A bacterial strain producing lactic acid by high-temperature fermentation and a method for producing lactic acid
A high-temperature fermentation and lactic acid technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as fermentation and production of lactic acid, and achieve the effects of good fermentation stability, improved adaptability, and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Screening preparation and identification of E.faecalis DUT1805:
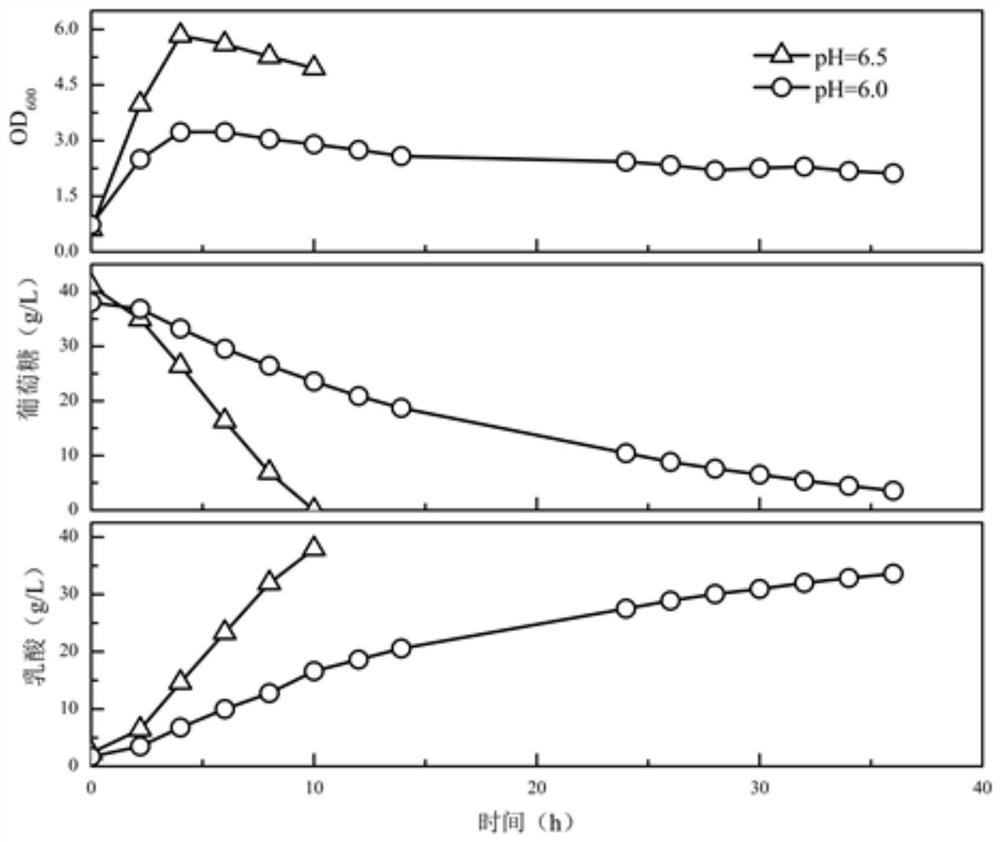
[0052] Take 0.1kg of the fresh content of bovine stomach in a Erlenmeyer flask with 100mL of normal saline, vortex for 2min, and inoculate the solid-liquid mixture into a vial with 100mL of enrichment medium for anaerobic enrichment culture. After 12 consecutive subcultures, the mixed bacteria with stable fermentation performance were obtained. The flora was inoculated into a 250mL vial containing 100mL RCM medium, heat-treated at 90°C for 20 minutes, and then spread on an RCM plate. After the plate was anaerobically cultured at 37°C for 24 hours, a single colony was picked for streaking and isolation, and then purified for 3 Conservation of species for future generations. The isolated and purified single bacterial DNA was extracted and amplified with 16S rDNA bacterial general primers (primer 27F: AGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG; 1492R: GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT). Through comparative analysis of 16S rDNA, it was confirmed...
Embodiment 2
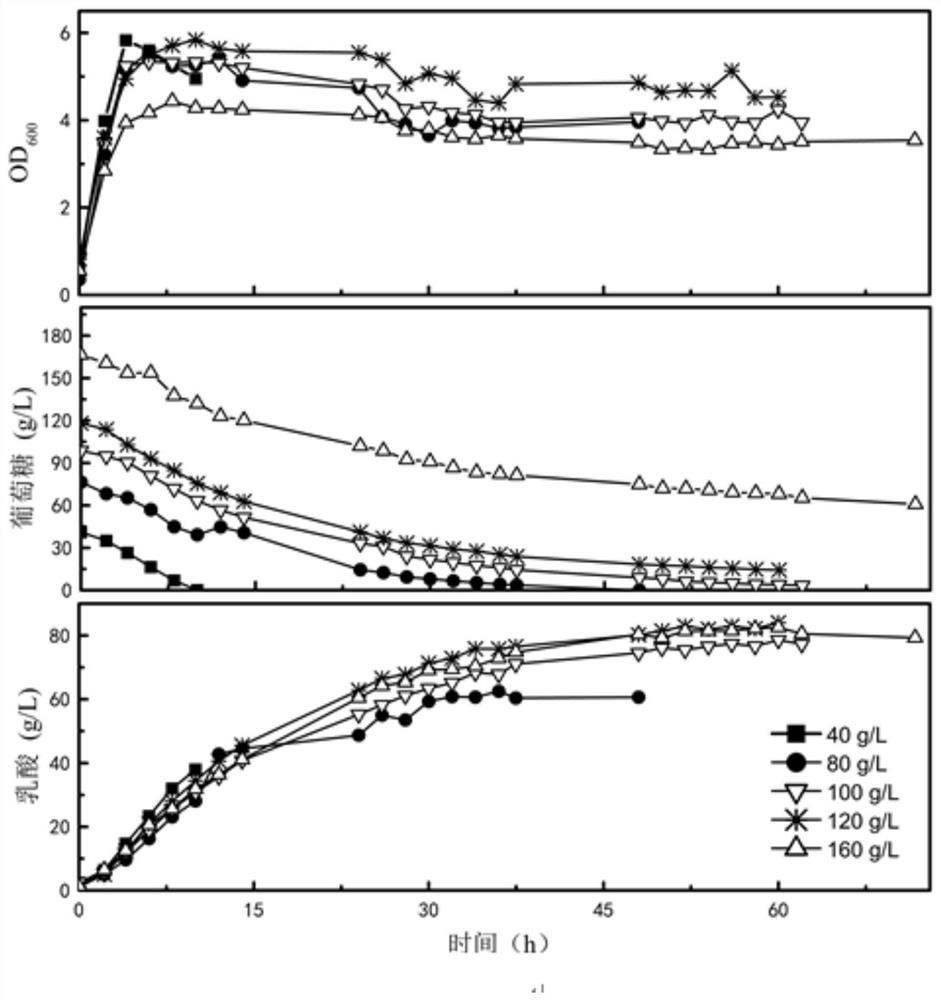
[0053] Example 2 Effect of glucose stress on the fermentation performance of E.faecalis DUT1805 at 50°C
[0054] After Enterococcus faecalis DUT1805 passed through the seed medium, it was inoculated into a 5L fermenter with 2LMRS medium at a volume ratio of 5%, and the temperature was gradually raised from 37°C to 50°C within 2 hours, and the glucose concentration was increased from 40g / L is gradually increased to 160g / L, the whole fermentation process is not ventilated, and the fermentation results are as follows: image 3 shown. The results showed that Enterococcus faecalis DUT1805 could tolerate 160g / L glucose at high temperature of 50℃. Among them, the batch fermentation efficiency is the highest when the glucose concentration is 40g / L, the final concentration of lactic acid is 37.92g / L, the conversion rate relative to glucose is 0.92g / g, the production intensity is 3.79g / (L.h), and the metabolic by-products There are acetic acid, succinic acid and ethanol, the concentr...
Embodiment 3
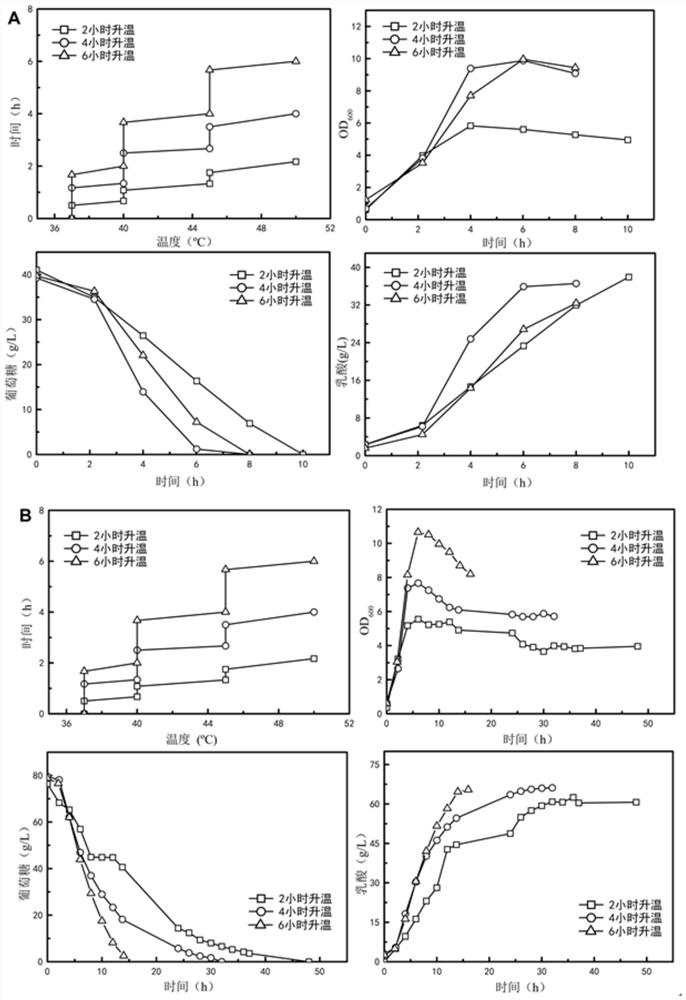
[0055] Example 3 Effects of different temperature control strategies on the fermentation performance of E.faecalis DUT1805 at 50°C
[0056] Enterococcus faecalis DUT1805 was inoculated into a 5L fermenter with 2L MRS medium at a volume ratio of 5% after the seed medium, and the whole fermentation process was not ventilated. To explore the effect of different gradient heating methods on E.faecalis DUT1805 using glucose fermentation Effects on the production of lactic acid. Fermentation results such as Figure 4 shown. When the substrate was 40g / L glucose, the experimental group whose temperature was raised from 37°C to 50°C within 4 hours had better cell growth, glucose consumption rate and lactic acid production rate than the experimental group whose temperature was gradually raised to 50°C within 2h and 6h. The final concentration of lactic acid was 36.56g / L, the conversion rate relative to glucose was 0.92g / g, the production intensity was 4.57g / (L.h), and the concentration...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com