Two-dimensional calculation method for composite material layer cracking
A composite material layer and calculation method technology, applied in the field of two-dimensional calculation of composite material spallation, can solve problems such as troublesome grid division, achieve the effects of low grid size requirements, avoid repeated iterations, and improve calculation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
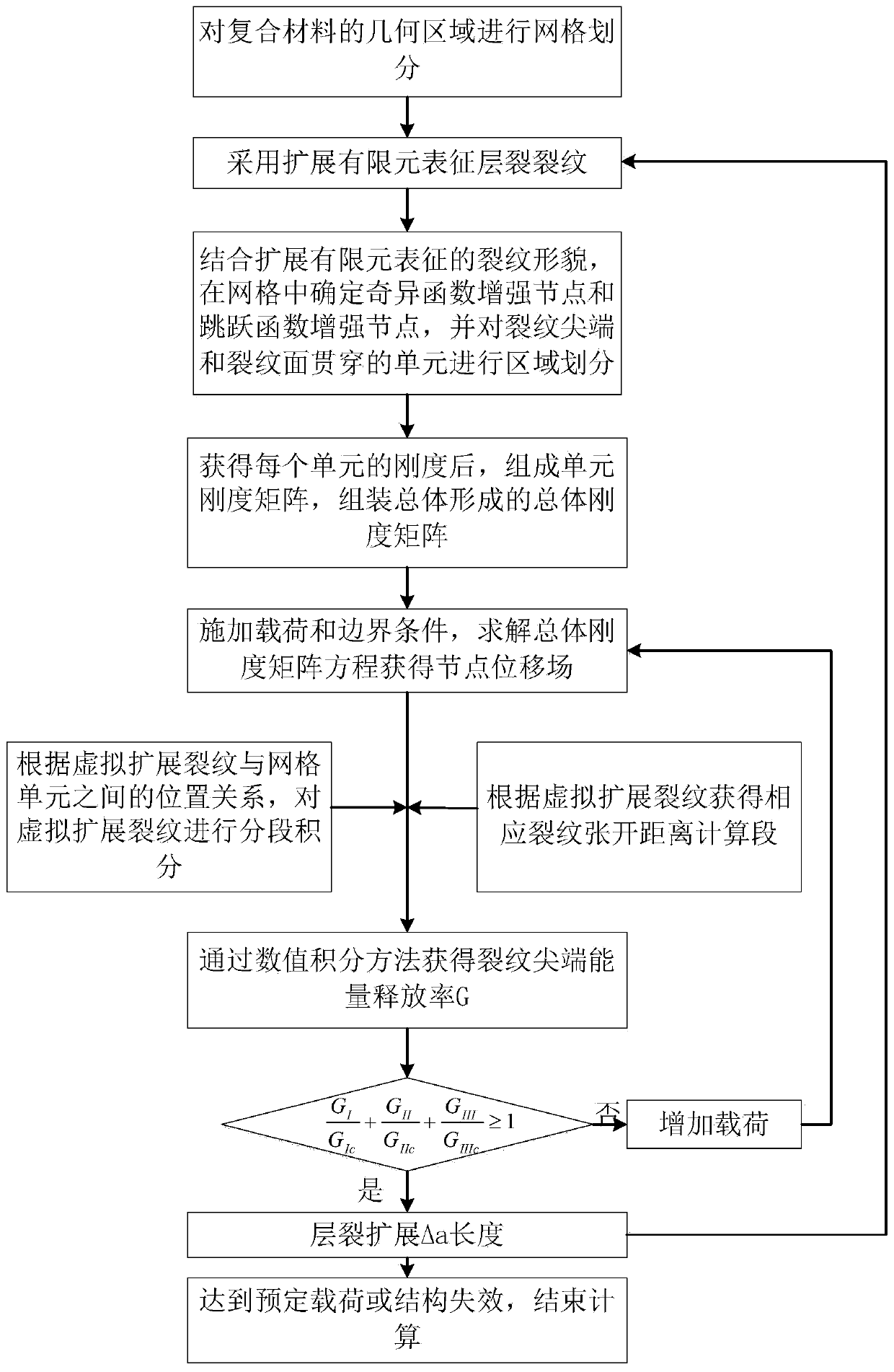
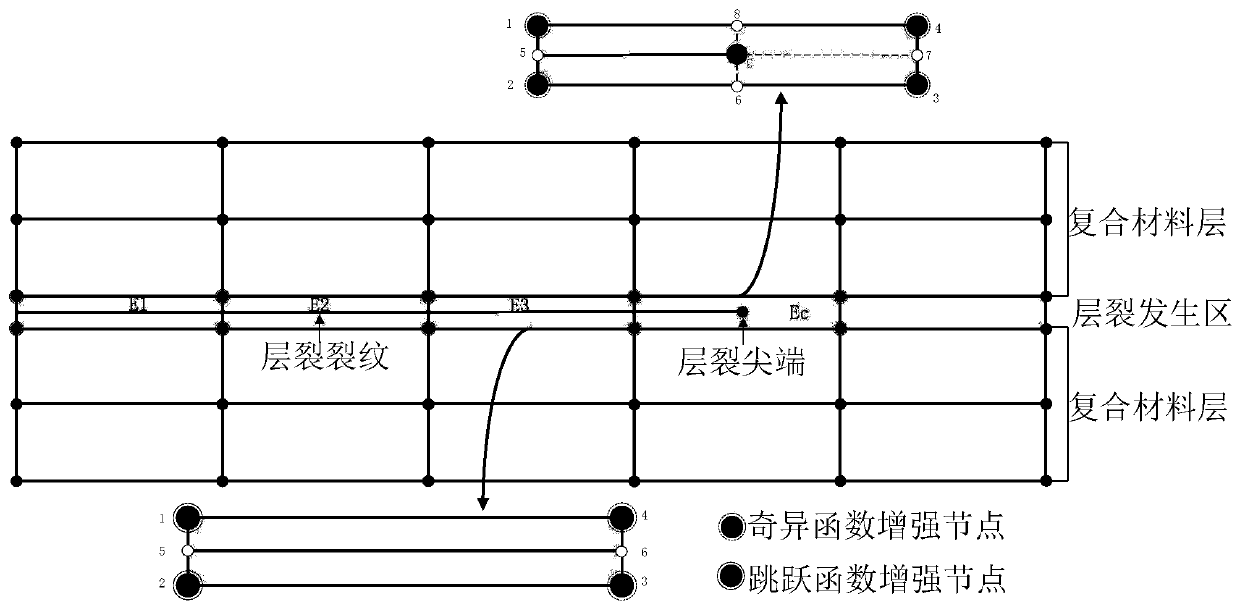
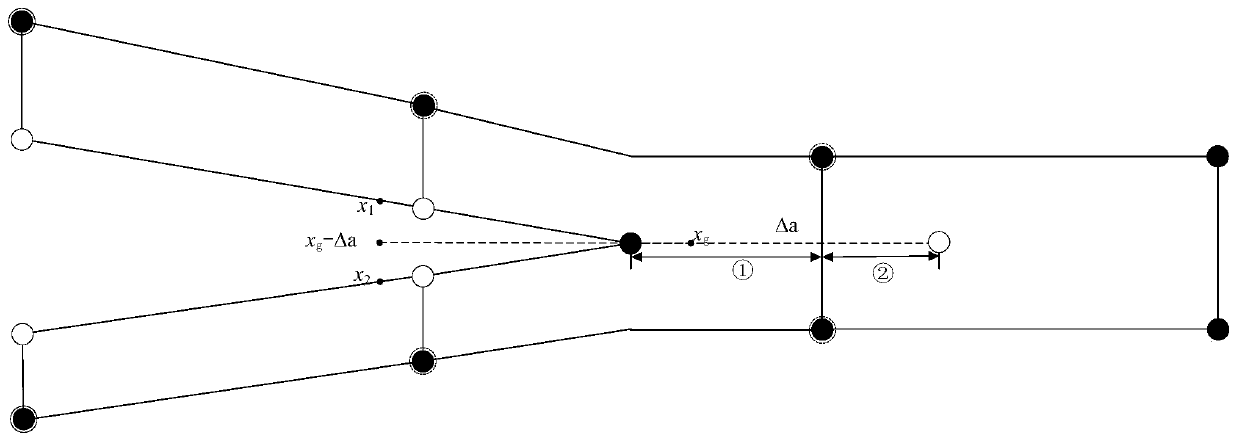
[0058] The embodiment adopted by the present invention is a double cantilever beam model, and the geometric dimensions are as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the left end of the model is fixed, and a pair of balance forces of equal magnitude and opposite directions are applied to the upper and lower vertices of the right end, and the magnitude is P. The model includes two layers of composite materials and an intermediate layer. The intermediate layer is the layer where spallation occurs. Layer prefabricated 30mm long layer cracks, according to Figure 8 As shown, it can be judged that the crack is a type I crack. The material constant of the composite layer is: Young's modulus E in the fiber direction 11 =150GPa, transverse Young's modulus E 22 =11GPa, shear modulus G 12 =60GPa, Poisson's ratio υ 12 = 0.21. The middle layer is isotropic material, its Young's modulus is E=10GPa, Poisson's ratio υ=0.3, fracture toughness G IC =0.026Nmm -1 .
[0059] This embodiment adopts t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com