[0058] Build in PSCAD / EMTDC simulation software Figure 4 The system verification power network shown carries out the verification of the results of the present invention. Assume that a phase-to-ground fault occurs on line L1 at 0.1s, circuit breaker B2 receives a trip command at 0.2s, and the current rating of the current transformer CT secondary side current I n It is 5A, the time constant of CT secondary side is 70ms, and the action time of circuit breaker B2 is 90ms. The experiment simulates the correct tripping and malfunctioning of the circuit breaker B2 respectively. The simulation results of the tail current half-wave recognition method are shown in Table 1.
[0059] Table 1 Simulation results of tailing current invention algorithm identification method
[0060]
[0061] Combining the simulation waveforms obtained from the above five groups of experiments with the tailing current identification results of the traditional method and the inventive algorithm, the PSC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com